Else If Statement in Go
In this tutorial, we will learn about else-if statements in Go. We will cover the basics of conditional execution using if-else-if statements.
What is an Else-If statement
An else-if statement is a conditional statement that allows multiple conditions to be tested sequentially. It provides a way to execute different code blocks based on different conditions.
Syntax
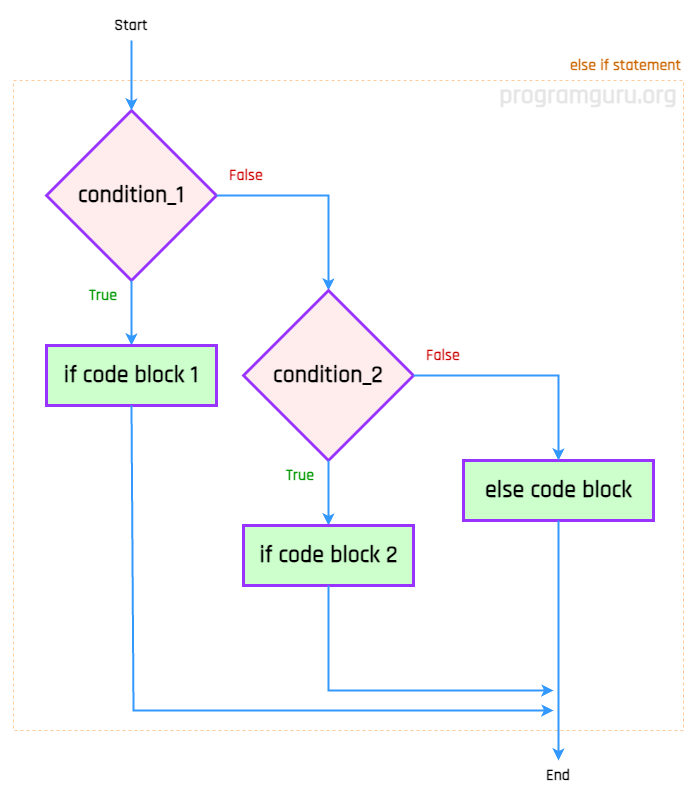
The syntax for the else-if statement in Go is:
if condition1 {
// Code block to execute if condition1 is true
} else if condition2 {
// Code block to execute if condition2 is true
} else {
// Code block to execute if none of the conditions are true
}The else-if statement evaluates the specified conditions in order. The first condition that is true will have its code block executed; if none of the conditions are true, the code block inside the else statement is executed.
Example 1: Checking if a Number is Positive, Negative, or Zero
- Declare an integer variable
num. - Assign a value to
num. - Use an if-else-if statement to check if
numis positive, negative, or zero. - Print a message indicating whether
numis positive, negative, or zero.
Go Program
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
num := -5
if num > 0 {
fmt.Println(num, "is positive.")
} else if num < 0 {
fmt.Println(num, "is negative.")
} else {
fmt.Println(num, "is zero.")
}
}Output
-5 is negative.
Example 2: Checking the Grade of a Student
- Declare an integer variable
marks. - Assign a value to
marks. - Use an if-else-if statement to check the grade based on the
marks. - Print a message indicating the grade.
Go Program
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
marks := 85
if marks >= 90 {
fmt.Println("Grade: A")
} else if marks >= 80 {
fmt.Println("Grade: B")
} else if marks >= 70 {
fmt.Println("Grade: C")
} else if marks >= 60 {
fmt.Println("Grade: D")
} else {
fmt.Println("Grade: F")
}
}Output
Grade: B
Example 3: Checking the Temperature Range
- Declare a float variable
temperature. - Assign a value to
temperature. - Use an if-else-if statement to check the range of the
temperature. - Print a message indicating the temperature range.
Go Program
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
temperature := 75.5
if temperature > 100 {
fmt.Println("It's extremely hot.")
} else if temperature > 85 {
fmt.Println("It's hot.")
} else if temperature > 60 {
fmt.Println("It's warm.")
} else if temperature > 32 {
fmt.Println("It's cold.")
} else {
fmt.Println("It's freezing.")
}
}Output
It's warm.