PostgreSQL DROP TABLE Statement
PostgreSQL DROP TABLE Statement
The PostgreSQL DROP TABLE statement is used to remove an existing table from a database. This statement is essential for deleting tables that are no longer needed or require replacement.
Syntax
DROP TABLE [IF EXISTS] table_name [CASCADE | RESTRICT];
The DROP TABLE statement has the following components:
IF EXISTS: Optional. If specified, it will drop the table only if it exists, avoiding an error if the table does not exist.table_name: The name of the table to be dropped.CASCADE: Optional. Automatically drops objects that depend on the table, such as views or foreign key constraints.RESTRICT: Optional. Refuses to drop the table if there are any dependent objects. This is the default behavior.
Example PostgreSQL DROP TABLE Statement Queries
Let's look at some examples of PostgreSQL DROP TABLE statement queries:
1. Basic DROP TABLE Example
DROP TABLE employees;
This query drops the table named employees from the database. If the table does not exist, an error will be returned.
2. DROP TABLE IF EXISTS
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS employees;
This query drops the table named employees only if it exists. If the table does not exist, no error will be returned.
3. DROP TABLE with CASCADE
DROP TABLE employees CASCADE;
This query drops the table named employees and automatically drops all objects that depend on this table, such as views or foreign key constraints.
4. DROP TABLE with RESTRICT
DROP TABLE employees RESTRICT;
This query drops the table named employees only if no other objects depend on it. This is the default behavior if neither CASCADE nor RESTRICT is specified.
Full Example
Let's go through a complete example that includes creating a table, inserting data, and then dropping the table.
Step 1: Creating a Table
This step involves creating a new table named employees to store employee data.
CREATE TABLE employees (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
first_name VARCHAR(50),
last_name VARCHAR(50),
email VARCHAR(100)
);
In this example, we create a table named employees with columns for id, first_name, last_name, and email.
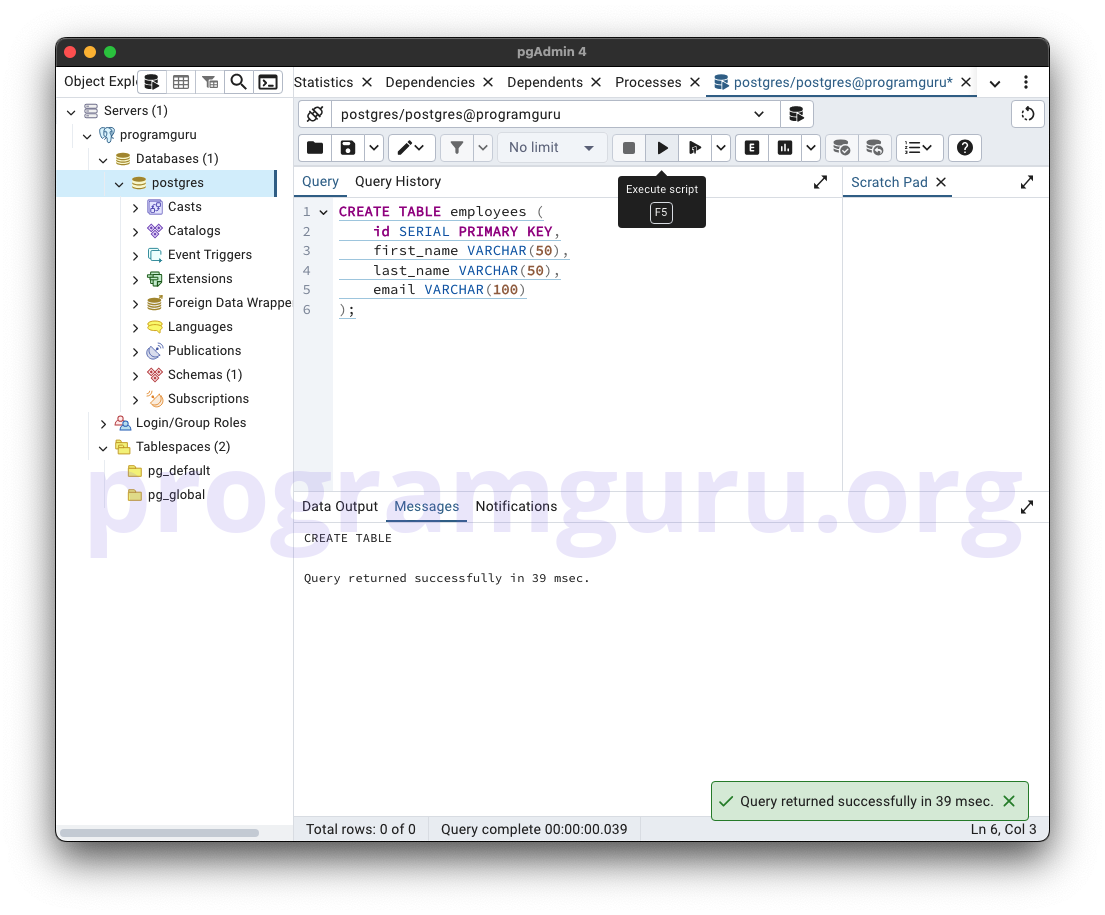
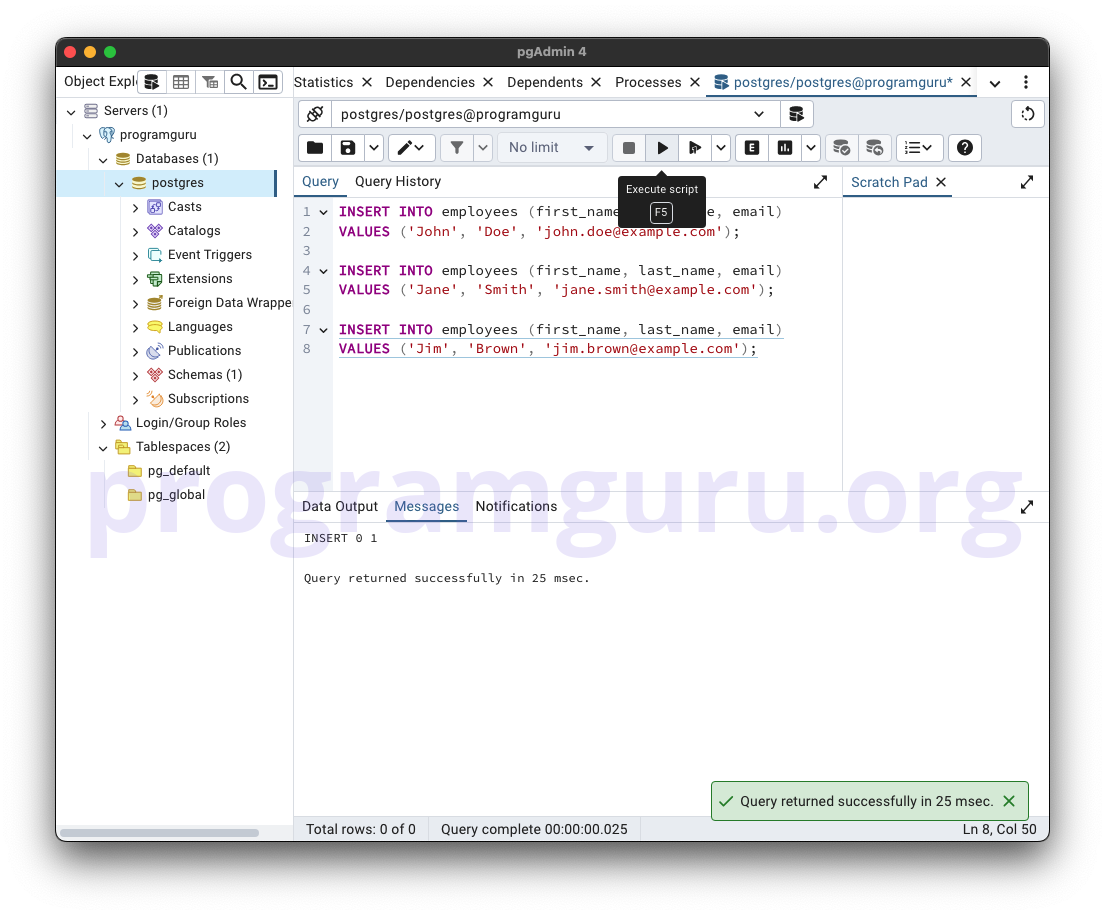
Step 2: Inserting Data into the Table
This step involves inserting some sample data into the employees table.
INSERT INTO employees (first_name, last_name, email)
VALUES ('John', 'Doe', 'john.doe@example.com');
INSERT INTO employees (first_name, last_name, email)
VALUES ('Jane', 'Smith', 'jane.smith@example.com');
INSERT INTO employees (first_name, last_name, email)
VALUES ('Jim', 'Brown', 'jim.brown@example.com');
Here, we insert data into the employees table.
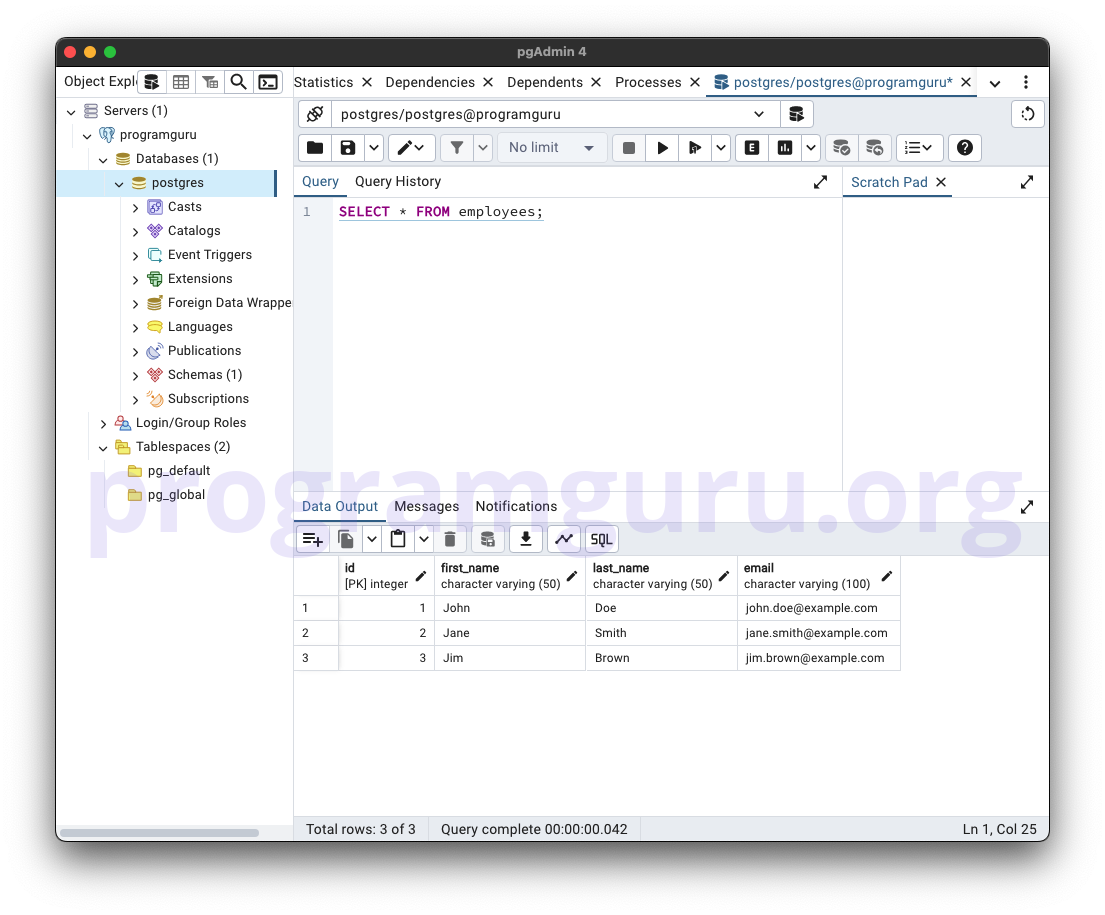
Run SELECT query to see the rows in the table.
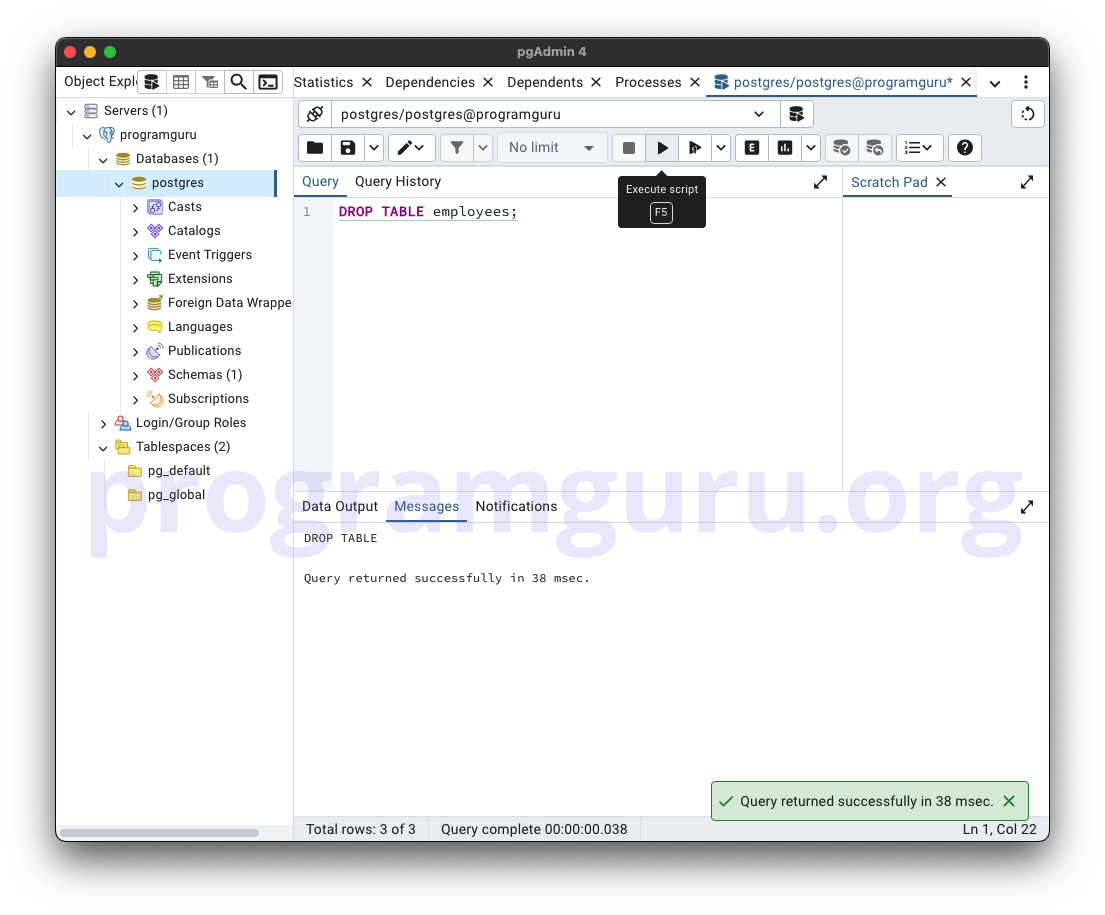
Step 3: Dropping the Table
This step involves dropping the employees table from the database.
DROP TABLE employees;
This query removes the employees table from the database.
Run SELECT query to see the rows in the table.
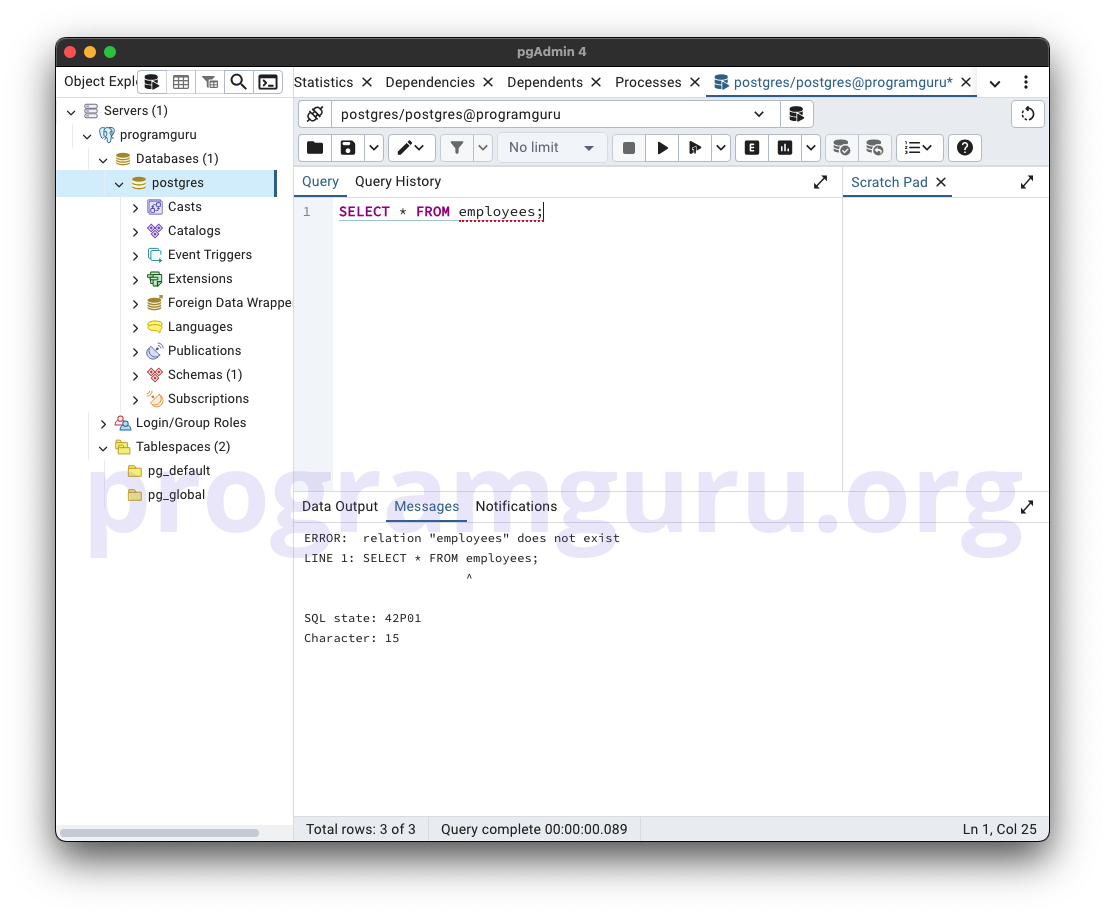
Since the table is dropped from the database, the SELECT query on the table returned an error ERROR: relation "employees" does not exist.
Conclusion
The PostgreSQL DROP TABLE statement is a fundamental tool for removing tables from a database. Understanding how to use the DROP TABLE statement and its syntax is essential for effective database management and cleanup in PostgreSQL.