For Loop in Go
In this tutorial, we will learn about for loops in Go. We will cover the basics of iterative execution using for loops.
What is a For Loop
A for loop is a control flow statement that allows code to be executed repeatedly based on a given Boolean condition. The loop is typically used when the number of iterations is known before entering the loop.
Syntax
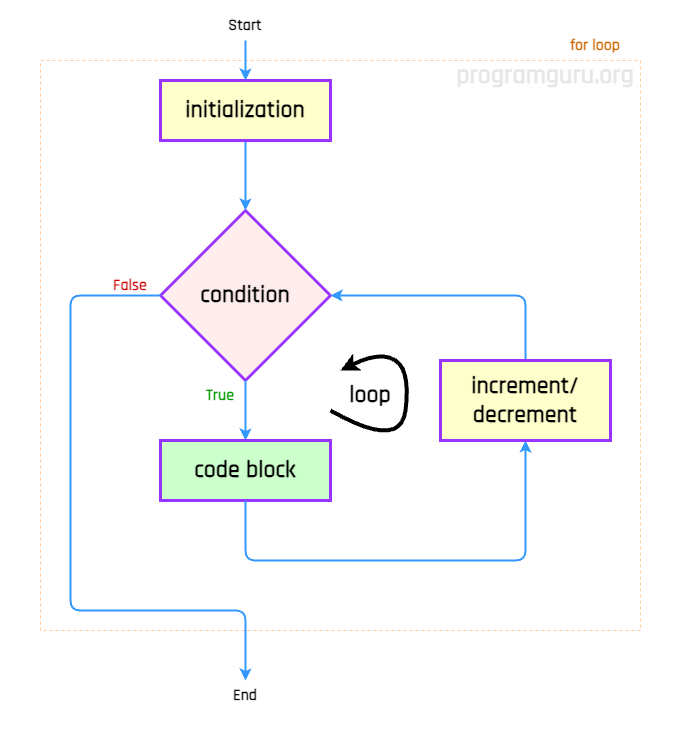
The syntax for the for loop in Go is:
for initialization; condition; increment {
// Code block to be executed
}The for loop evaluates the initialization statement, then the condition. If the condition is true, the code block inside the loop is executed. After each iteration, the increment statement is executed, and the condition is re-evaluated. This process repeats until the condition becomes false.
Example 1: Printing Numbers from 1 to 10
- Declare an integer variable
i. - Use a for loop to print numbers from 1 to 10.
Go Program
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
for i := 1; i <= 10; i++ {
fmt.Print(i, " ")
}
}Output
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Example 2: Calculating the Factorial of a Number
- Declare an integer variable
nandfactorial. - Assign a value to
n. - Initialize
factorialto 1. - Use a for loop to calculate the factorial of
n. - Print the factorial.
Go Program
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
n := 5
factorial := 1
for i := 1; i <= n; i++ {
factorial *= i
}
fmt.Printf("Factorial of %d is %d", n, factorial)
}Output
Factorial of 5 is 120
Example 3: Summing the Elements of an Array
- Declare an array of integers
arrand an integer variablesum. - Initialize the array with values.
- Initialize
sumto 0. - Use a for loop to calculate the sum of the elements in
arr. - Print the sum.
Go Program
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
arr := []int{1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
sum := 0
for i := 0; i < len(arr); i++ {
sum += arr[i]
}
fmt.Printf("Sum of the elements in the array is %d", sum)
}Output
Sum of the elements in the array is 15