PostgreSQL ALTER TABLE Statement
PostgreSQL ALTER TABLE Statement
The PostgreSQL ALTER TABLE statement is used to modify the structure of an existing table. This statement is essential for adding, deleting, or modifying columns, as well as for adding and dropping constraints.
Syntax
ALTER TABLE table_name
ADD column_name datatype [constraints];
DROP COLUMN column_name;
ALTER COLUMN column_name [SET DATA TYPE datatype | SET DEFAULT default_value | DROP DEFAULT];
ADD CONSTRAINT constraint_name constraint_definition;
DROP CONSTRAINT constraint_name;
The ALTER TABLE statement has the following components:
table_name: The name of the table to be modified.ADD column_name datatype [constraints]: Adds a new column to the table.DROP COLUMN column_name: Deletes a column from the table.ALTER COLUMN column_name: Modifies an existing column's data type or default value.ADD CONSTRAINT constraint_name constraint_definition: Adds a new constraint to the table.DROP CONSTRAINT constraint_name: Removes a constraint from the table.
Example PostgreSQL ALTER TABLE Statement Queries
Let's look at some examples of PostgreSQL ALTER TABLE statement queries:
1. Adding a Column
ALTER TABLE employees
ADD birth_date DATE;
This query adds a new column named birth_date of type DATE to the employees table.
2. Dropping a Column
ALTER TABLE employees
DROP COLUMN birth_date;
This query removes the birth_date column from the employees table.
3. Modifying a Column
ALTER TABLE employees
ALTER COLUMN email SET DATA TYPE TEXT;
This query changes the data type of the email column in the employees table to TEXT.
4. Adding a Constraint
ALTER TABLE employees
ADD CONSTRAINT email_unique UNIQUE (email);
This query adds a unique constraint named email_unique on the email column in the employees table.
5. Dropping a Constraint
ALTER TABLE employees
DROP CONSTRAINT email_unique;
This query removes the unique constraint named email_unique from the email column in the employees table.
Full Example
Let's go through a complete example that includes creating a table, altering the table by adding and modifying columns, and then adding and dropping constraints.
Step 1: Creating a Table
This step involves creating a new table named employees to store employee data.
CREATE TABLE employees (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
first_name VARCHAR(50),
last_name VARCHAR(50),
email VARCHAR(100)
);
In this example, we create a table named employees with columns for id, first_name, last_name, and email.


Step 2: Adding a Column
This step involves adding a new column named birth_date to the employees table.
ALTER TABLE employees
ADD birth_date DATE;
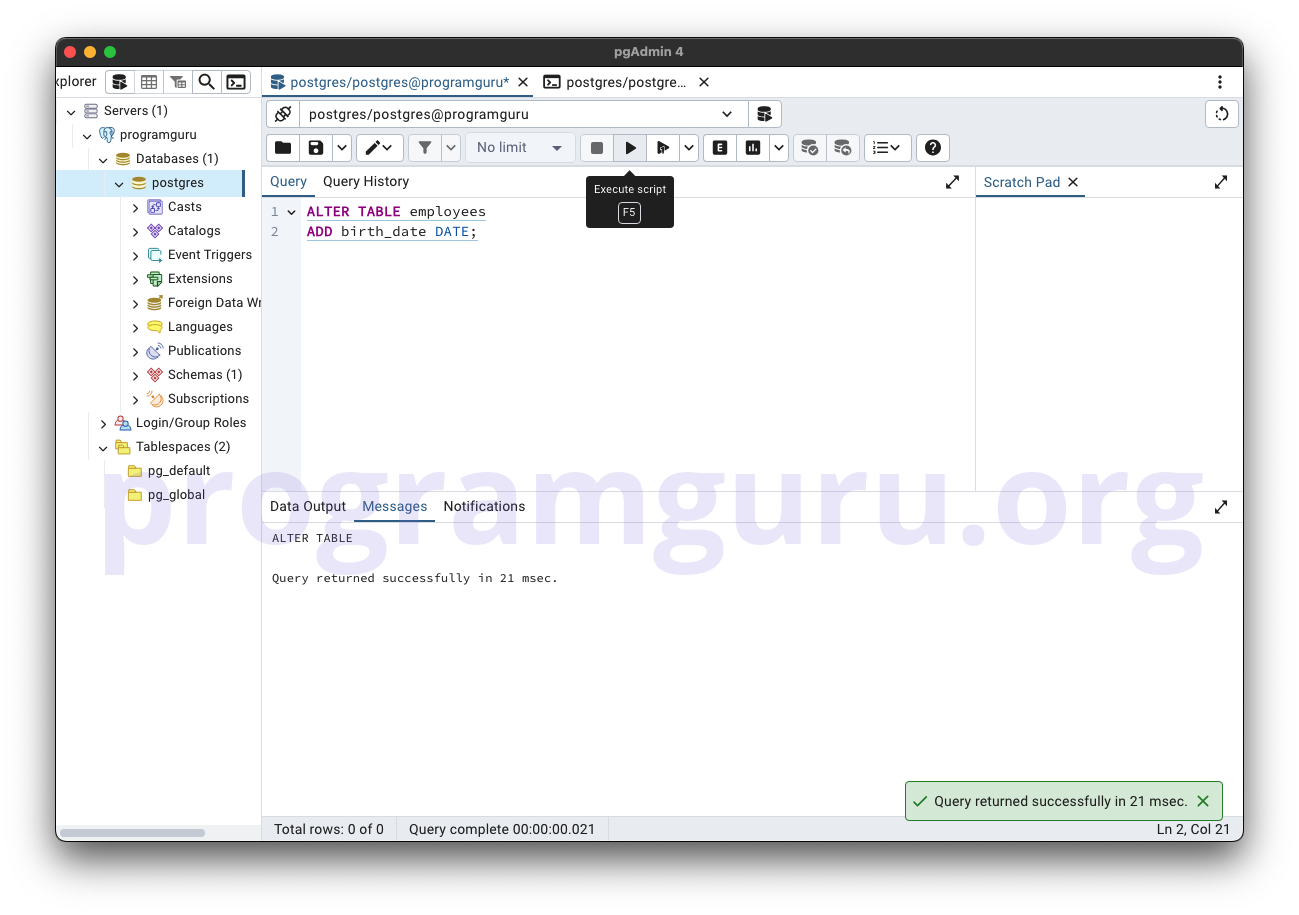
Here, we add a column named birth_date of type DATE to the employees table.
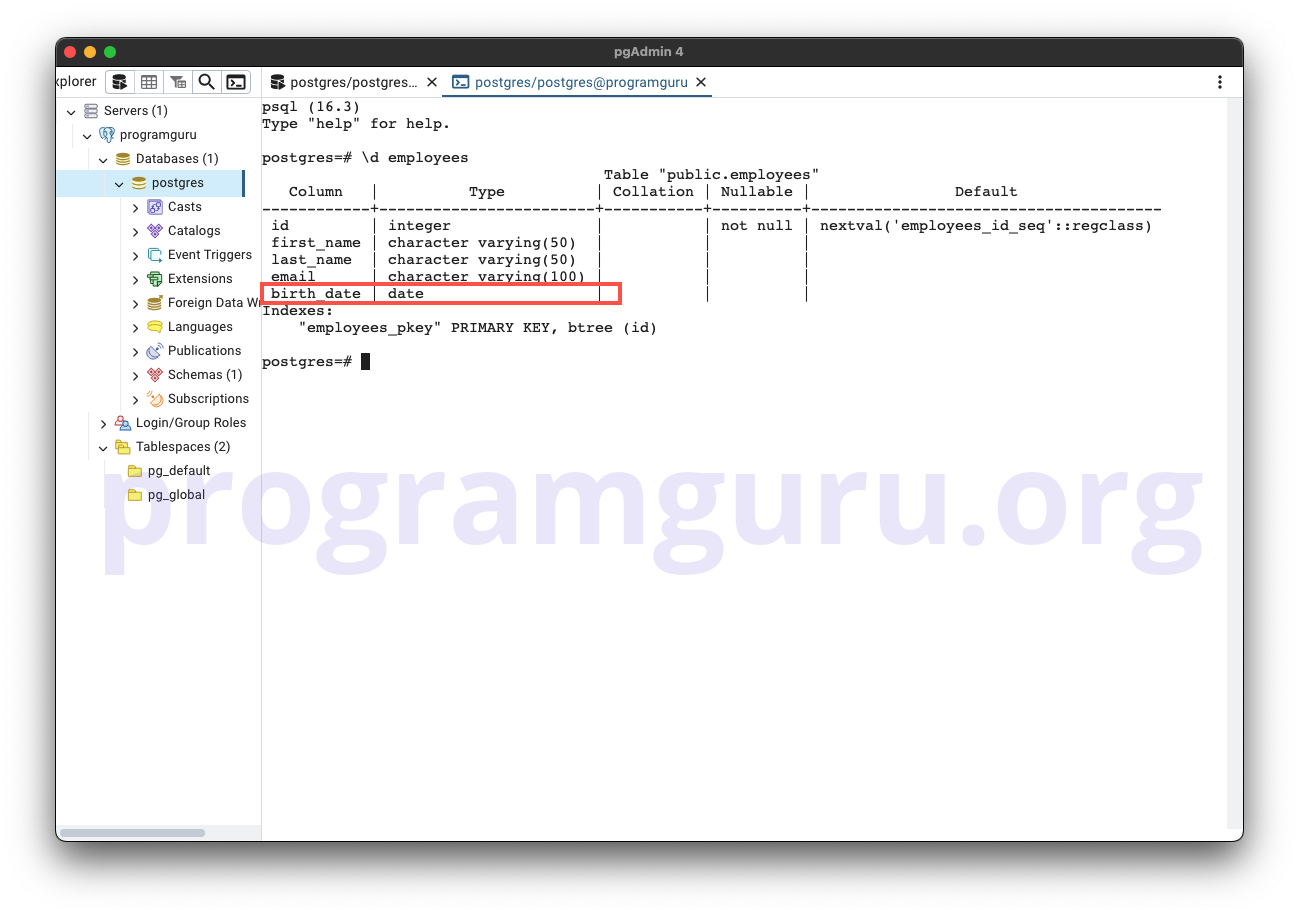
Step 3: Modifying a Column
This step involves changing the data type of the email column to TEXT.
ALTER TABLE employees
ALTER COLUMN email SET DATA TYPE TEXT;
Here, we change the data type of the email column in the employees table to TEXT.

Step 4: Adding a Constraint
This step involves adding a unique constraint on the email column.
ALTER TABLE employees
ADD CONSTRAINT email_unique UNIQUE (email);
Here, we add a unique constraint named email_unique on the email column in the employees table.
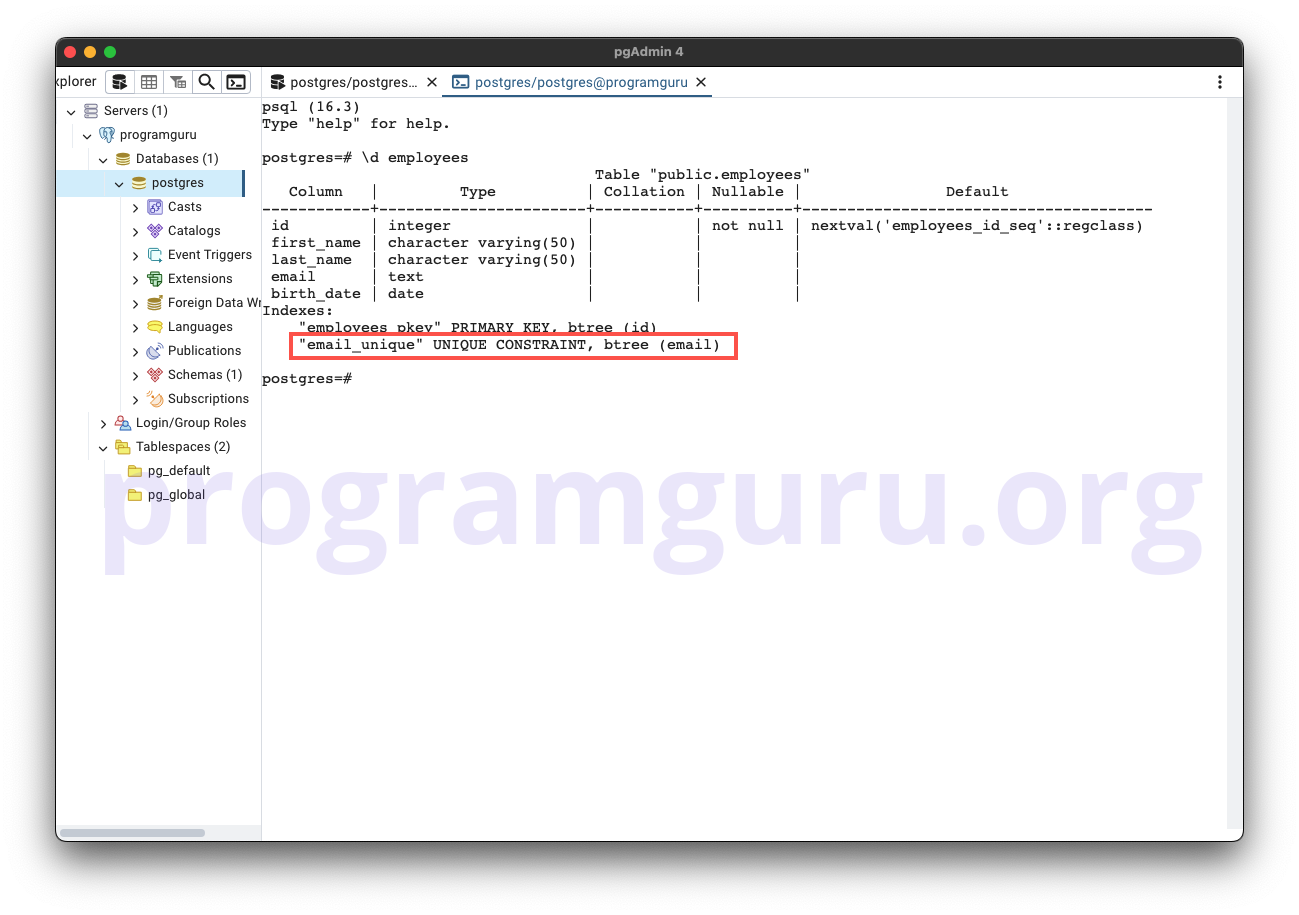
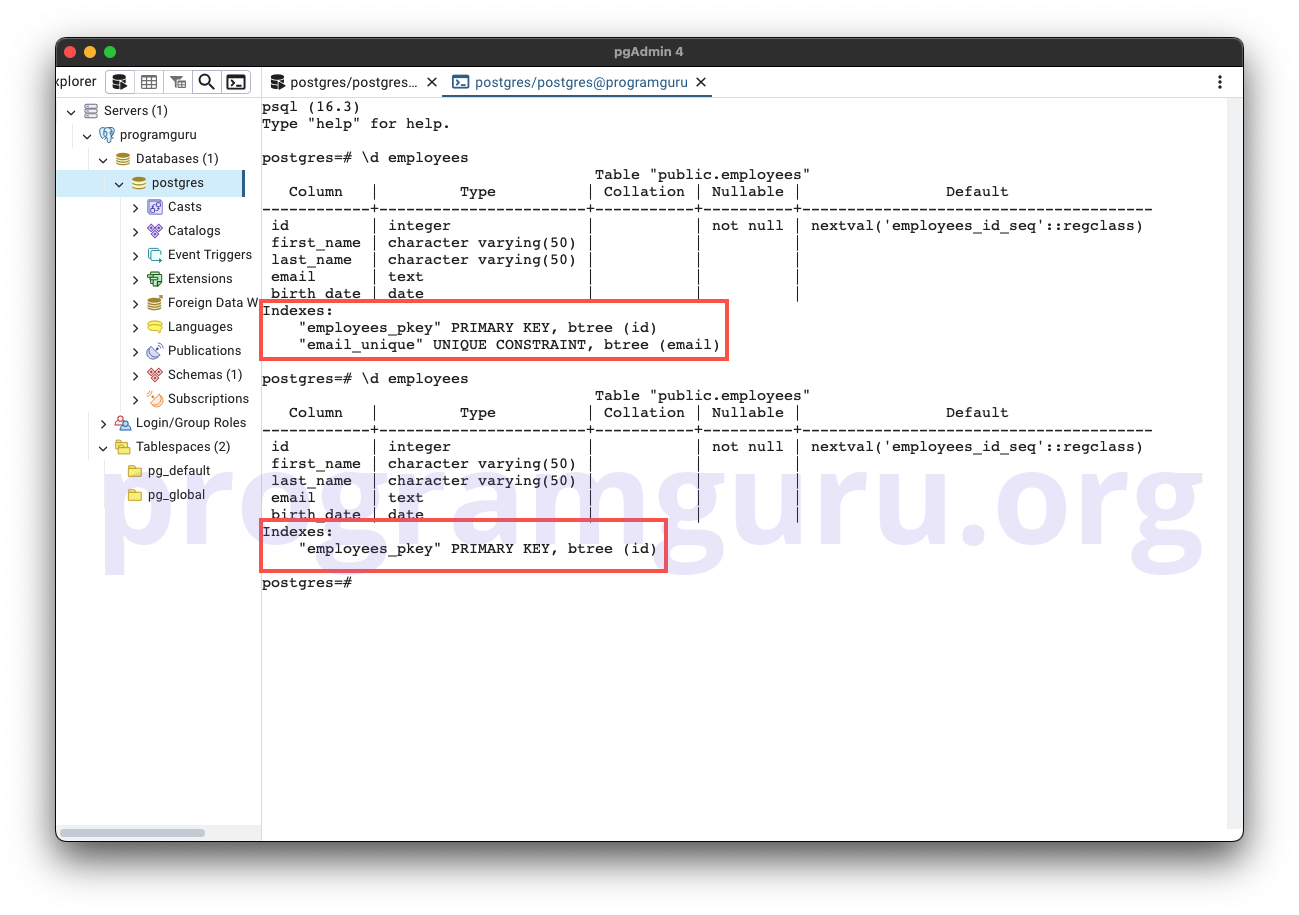
Step 5: Dropping a Constraint
This step involves removing the unique constraint from the email column.
ALTER TABLE employees
DROP CONSTRAINT email_unique;
Here, we remove the unique constraint named email_unique from the email column in the employees table.
Conclusion
The PostgreSQL ALTER TABLE statement is a fundamental tool for modifying the structure of an existing table. Understanding how to use the ALTER TABLE statement and its syntax is essential for effective database schema management and modification in PostgreSQL.