If Statement in Java
In this tutorial, we will learn about if statements in Java. We will cover the basics of conditional execution using if statements.
What is an If statement
An if statement is a conditional statement that executes a block of code if a specified condition is true.
Syntax
The syntax for the if statement in Java is:
if (condition) {
// Code block to execute if condition is true
}The if statement evaluates the specified condition. If the condition is true, the code block inside the if statement is executed; otherwise, it is skipped.
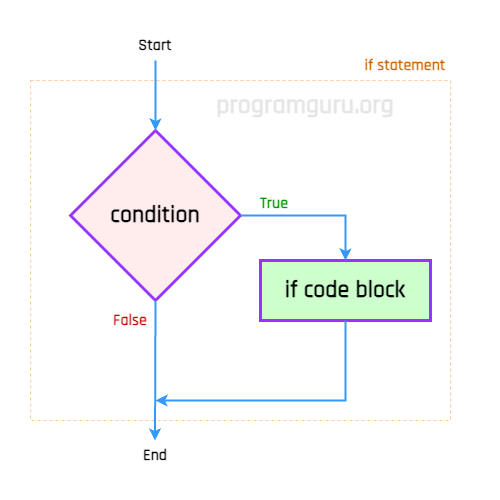
The following is the flowchart of how execution flows from start to the end of an if statement.
Example 1: Checking if a Number is Even
- Declare an integer variable
num. - Assign a value to
num. - Use an if statement to check if
numis even. - Print a message indicating whether
numis even or not.
Java Program
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num = 10;
if (num % 2 == 0) {
System.out.println(num + " is even.");
}
}
}Output
10 is even.
Example 2: Checking if a String Starts with a Specific Value
- Declare a string variable
str. - Assign a value to
str. - Use an if statement to check if
strstarts with a specific value. - Print a message indicating the result of the check.
Java Program
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "Hello, world!";
if (str.startsWith("Hello")) {
System.out.println("String starts with 'Hello'.");
}
}
}Output
String starts with 'Hello'.
Example 3: Checking if a Number is Positive
- Declare an integer variable
num. - Assign a value to
num. - Use an if statement to check if
numis positive. - Print a message indicating whether
numis positive or not.
Java Program
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num = -5;
if (num > 0) {
System.out.println(num + " is positive.");
}
}
}