Create MongoDB Database - PyMongo - Examples
Create a Database using PyMongo
To create a Database in MongoDB from Python using PyMongo, follow these steps:
- Create a client to the MongoDB instance.
- Provide the name of the database to the client. It returns a reference to the database.
- Now you can use this database reference to modify your collections or documents.
Examples
1. Create MongoDB Database Named "organisation"
In the following program, we create a database named organisation.
Python Program
import pymongo
myclient = pymongo.MongoClient("mongodb://localhost:27017/")
# Use database named "organisation"
mydb = myclient["organisation"]Explanation:
- We first import the
pymongolibrary. - We create a MongoDB client object
myclientto connect to the local MongoDB instance. - We reference the database
organisationby providing its name to themyclientobject. This does not create the database yet. - Database creation happens only once we insert at least one document into it, which we will demonstrate next.
Note: A database is created in MongoDB only after there is content (such as a document) inserted into it. To see the database in the list of databases, we need to insert a document.
2. Create a Database and Insert a Document
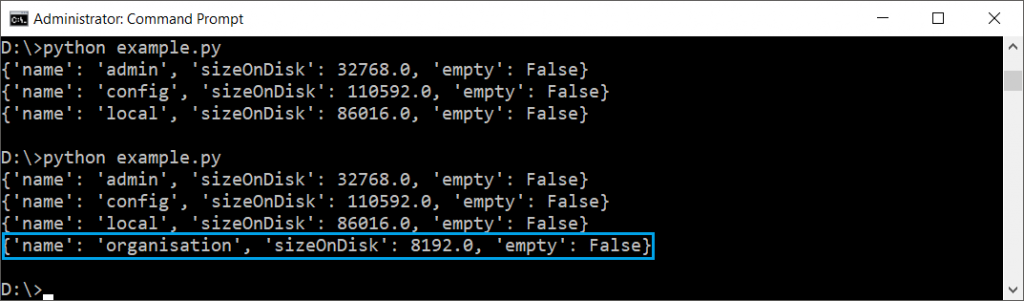
In this example, we will create a database, insert a document into it, and then list the available databases to confirm the creation.
Python Program
import pymongo
myclient = pymongo.MongoClient("mongodb://localhost:27017/")
# Use database named "organisation"
mydb = myclient["organisation"]
# Use collection named "developers"
mycol = mydb["developers"]
# A document
developer = { "name": "Lini", "address": "Sweden" }
# Insert a document to the collection
x = mycol.insert_one(developer)
# List the databases
for db in myclient.list_databases():
print(db)Explanation:
- After referencing the
organisationdatabase, we create a collection nameddeveloperswithin it. - We create a sample document
developerwith fields for name and address. - The document is inserted into the collection using
insert_one()method. This action triggers the creation of the database in MongoDB. - Finally, we use the
list_databases()method to list all databases and confirm thatorganisationnow exists.
Output:
3. Create and List a Database in Remote MongoDB Instance
In this example, we will connect to a remote MongoDB instance, create a database, and list it.
Python Program
import pymongo
myclient = pymongo.MongoClient("mongodb://remote_host:27017/")
# Use database named "company"
mydb = myclient["company"]
# Use collection named "employees"
mycol = mydb["employees"]
# A document
employee = { "name": "Alice", "position": "Engineer" }
# Insert a document
x = mycol.insert_one(employee)
# List the databases
for db in myclient.list_databases():
print(db)Explanation:
- This program is similar to the previous one, but it connects to a remote MongoDB instance instead of the local one.
- We connect to the MongoDB server running on a remote host
remote_hostat port 27017. - We proceed with the same steps to create the
companydatabase, insert an employee document, and list the databases.
Output:

Summary
In this PyMongo Tutorial, we learned how to create a MongoDB database, with examples showing how to:
- Create a database with a given name.
- Insert a document into a database to trigger its creation.
- Connect to a remote MongoDB instance.
- List all databases to verify creation.