PostgreSQL UPDATE
PostgreSQL UPDATE Statement
The PostgreSQL UPDATE statement is used to modify existing rows in a table. This statement is essential for changing data within a table, whether it's correcting information, updating values, or setting data to new conditions.
Syntax
UPDATE table_name
SET column1 = value1, column2 = value2, ...
WHERE condition;
The UPDATE statement has the following components:
table_name: The name of the table to update.column1, column2, ...: The columns to be updated with their new values.value1, value2, ...: The new values to assign to the specified columns.condition: The condition to identify which rows to update.
Example PostgreSQL UPDATE Statement Queries
Let's look at some examples of PostgreSQL UPDATE statement queries:
1. Basic UPDATE Example
UPDATE employees
SET email = 'john.doe@newdomain.com'
WHERE id = 1;
This query updates the email column of the row in the employees table where the id is 1.
2. UPDATE Multiple Columns
UPDATE employees
SET first_name = 'Jane', last_name = 'Doe'
WHERE id = 2;
This query updates both the first_name and last_name columns of the row in the employees table where the id is 2.
3. UPDATE with Condition
UPDATE employees
SET salary = salary * 1.1
WHERE department_id = 1;
This query updates the salary column of all rows in the employees table where the department_id is 1, increasing the salary by 10%.
Full Example
Let's go through a complete example that includes creating a table, inserting data, and using the UPDATE statement to modify the data.
Step 1: Creating a Table
This step involves creating a new table named employees to store employee data.
CREATE TABLE employees (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
first_name VARCHAR(50),
last_name VARCHAR(50),
email VARCHAR(100),
salary NUMERIC(10, 2),
department_id INT
);
In this example, we create a table named employees with columns for id, first_name, last_name, email, salary, and department_id.
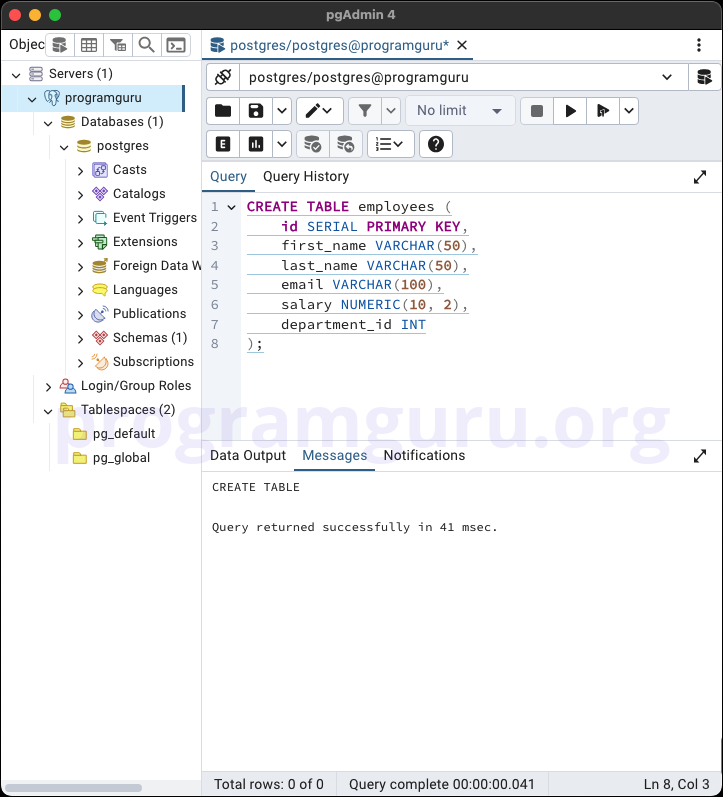
Step 2: Inserting Data into the Table
This step involves inserting some sample data into the employees table.
INSERT INTO employees (first_name, last_name, email, salary, department_id)
VALUES ('John', 'Doe', 'john.doe@example.com', 50000, 1);
INSERT INTO employees (first_name, last_name, email, salary, department_id)
VALUES ('Jane', 'Smith', 'jane.smith@example.com', 60000, 2);
INSERT INTO employees (first_name, last_name, email, salary, department_id)
VALUES ('Jim', 'Brown', 'jim.brown@example.com', 55000, 1);
Here, we insert data into the employees table.
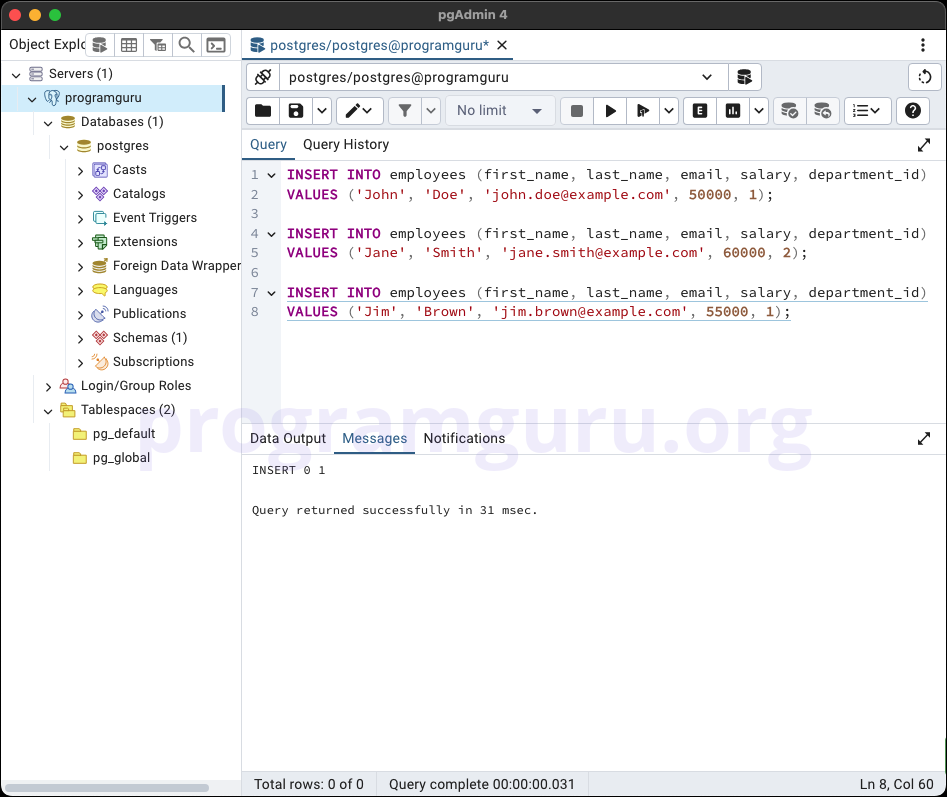
Step 3: Updating Data in the Table
This step involves using the UPDATE statement to modify data in the employees table.
Basic UPDATE
UPDATE employees
SET email = 'john.doe@newdomain.com'
WHERE id = 1;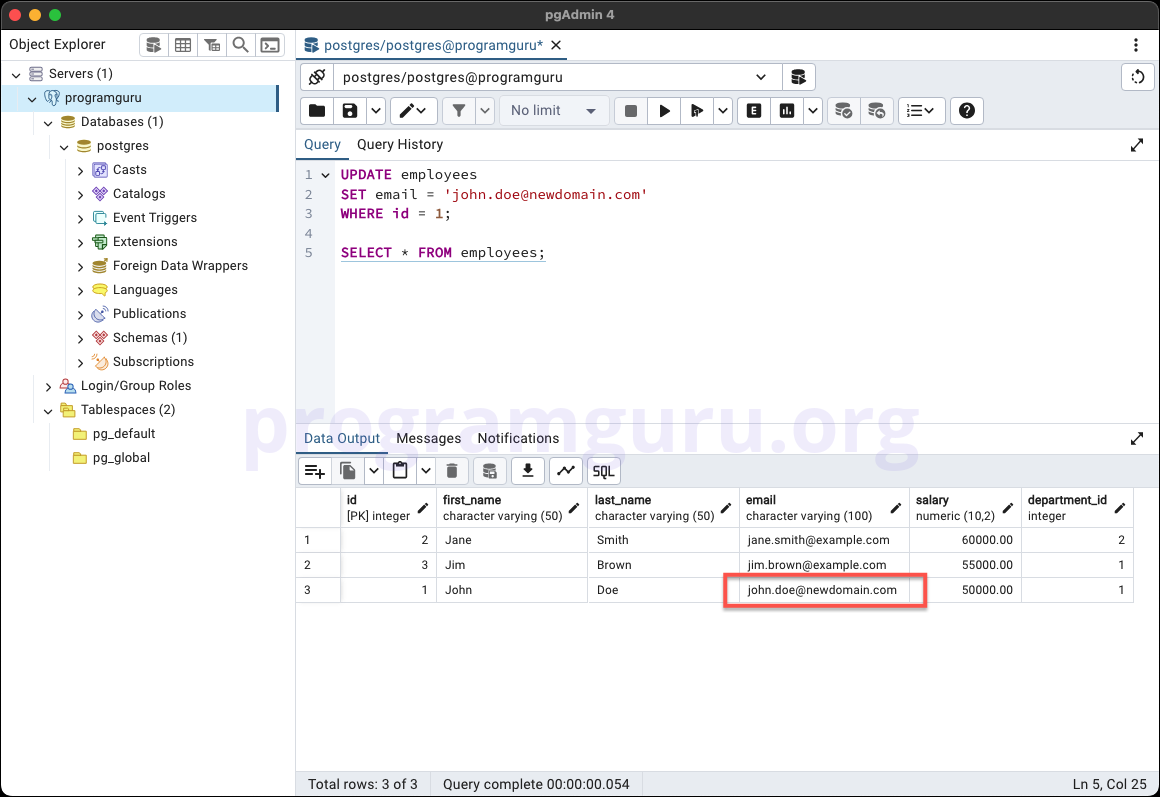
UPDATE Multiple Columns
UPDATE employees
SET first_name = 'Jane', last_name = 'Doe'
WHERE id = 2;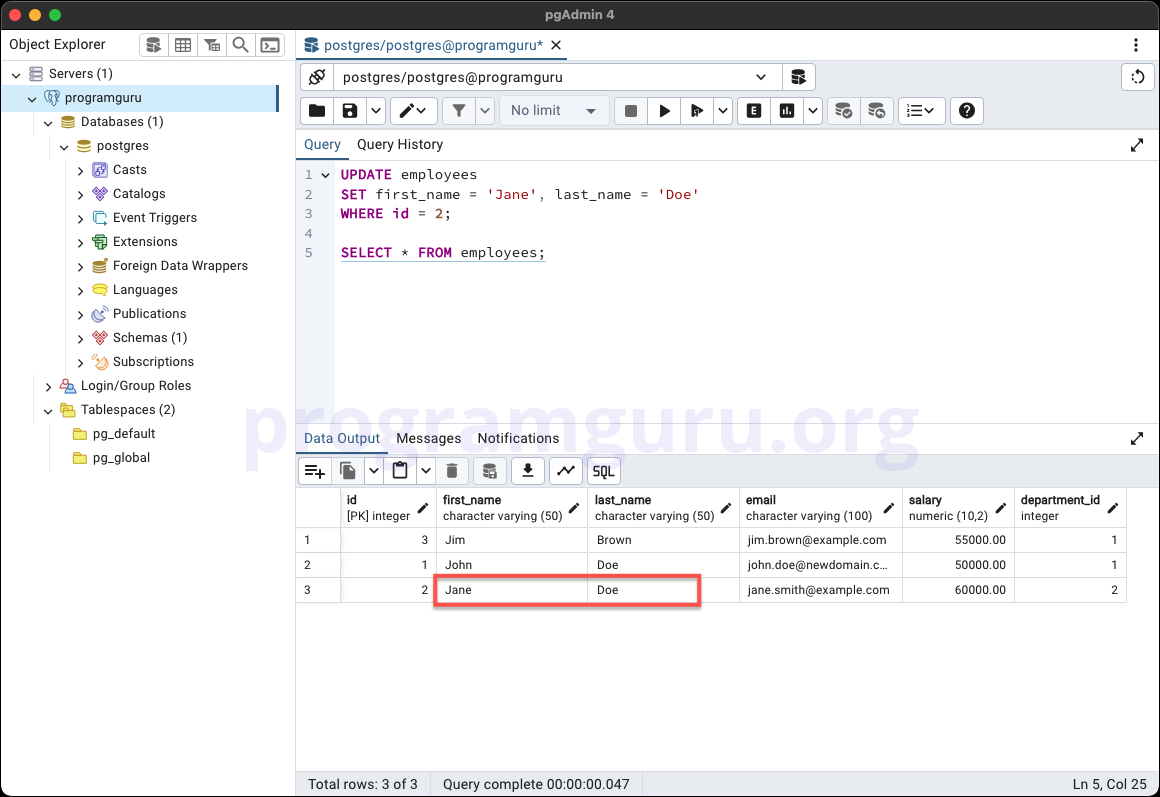
UPDATE with Condition
UPDATE employees
SET salary = salary * 1.1
WHERE department_id = 1;
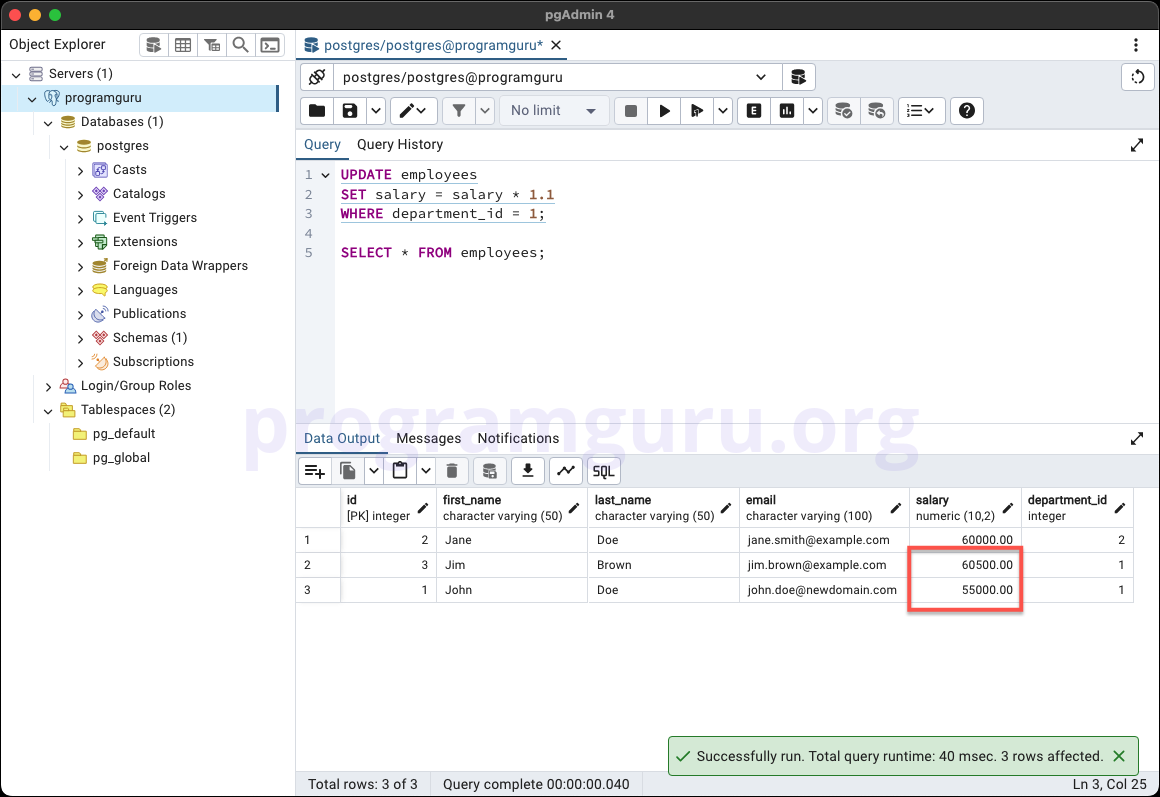
These queries demonstrate how to use the UPDATE statement to modify data in the employees table, including updating a single column, multiple columns, and updating based on a condition.
Conclusion
The PostgreSQL UPDATE statement is a fundamental tool for modifying existing rows in a table. Understanding how to use the UPDATE statement and its syntax is essential for effective data management and manipulation in PostgreSQL databases.