Create Collection - PyMongo - Examples
PyMongo - Create a Collection in MongoDB Database
To create a collection in a MongoDB database using PyMongo in Python, follow these steps:
- Create a client to the MongoDB instance.
- Provide the name of the database to the client. This returns a reference to the database.
- Provide the name of the new collection by indexing the database reference with the collection name.
This returns a reference to the collection. The collection is created when the first document is inserted into it.
Examples
1. Create a MongoDB Collection Named "testers"
The following Python program creates a collection named testers.
Python Program
import pymongo
myclient = pymongo.MongoClient("mongodb://localhost:27017/")
# Use the database named "organisation"
mydb = myclient["organisation"]
# Create a new collection named "testers"
mycol = mydb["testers"]Explanation:
- We import the
pymongolibrary and establish a connection to the MongoDB instance usingMongoClient. - We select the
organisationdatabase usingmyclient["organisation"]. - We create a new collection named
testersby referencing the database with the collection name. - Note that the collection is created only when a document is inserted into it, so it won't show up in
list_collection_names()until content is added.
Output
No output yet. The collection "testers" is created only after inserting data.Note: The collection is not physically created until at least one document is inserted. You can check this by listing the collections after inserting a document into the collection.
2. Insert a Document and Verify Collection Creation
In this example, we create the collection and insert a document to confirm its creation.
Python Program
import pymongo
myclient = pymongo.MongoClient("mongodb://localhost:27017/")
# Use the database named "organisation"
mydb = myclient["organisation"]
# Use the collection named "testers"
mycol = mydb["testers"]
# A document to insert
tester = { "name": "Ram", "address": "India" }
# Insert the document into the collection
x = mycol.insert_one(tester)
# List the collections after inserting the document
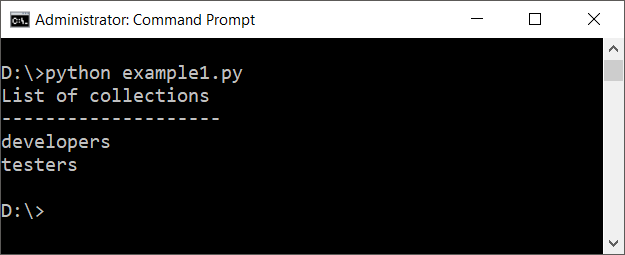
print("List of collections\n--------------------")
for coll in mydb.list_collection_names():
print(coll)Explanation:
- We select the
organisationdatabase and thetesterscollection as before. - We define a
testerdictionary with a name and address. - The document is inserted into the collection using
insert_one(). - Finally, we list the collections in the database. The
testerscollection should now appear in the list since the document was inserted.
Output
3. Create Collection with Specific Options
In this example, we create a collection with specific options such as creating an index on the collection.
Python Program
import pymongo
myclient = pymongo.MongoClient("mongodb://localhost:27017/")
# Use the database named "organisation"
mydb = myclient["organisation"]
# Create a collection named "employees" with an index on the "name" field
mycol = mydb.create_collection("employees", codec_options=pymongo.codec_options.CodecOptions(tz_aware=True))
# Create an index on the "name" field
mycol.create_index([("name", pymongo.ASCENDING)])Explanation:
- We create a collection named
employeeswith specific options, such as enabling timezone-aware datetime support usingcodec_options. - We then create an index on the
namefield of the collection usingcreate_index()withASCENDINGorder. - This is useful for optimizing query performance when filtering or sorting by the
namefield.
Output:
No output yet. The collection "employees" with an index on "name" is now created.Summary
In this PyMongo Tutorial, we learned how to create a collection in a MongoDB database using the following approaches:
- Creating a basic collection when a document is inserted for the first time.
- Inserting a document to verify collection creation and list collections in the database.
- Creating a collection with specific options, such as setting up indexes for performance optimization.