PostgreSQL CREATE TABLE Statement
PostgreSQL CREATE TABLE Statement
The PostgreSQL CREATE TABLE statement is used to create a new table in a database. This statement is essential for defining the structure of the table and the data types of its columns.
Syntax
CREATE TABLE table_name (
column1 datatype1 [constraints],
column2 datatype2 [constraints],
column3 datatype3 [constraints],
...
);
The CREATE TABLE statement has the following components:
table_name: The name of the table to be created.column1, column2, column3, ...: The columns in the table, each followed by its datatype and optional constraints.
Example PostgreSQL CREATE TABLE Statement Queries
Let's look at some examples of PostgreSQL CREATE TABLE statement queries:
1. Basic CREATE TABLE Example
CREATE TABLE employees (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
first_name VARCHAR(50),
last_name VARCHAR(50),
email VARCHAR(100)
);
This query creates a new table named employees with columns for id, first_name, last_name, and email. The id column is set as the primary key and is auto-incremented.
2. CREATE TABLE with Constraints
CREATE TABLE products (
product_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
product_name VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
price NUMERIC(10, 2) CHECK (price > 0),
stock INT DEFAULT 0
);
This query creates a new table named products with constraints on the product_name, price, and stock columns.
3. CREATE TABLE with Foreign Key
CREATE TABLE orders (
order_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
customer_id INT REFERENCES customers(customer_id),
order_date DATE NOT NULL
);
This query creates a new table named orders with a foreign key constraint on the customer_id column, referencing the customer_id column in the customers table.
Full Example
Let's go through a complete example that includes creating tables with primary and foreign key constraints.
Step 1: Creating the Customers Table
This step involves creating a new table named customers to store customer data.
CREATE TABLE customers (
customer_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
first_name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
last_name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
email VARCHAR(100) UNIQUE NOT NULL
);
In this example, we create a table named customers with columns for customer_id, first_name, last_name, and email.

Step 2: Creating the Orders Table
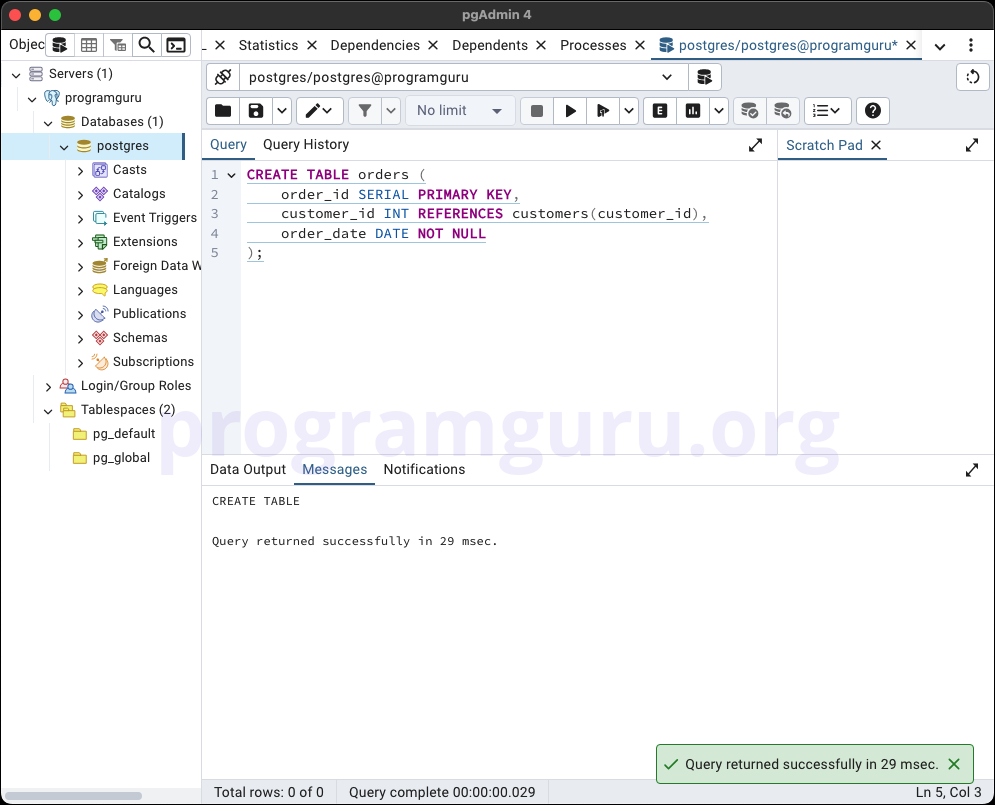
This step involves creating a new table named orders to store order data, with a foreign key reference to the customers table.
CREATE TABLE orders (
order_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
customer_id INT REFERENCES customers(customer_id),
order_date DATE NOT NULL
);
Here, we create a table named orders with columns for order_id, customer_id, and order_date, including a foreign key constraint on the customer_id column.
Step 3: Querying the Tables
This step involves selecting the data from the customers and orders tables to view the inserted records.
SELECT * FROM customers;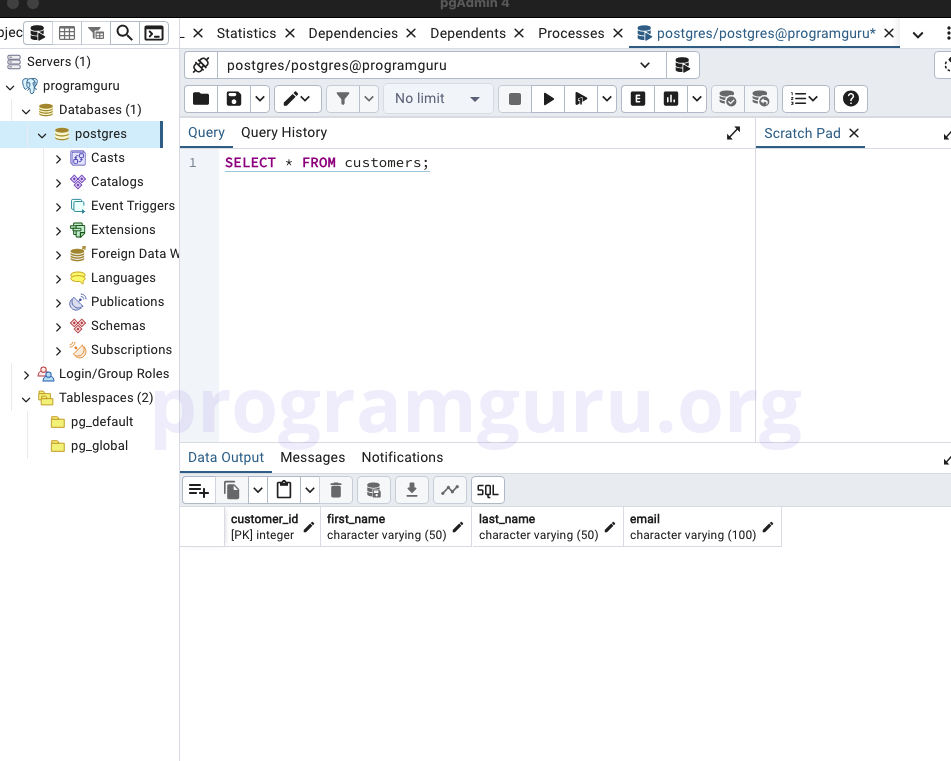
SELECT * FROM orders;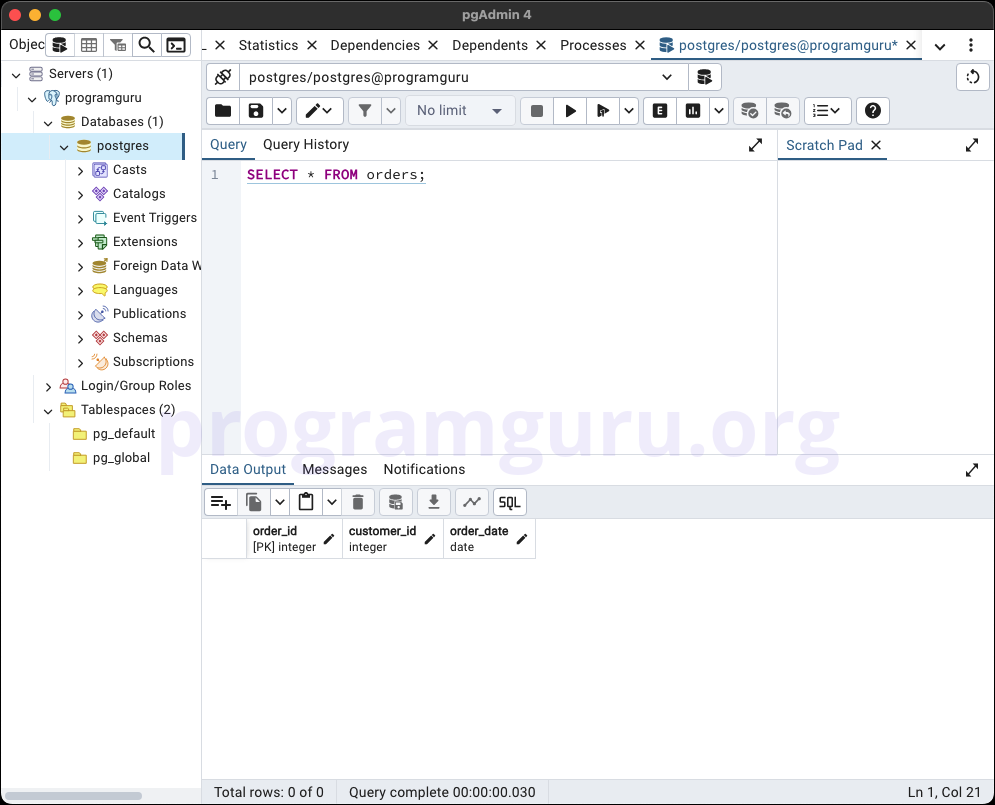
These queries retrieve all the rows from the customers and orders tables. Since we only created the tables and not inserted any rows, the tables are displayed as empty.
Conclusion
The PostgreSQL CREATE TABLE statement is a fundamental tool for defining the structure of a new table in a database. Understanding how to use the CREATE TABLE statement and its syntax is essential for effective database schema design and management in PostgreSQL.