Iterate over Rows in Table in Python MySQL
Python MySQL - Iterate over rows in Table
To iterate over rows of a MySQL table in Python program,
- Create a connection to the MySQL database with user credentials and database name, using connect() function.
- Get cursor object to the database using cursor() function.
- Call execute() function on the cursor object, and pass the SELECT FROM table query.
- Call fetchall() function on the cursor object. The function returns an iterator to the records in the table. Each record is a tuple.
- Use a For loop statement to iterate over the rows/records from the fetchall() function.
Example
Consider that there is a schema named mydatabase in MySQL. The credentials to access this database are, user: root and password: admin1234, and there is a table named fruits in mydatabase.
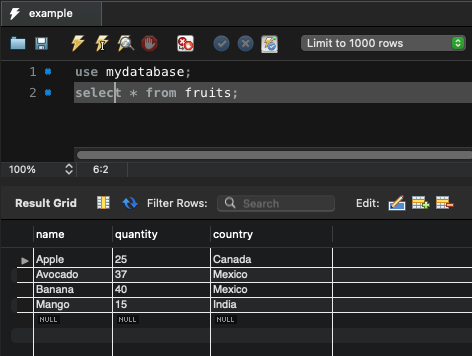
In the following program, we fetch all the records from fruits table, iterate over them using For loop, and print them to output.
Each row is a tuple, and we can access the individual column values using index as shown in the For loop.
Python Program
import mysql.connector
mydb = mysql.connector.connect(
host="localhost",
user="root",
password="admin1234",
database="mydatabase"
)
mycursor = mydb.cursor()
mycursor.execute("SELECT * FROM fruits")
myresult = mycursor.fetchall()
for row in myresult:
print(row[0], '-', row[1], '-', row[2])Output
Apple - 25 - Canada
Avocado - 37 - Mexico
Banana - 40 - Mexico
Mango - 15 - IndiaSummary
In this tutorial of Python Examples, we learned how to iterate over the records of a table in MySQL database, from a Python program.