PostgreSQL TRUNCATE TABLE Statement
PostgreSQL TRUNCATE TABLE Statement
The PostgreSQL TRUNCATE TABLE statement is used to quickly remove all rows from a table, effectively resetting the table while preserving its structure. This statement is essential for efficiently clearing out large tables without the overhead of individual row deletions.
Syntax
TRUNCATE TABLE table_name [CASCADE | RESTRICT];
The TRUNCATE TABLE statement has the following components:
table_name: The name of the table to be truncated.CASCADE: Optional. Automatically truncates all tables that have foreign-key references to the truncated table.RESTRICT: Optional. Refuses to truncate the table if there are any foreign-key references to it. This is the default behavior.
Example PostgreSQL TRUNCATE TABLE Statement Queries
Let's look at some examples of PostgreSQL TRUNCATE TABLE statement queries:
1. Basic TRUNCATE TABLE Example
TRUNCATE TABLE employees;
This query removes all rows from the employees table.
2. TRUNCATE TABLE with CASCADE
TRUNCATE TABLE employees CASCADE;
This query removes all rows from the employees table and automatically truncates all tables that have foreign-key references to it.
3. TRUNCATE TABLE with RESTRICT
TRUNCATE TABLE employees RESTRICT;
This query removes all rows from the employees table only if there are no foreign-key references to it. This is the default behavior.
Full Example
Let's go through a complete example that includes creating a table, inserting data, and then truncating the table.
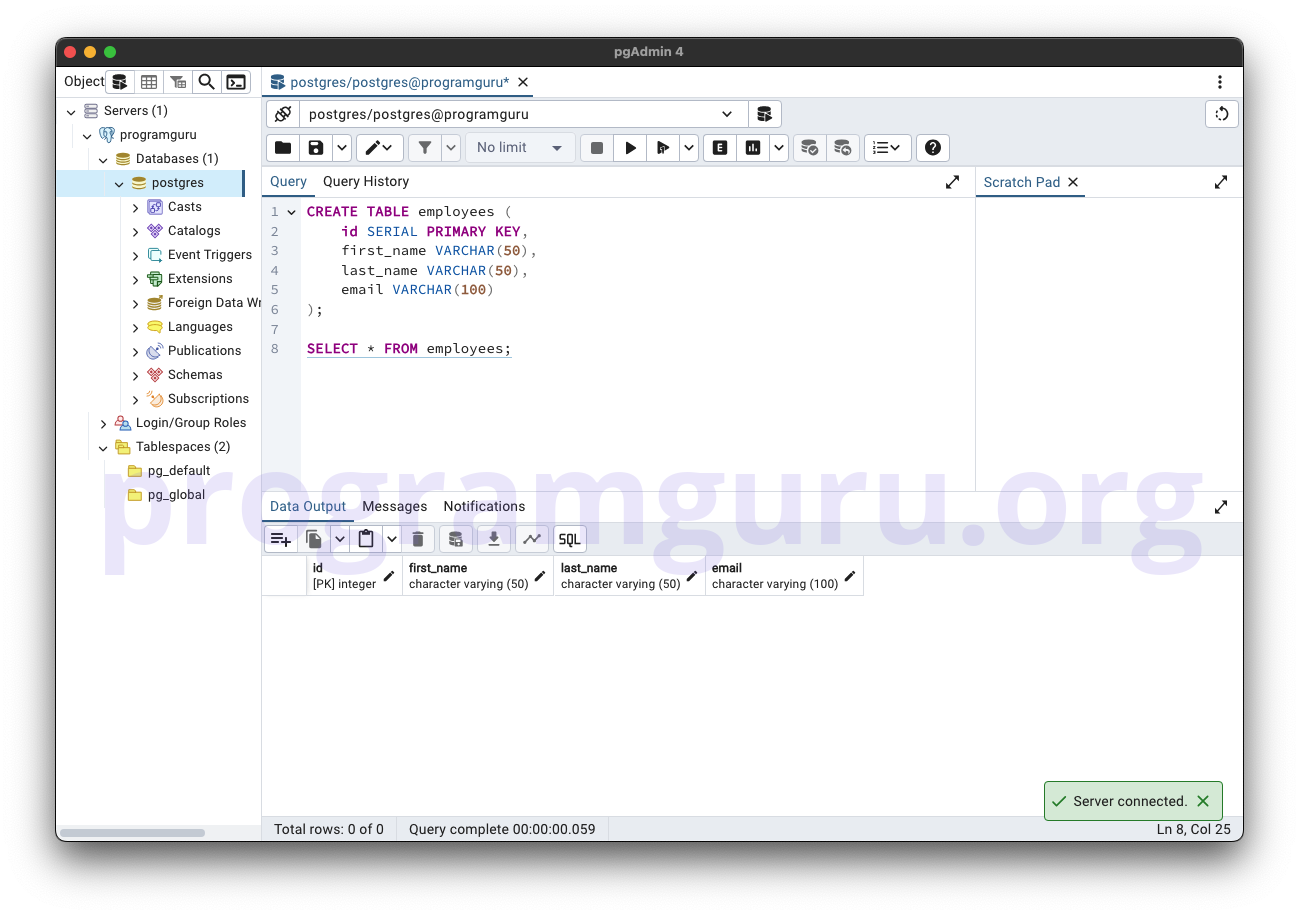
Step 1: Creating a Table
This step involves creating a new table named employees to store employee data.
CREATE TABLE employees (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
first_name VARCHAR(50),
last_name VARCHAR(50),
email VARCHAR(100)
);
In this example, we create a table named employees with columns for id, first_name, last_name, and email.
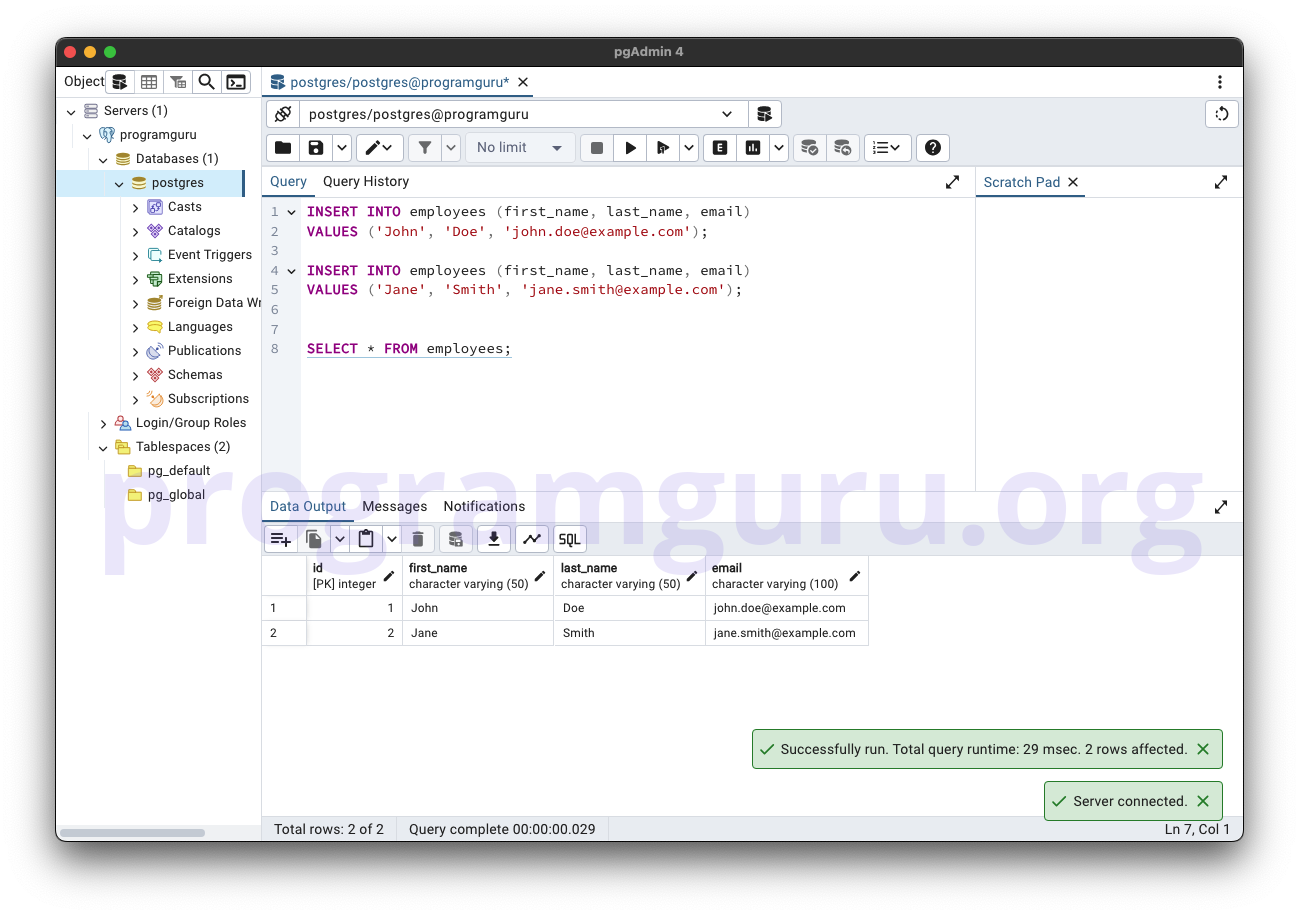
Step 2: Inserting Data into the Table
This step involves inserting some sample data into the employees table.
INSERT INTO employees (first_name, last_name, email)
VALUES ('John', 'Doe', 'john.doe@example.com');
INSERT INTO employees (first_name, last_name, email)
VALUES ('Jane', 'Smith', 'jane.smith@example.com');
Here, we insert data into the employees table, including values for the first_name, last_name, and email columns.
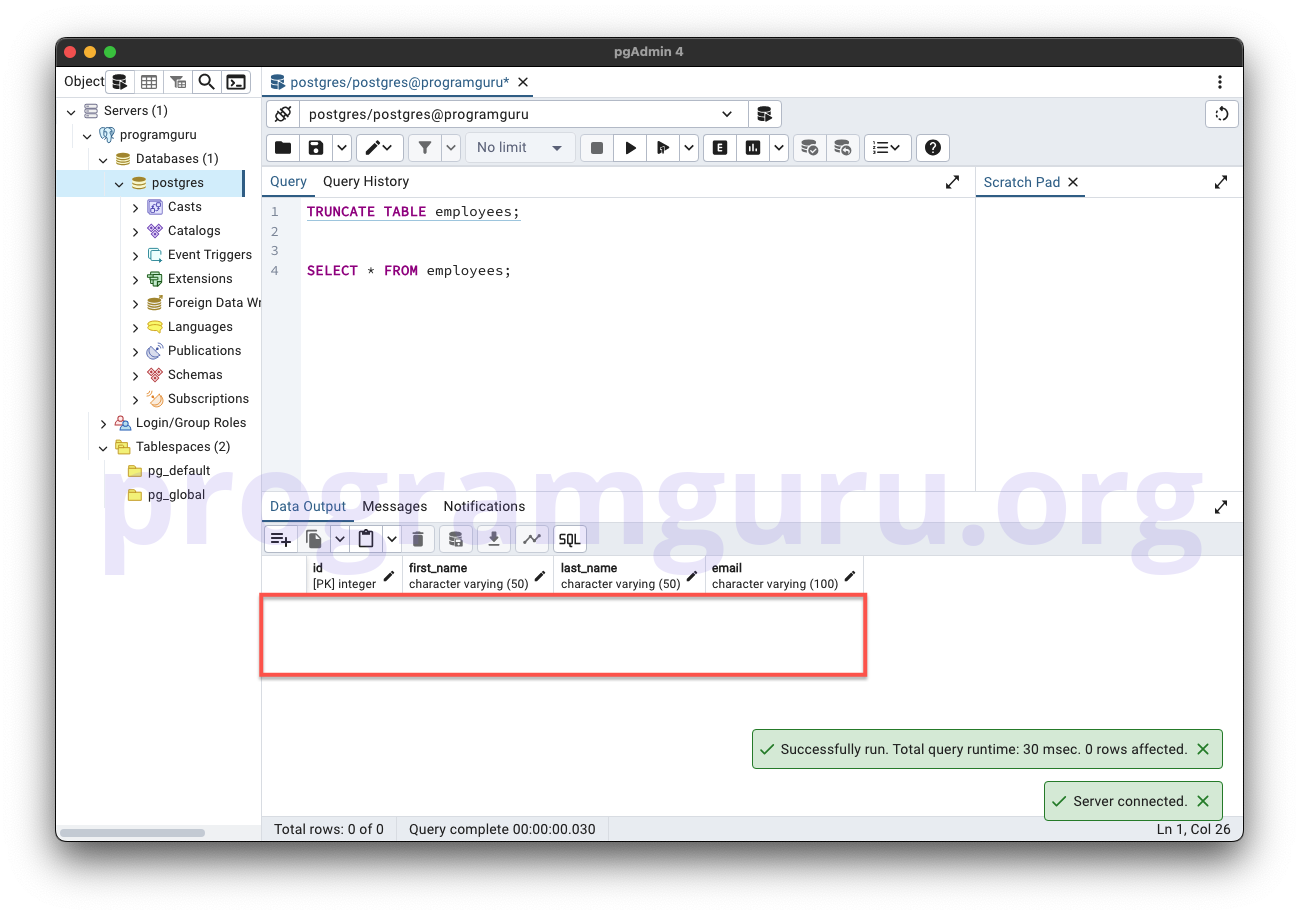
Step 3: Truncating the Table
This step involves removing all rows from the employees table.
TRUNCATE TABLE employees;
Here, we truncate the employees table, effectively removing all rows while preserving the table structure.
Conclusion
The PostgreSQL TRUNCATE TABLE statement is a fundamental tool for efficiently clearing out large tables. Understanding how to use the TRUNCATE TABLE statement and its syntax is essential for effective database management and maintenance in PostgreSQL.