Bash Integers
Bash Integers
In Bash scripting, integers are used for numerical calculations and comparisons. Understanding how to define, manipulate, and perform operations on integers is crucial for effective shell scripting.
Defining Integers
Integers in Bash can be defined by assigning numerical values to variables.
#!/bin/bash
# Define integers
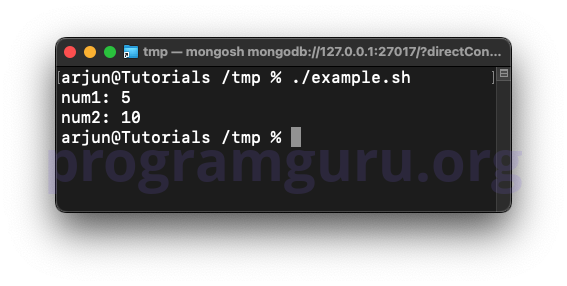
num1=5
num2=10
# Print integers
echo "num1: $num1"
echo "num2: $num2"
In this example, num1 and num2 are defined with the values 5 and 10, respectively.
Arithmetic Operations
Bash supports basic arithmetic operations using the $(( ... )) syntax.
#!/bin/bash
num1=8
num2=3
# Perform arithmetic operations
sum=$((num1 + num2))
difference=$((num1 - num2))
product=$((num1 * num2))
quotient=$((num1 / num2))
# Print results
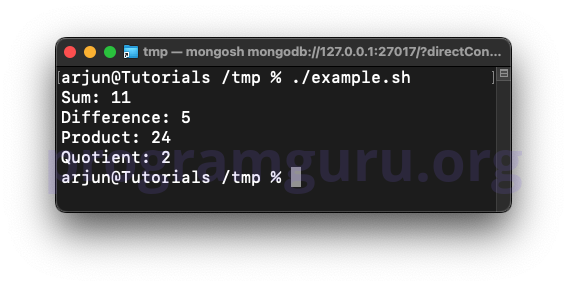
echo "Sum: $sum"
echo "Difference: $difference"
echo "Product: $product"
echo "Quotient: $quotient"
In this example, the script performs addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division on num1 and num2, and prints the results.
Increment and Decrement
Integers can be incremented or decremented using the ++ and -- operators.
#!/bin/bash
# Increment and decrement
num=5
((num++))
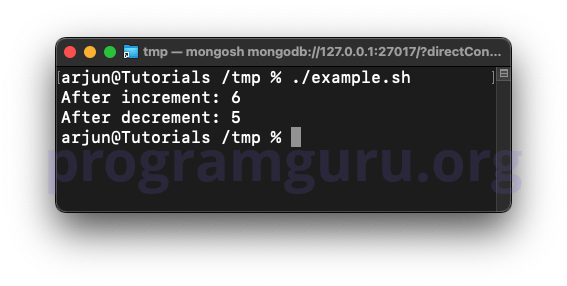
echo "After increment: $num"
((num--))
echo "After decrement: $num"
In this example, num is incremented and decremented, and the results are printed.
Numerical Comparisons
Numerical comparisons in Bash can be performed using comparison operators within an if statement.
#!/bin/bash
# Numerical comparisons
num1=5
num2=10
if [ $num1 -lt $num2 ]; then
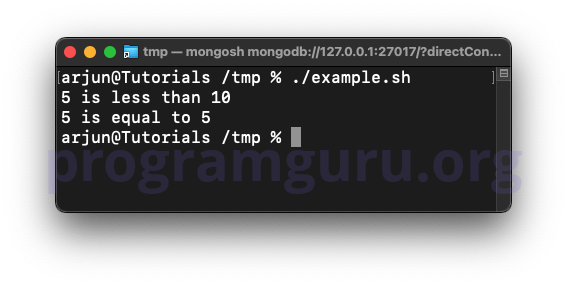
echo "$num1 is less than $num2"
fi
if [ $num1 -eq 5 ]; then
echo "$num1 is equal to 5"
fi
In this example, the script uses the -lt (less than) and -eq (equal) operators to compare num1 and num2.
Using Integers with Loops
Integers are often used with loops for iteration.
#!/bin/bash
# Using integers with loops
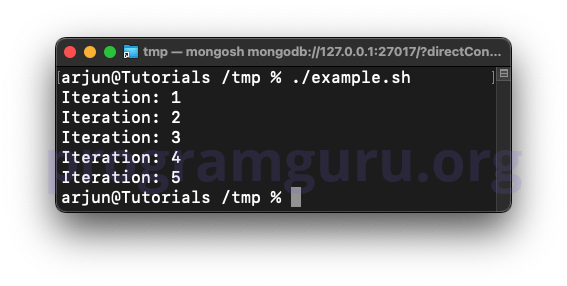
for (( i=1; i<=5; i++ )); do
echo "Iteration: $i"
done
In this example, a for loop is used to iterate from 1 to 5, printing the iteration number each time.
Integer Arrays
Arrays in Bash can also store integers, allowing for more complex data management.
#!/bin/bash
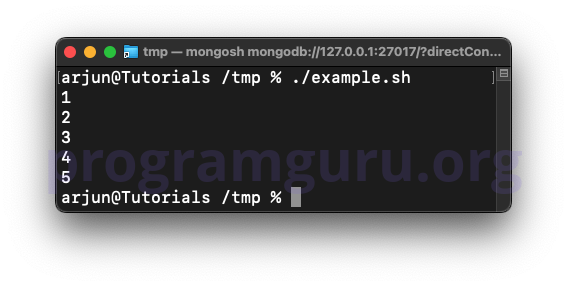
# Define an integer array
array=(1 2 3 4 5)
# Print array elements
for num in "${array[@]}"; do
echo "$num"
done
In this example, the array array is defined with integer elements and printed using a for loop.
Conclusion
Working with integers in Bash is essential for performing arithmetic operations and numerical comparisons in shell scripts. Understanding how to define, manipulate, perform operations on, compare, and use integers with loops can help you write more effective and robust Bash scripts.