Get all Rows from Table in Python MySQL
Python MySQL - Get all rows from Table
To get all rows from MySQL table in Python,
- Create a connection to the MySQL database with user credentials and database name, using connect() function.
- Get cursor object to the database using cursor() function.
- Call execute() function on the cursor object, and pass the SELECT FROM table query.
- Call fetchall() function on the cursor object. The function returns an iterator to the records in the table. Each record is a tuple.
Example
Consider that there is a schema named mydatabase in MySQL. The credentials to access this database are: user: root and password: admin1234, and there is a table named fruits in mydatabase.
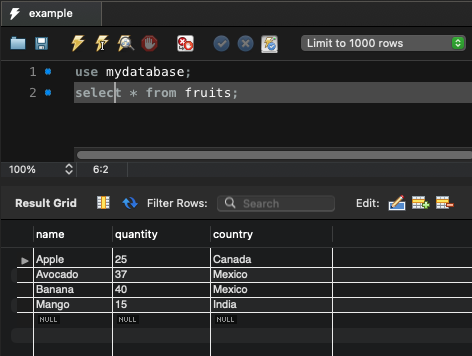
In the following program, we fetch all the records from fruits table and print them to output.
Python Program
import mysql.connector
mydb = mysql.connector.connect(
host="localhost",
user="root",
password="admin1234",
database="mydatabase"
)
mycursor = mydb.cursor()
mycursor.execute("SELECT * FROM fruits")
myresult = mycursor.fetchall()
for row in myresult:
print(row)Output
('Apple', 25, 'Canada')
('Avocado', 37, 'Mexico')
('Banana', 40, 'Mexico')
('Mango', 15, 'India')Summary
In this tutorial of Python Examples, we learned how to get all the records from a table in MySQL database, from a Python program.