If-Else Statement in TypeScript
In this tutorial, we will learn about if-else statements in TypeScript. We will cover the basics of conditional execution using if-else statements.
What is an If-Else statement
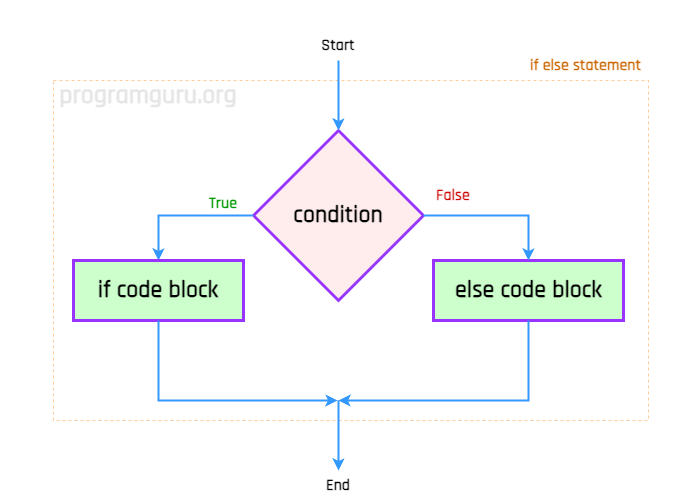
An if-else statement is a conditional statement that executes one block of code if a specified condition is true, and another block of code if the condition is false.
Syntax
The syntax for the if-else statement in TypeScript is:
if (condition) {
// Code block to execute if condition is true
} else {
// Code block to execute if condition is false
}The if-else statement evaluates the specified condition. If the condition is true, the code block inside the if statement is executed; otherwise, the code block inside the else statement is executed.
Example 1: Checking if a Number is Even or Odd
- Declare a variable
num. - Assign a value to
num. - Use an if-else statement to check if
numis even or odd. - Print a message indicating whether
numis even or odd.
TypeScript Program
let num: number = 10;
if (num % 2 === 0) {
console.log(`${num} is even.`);
} else {
console.log(`${num} is odd.`);
}Output
10 is even.
Example 2: Checking if a String Starts with a Specific Value
- Declare a variable
str. - Assign a value to
str. - Use an if-else statement to check if
strstarts with a specific value. - Print a message indicating the result of the check.
TypeScript Program
let str: string = 'Hello, world!';
if (str.startsWith('Hello')) {
console.log('String starts with 'Hello'.');
} else {
console.log('String does not start with 'Hello'.');
}Output
String starts with 'Hello'.
Example 3: Checking if a Number is Positive or Negative
- Declare a variable
num. - Assign a value to
num. - Use an if-else statement to check if
numis positive or negative. - Print a message indicating whether
numis positive or negative.
TypeScript Program
let num: number = -5;
if (num > 0) {
console.log(`${num} is positive.`);
} else {
console.log(`${num} is negative or zero.`);
}Output
-5 is negative or zero.