How to Concatenate DataFrames in Pandas? Examples
Concatenate DataFrames - pandas.concat()
You can concatenate two or more Pandas DataFrames with similar columns. To concatenate Pandas DataFrames, usually with similar columns, use pandas.concat() function.
In this tutorial, we will learn how to concatenate DataFrames with similar and different columns.

Syntax of pandas.concat() method
The syntax of pandas.concat() is:
pandas.concat(objs, axis=0, join='outer', join_axes=None, ignore_index=False, keys=None, levels=None, names=None, verify_integrity=False, sort=None, copy=True)Video Tutorial
Examples
1. Concatenate DataFrames with similar columns
In this example, we take two DataFrames with same column names and concatenate them using concat() function.
Python Program
import pandas as pd
df_1 = pd.DataFrame(
[['Somu', 68, 84, 78, 96],
['Kiku', 74, 56, 88, 85],
['Ajit', 77, 73, 82, 87]],
columns=['name', 'physics', 'chemistry','algebra','calculus'])
df_2 = pd.DataFrame(
[['Amol', 72, 67, 91, 83],
['Lini', 78, 69, 87, 92]],
columns=['name', 'physics', 'chemistry','algebra','calculus'])
frames = [df_1, df_2]
#concatenate dataframes
df = pd.concat(frames, sort=False)
#print dataframe
print("df_1\n------\n",df_1)
print("\ndf_2\n------\n",df_2)
print("\ndf\n--------\n",df)Explanation
- The program imports the
pandaslibrary, which is used for working with structured data. - Two DataFrames,
df_1anddf_2, are created using thepd.DataFrame()function: df_1: Contains data for three students with their scores in'physics','chemistry','algebra', and'calculus'.df_2: Contains data for two additional students with similar columns asdf_1.- A list named
framesis created to hold bothdf_1anddf_2for further processing. - The
pd.concat()function is used to concatenate the two DataFrames along the rows. The argumentsort=Falseensures that the columns are not re-ordered, even if they are not in the same order in both DataFrames. - The concatenated DataFrame,
df, contains all the rows from both DataFrames, with any missing columns filled withNaN. - Finally, the program prints the individual DataFrames
df_1anddf_2, followed by the concatenated DataFramedf, to show how the data is combined.
Output
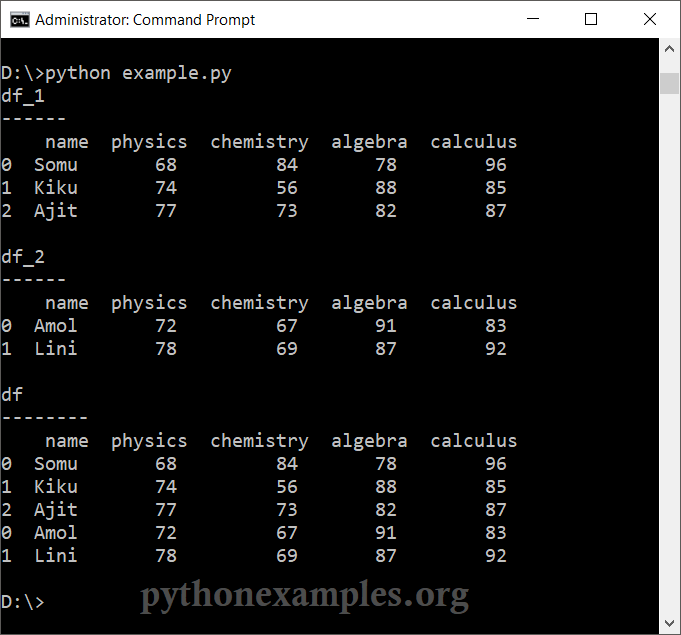
The two DataFrames are concatenated. But the index is not in order. You can reset the index by using reset_index() function.
Python Program
import pandas as pd
df_1 = pd.DataFrame(
[['Somu', 68, 84, 78, 96],
['Kiku', 74, 56, 88, 85],
['Ajit', 77, 73, 82, 87]],
columns=['name', 'physics', 'chemistry','algebra','calculus'])
df_2 = pd.DataFrame(
[['Amol', 72, 67, 91, 83],
['Lini', 78, 69, 87, 92]],
columns=['name', 'physics', 'chemistry','algebra','calculus'])
frames = [df_1, df_2]
#concatenate dataframes
df = pd.concat(frames)
# reset index
df.reset_index(drop=True, inplace=True)
#print dataframe
print(df)Explanation
- The program imports the
pandaslibrary for creating and manipulating tabular data. - Two DataFrames,
df_1anddf_2, are created using thepd.DataFrame()function: df_1: Contains three students' names and their scores in'physics','chemistry','algebra', and'calculus'.df_2: Contains two additional students with the same column structure asdf_1.- A list named
framesis created to hold both DataFrames. - The
pd.concat()function is used to concatenate the DataFrames along their rows, combining all records into a single DataFrame nameddf. - After concatenation, the indices from the original DataFrames are preserved. To create a new sequential index, the
reset_index()method is called withdrop=True. This drops the old indices and resets the index to start from zero. - The final DataFrame,
df, contains all rows fromdf_1anddf_2with a reset index, making the data more structured and consistent for further analysis. - The program prints the updated DataFrame
df, showing all rows with a uniform index.
Output
name physics chemistry algebra calculus
0 Somu 68 84 78 96
1 Kiku 74 56 88 85
2 Ajit 77 73 82 87
3 Amol 72 67 91 83
4 Lini 78 69 87 922. Concatenate two DataFrames with different columns
In this following example, we take two DataFrames. The second dataframe has a new column, and does not contain one of the column that first dataframe has.
pandas.concat() function concatenates the two DataFrames and returns a new dataframe with the new columns as well. The dataframe row that has no value for the column will be filled with NaN short for Not a Number.
Python Program
import pandas as pd
df_1 = pd.DataFrame(
[['Somu', 68, 84, 78, 96],
['Kiku', 74, 56, 88, 85],
['Ajit', 77, 73, 82, 87]],
columns=['name', 'physics', 'chemistry','algebra','calculus'])
df_2 = pd.DataFrame(
[['Amol', 72, 67, 91, 83],
['Lini', 78, 69, 87, 92]],
columns=['name', 'physics', 'chemistry','geometry','calculus'])
frames = [df_1, df_2]
#concatenate dataframes
df = pd.concat(frames, sort=False)
#print dataframe
print("df_1\n------\n",df_1)
print("\ndf_2\n------\n",df_2)
print("\ndf\n--------\n",df)Explanation
- The program imports the
pandaslibrary, which is commonly used for handling and analyzing tabular data. - Two DataFrames,
df_1anddf_2, are created using thepd.DataFrame()function: df_1: Contains student names and their scores in'physics','chemistry','algebra', and'calculus'.df_2: Contains student names and their scores in'physics','chemistry','geometry', and'calculus'.- Both DataFrames have the
'name'column in common but differ in some of the other column names ('algebra'vs.'geometry'). - A list named
framesis created, containingdf_1anddf_2as its elements. - The
pd.concat()function is used to concatenate the two DataFrames along their rows. The argumentsort=Falseensures that the column order remains as it is in the input DataFrames. - In the concatenated DataFrame
df: - Columns present in both DataFrames (
'name','physics','chemistry', and'calculus') are combined. - Columns unique to either DataFrame (
'algebra'or'geometry') are included, but missing values in these columns for rows from the other DataFrame are filled withNaN(Not a Number). - The individual DataFrames
df_1anddf_2, as well as the concatenated DataFramedf, are printed to the console.
Output
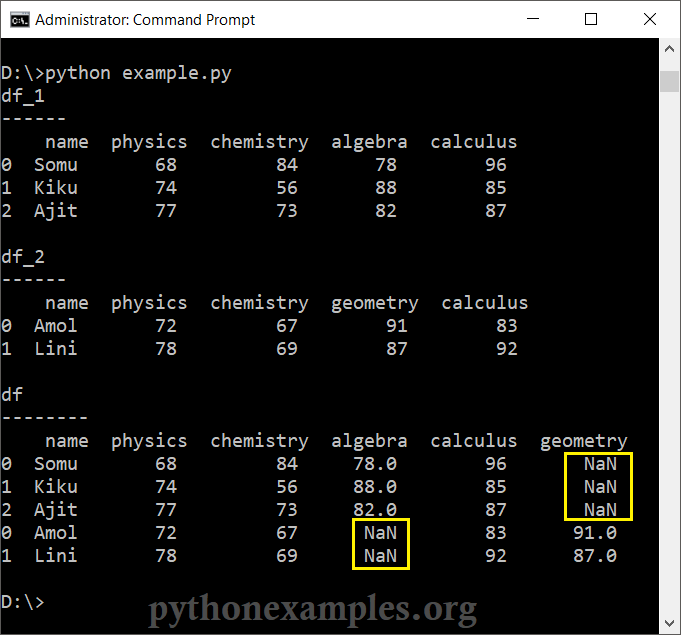
Summary
In this tutorial of Python Examples, we learned how to concatenate one or more DataFrames into a single DataFrame, with the help of well detailed examples.