PostgreSQL DISTINCT Keyword
PostgreSQL DISTINCT Keyword
The PostgreSQL DISTINCT keyword is used to remove duplicate rows from the result set of a query. This keyword is essential for ensuring that the query results contain only unique rows.
Syntax
SELECT DISTINCT column1, column2, ...
FROM table_name;
The DISTINCT keyword can be used with multiple columns to ensure that the combination of values in those columns is unique.
Example PostgreSQL DISTINCT Queries
Let's look at some examples of PostgreSQL DISTINCT keyword queries:
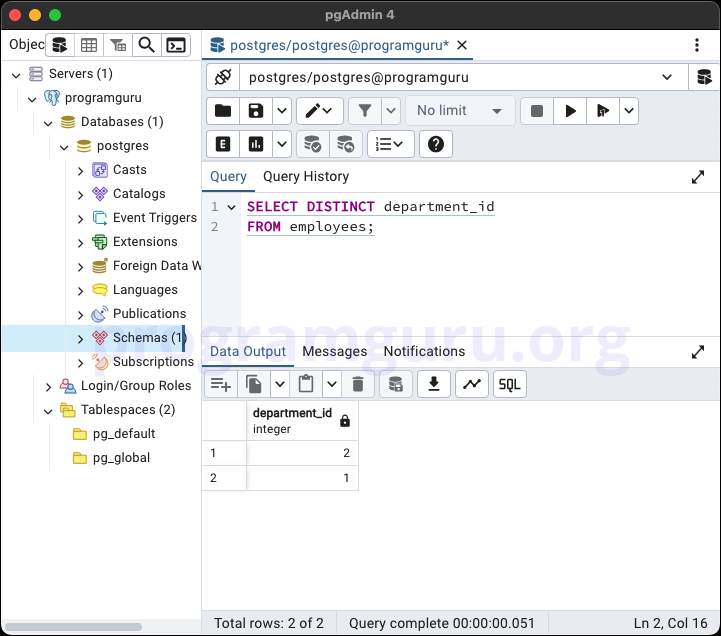
1. Basic DISTINCT Example
SELECT DISTINCT department_id
FROM employees;
This query retrieves the unique department_id values from the employees table.
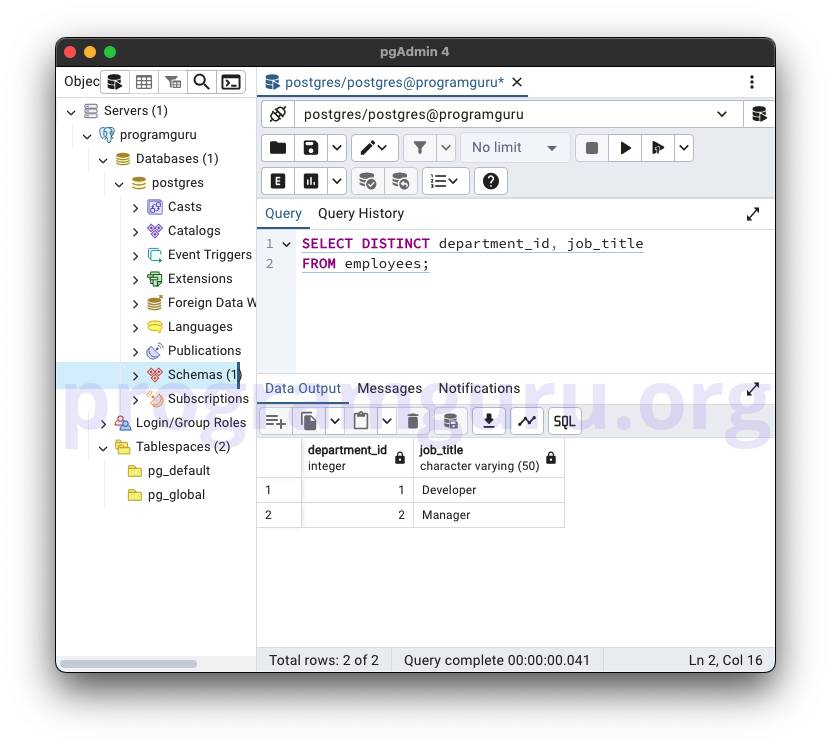
2. DISTINCT on Multiple Columns
SELECT DISTINCT department_id, job_title
FROM employees;
This query retrieves the unique combinations of department_id and job_title from the employees table.
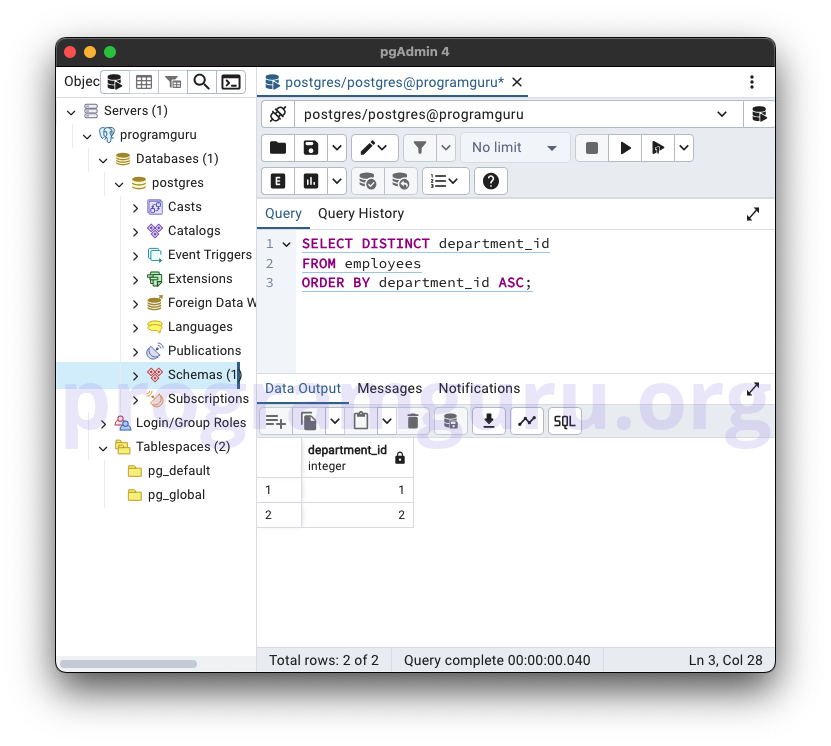
3. DISTINCT with ORDER BY Clause
SELECT DISTINCT department_id
FROM employees
ORDER BY department_id ASC;
This query retrieves the unique department_id values from the employees table and sorts them in ascending order.
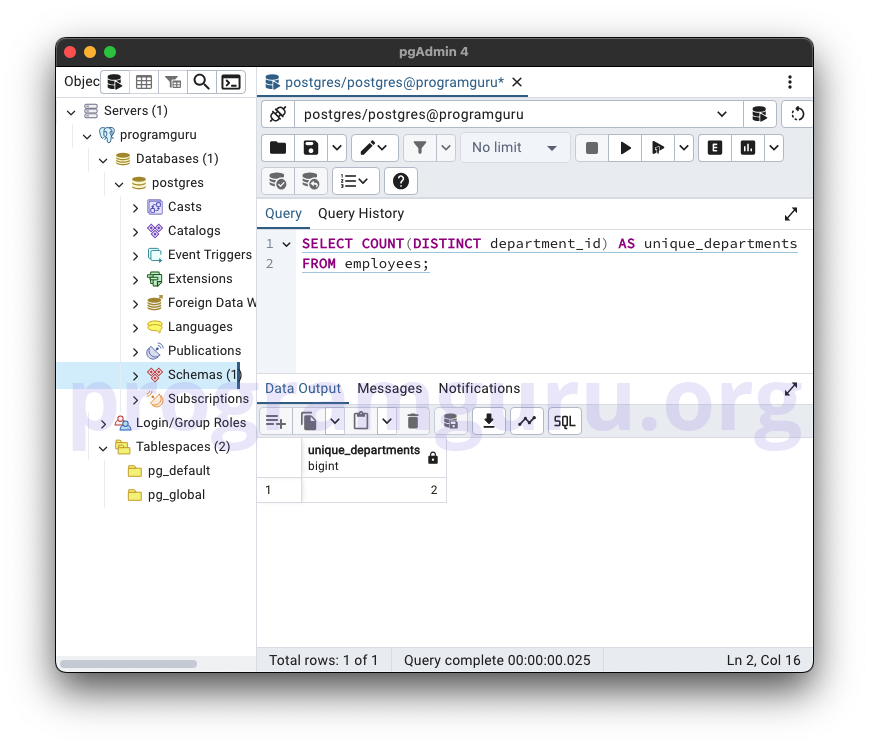
4. COUNT DISTINCT Values
SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT department_id) AS unique_departments
FROM employees;
This query counts the number of unique department_id values in the employees table.
Full Example
Let's go through a complete example that includes creating a table, inserting data, and using the DISTINCT keyword to retrieve unique rows.
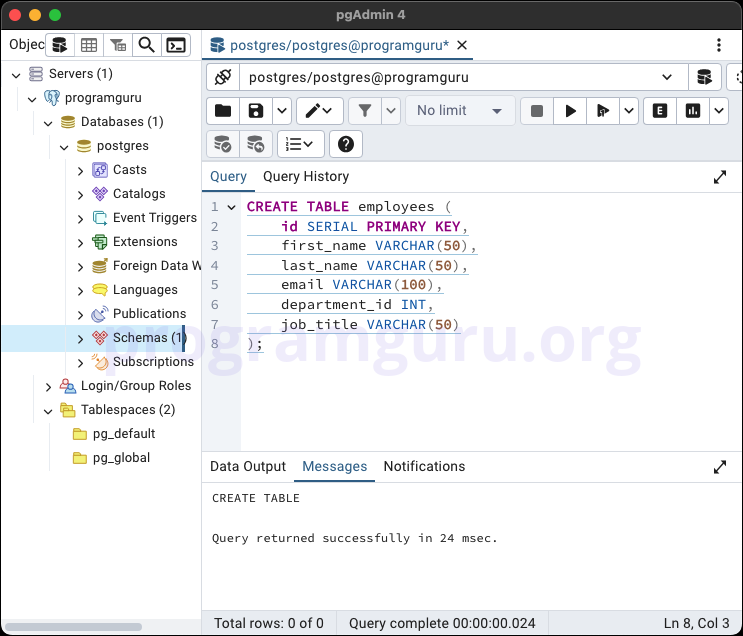
Step 1: Creating a Table
This step involves creating a new table named employees to store employee data.
CREATE TABLE employees (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
first_name VARCHAR(50),
last_name VARCHAR(50),
email VARCHAR(100),
department_id INT,
job_title VARCHAR(50)
);
In this example, we create a table named employees with columns for id, first_name, last_name, email, department_id, and job_title.
Step 2: Inserting Data into the Table
This step involves inserting some sample data into the employees table.
INSERT INTO employees (first_name, last_name, email, department_id, job_title)
VALUES ('John', 'Doe', 'john.doe@example.com', 1, 'Developer');
INSERT INTO employees (first_name, last_name, email, department_id, job_title)
VALUES ('Jane', 'Smith', 'jane.smith@example.com', 2, 'Manager');
INSERT INTO employees (first_name, last_name, email, department_id, job_title)
VALUES ('Jim', 'Brown', 'jim.brown@example.com', 1, 'Developer');
INSERT INTO employees (first_name, last_name, email, department_id, job_title)
VALUES ('Emily', 'Jones', 'emily.jones@example.com', 2, 'Manager');
Here, we insert data into the employees table.

Step 3: Retrieving Unique Rows with DISTINCT
This step involves using the DISTINCT keyword to retrieve unique rows from the employees table.
These queries demonstrate how to use the DISTINCT keyword to retrieve unique rows from the employees table, including using DISTINCT on single and multiple columns, sorting the unique results, and counting the number of unique values.
-- Basic DISTINCT
SELECT DISTINCT department_id
FROM employees;
-- DISTINCT on Multiple Columns
SELECT DISTINCT department_id, job_title
FROM employees;
-- DISTINCT with ORDER BY Clause
SELECT DISTINCT department_id
FROM employees
ORDER BY department_id ASC;
-- COUNT DISTINCT Values
SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT department_id) AS unique_departments
FROM employees;
Conclusion
The PostgreSQL DISTINCT keyword is a fundamental tool for ensuring that query results contain only unique rows. Understanding how to use the DISTINCT keyword and its syntax is essential for effective data retrieval and manipulation in PostgreSQL databases.