PostgreSQL INNER JOIN
PostgreSQL INNER JOIN Clause
The PostgreSQL INNER JOIN clause is used to combine rows from two or more tables based on a related column between them. This clause is essential for retrieving data that exists in both tables, ensuring a match between columns.
Syntax
SELECT columns
FROM table1
INNER JOIN table2
ON table1.column = table2.column;
The INNER JOIN clause has the following components:
columns: The columns to be retrieved from the tables.table1: The first table to join.table2: The second table to join.table1.column = table2.column: The condition to join the tables, typically involving matching columns from each table.
Example PostgreSQL INNER JOIN Queries
Let's look at some examples of PostgreSQL INNER JOIN queries:
1. Basic INNER JOIN Example
SELECT employees.first_name, employees.last_name, departments.department_name
FROM employees
INNER JOIN departments
ON employees.department_id = departments.id;
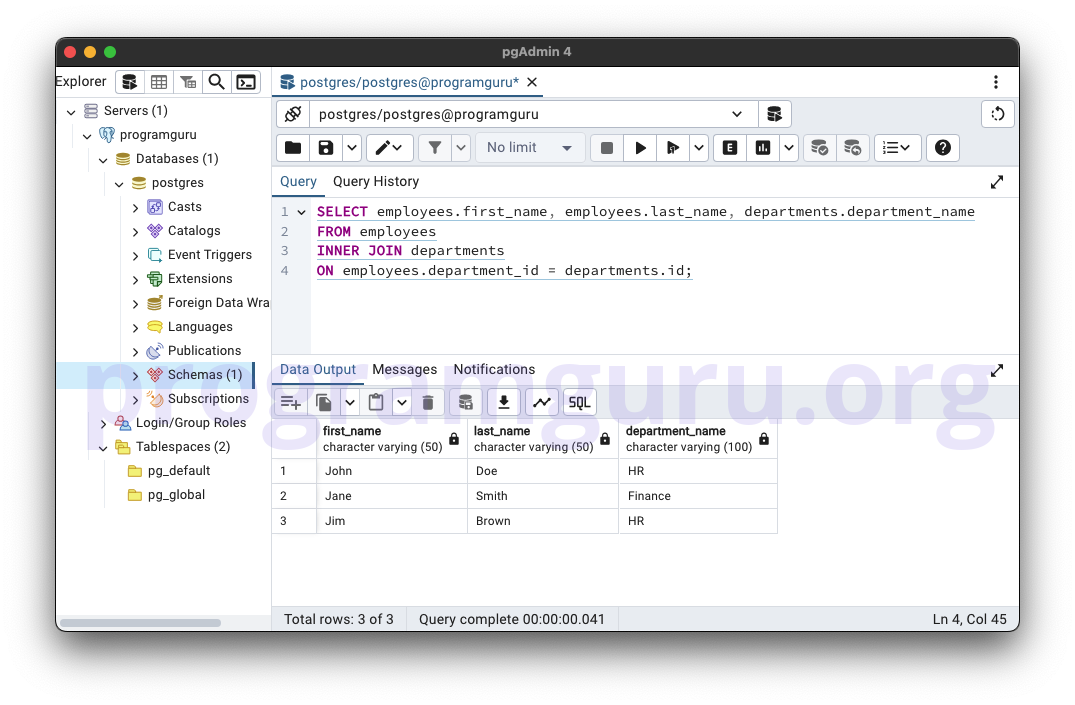
This query retrieves the first_name and last_name of employees along with the department_name from the departments table where there is a match between employees.department_id and departments.id.
2. INNER JOIN with Multiple Conditions
SELECT employees.first_name, employees.last_name, departments.department_name
FROM employees
INNER JOIN departments
ON employees.department_id = departments.id AND employees.salary > 50000;
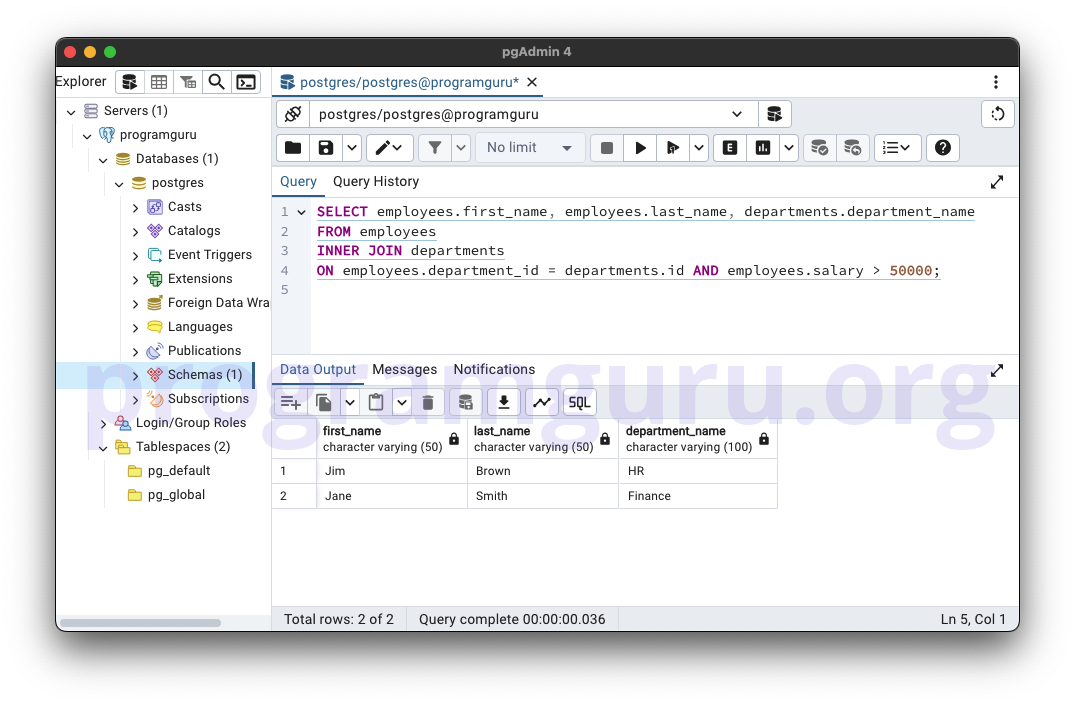
This query retrieves the first_name and last_name of employees along with the department_name from the departments table where there is a match between employees.department_id and departments.id and the employee's salary is greater than 50000.
3. INNER JOIN with Aliases
SELECT e.first_name, e.last_name, d.department_name
FROM employees e
INNER JOIN departments d
ON e.department_id = d.id;
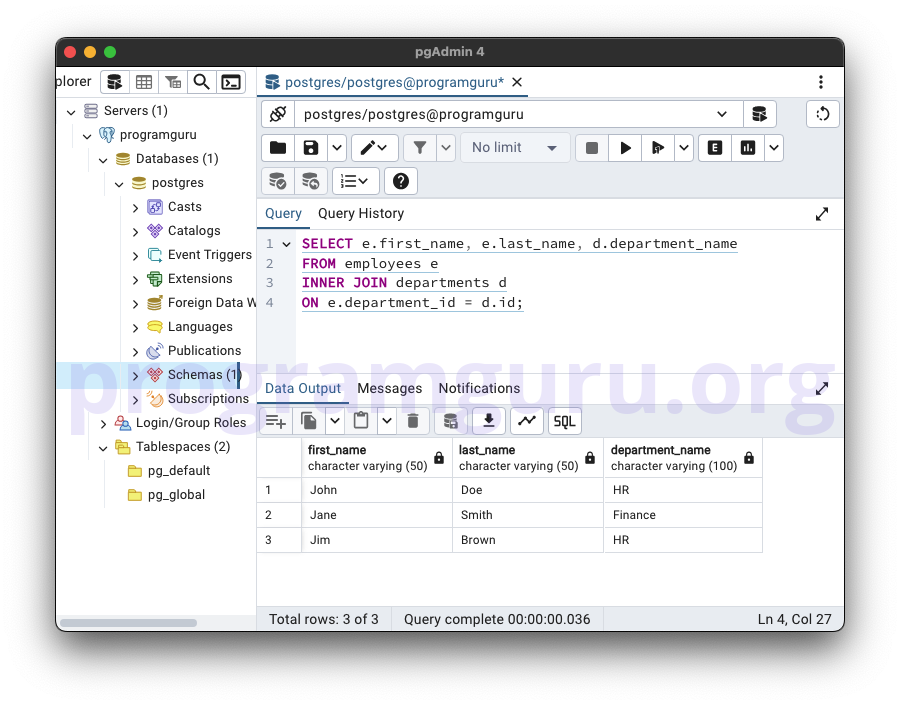
This query retrieves the first_name and last_name of employees along with the department_name from the departments table using table aliases e and d for simplicity.
4. INNER JOIN with Multiple Tables
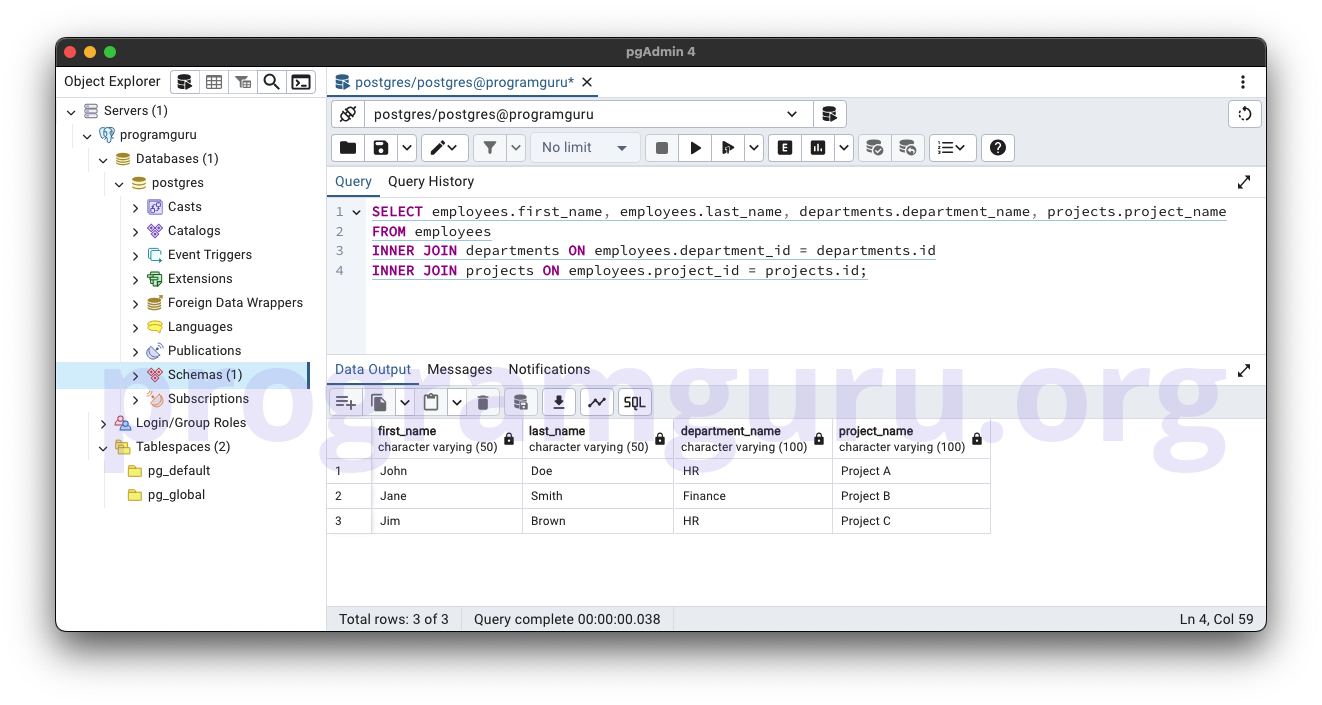
SELECT employees.first_name, employees.last_name, departments.department_name, projects.project_name
FROM employees
INNER JOIN departments ON employees.department_id = departments.id
INNER JOIN projects ON employees.project_id = projects.id;
This query retrieves the first_name and last_name of employees along with the department_name from the departments table and the project_name from the projects table where there is a match between employees.department_id and departments.id and between employees.project_id and projects.id.
Full Example
Let's go through a complete example that includes creating tables, inserting data, and using the INNER JOIN clause to retrieve combined data.
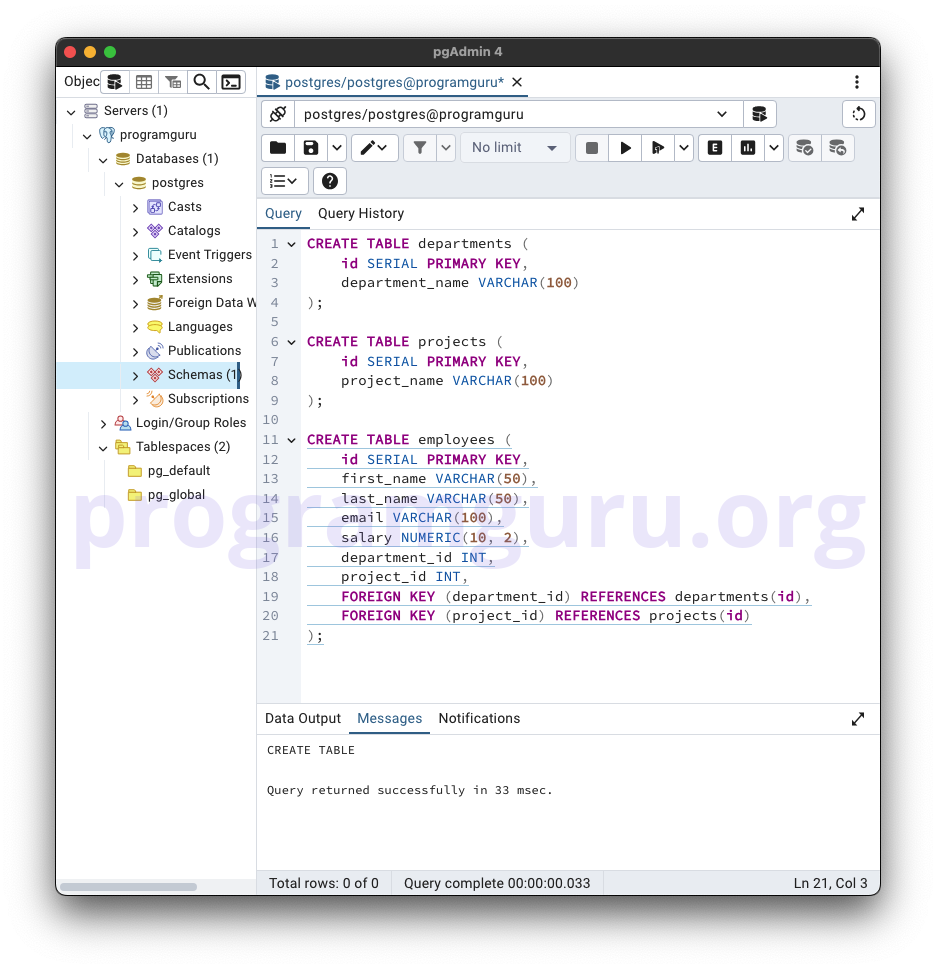
Step 1: Creating Tables
This step involves creating new tables named employees, departments, and projects to store data.
CREATE TABLE departments (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
department_name VARCHAR(100)
);
CREATE TABLE projects (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
project_name VARCHAR(100)
);
CREATE TABLE employees (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
first_name VARCHAR(50),
last_name VARCHAR(50),
email VARCHAR(100),
salary NUMERIC(10, 2),
department_id INT,
project_id INT,
FOREIGN KEY (department_id) REFERENCES departments(id),
FOREIGN KEY (project_id) REFERENCES projects(id)
);
In this example, we create three tables: departments with columns for id and department_name, projects with columns for id and project_name, and employees with columns for id, first_name, last_name, email, salary, department_id, and project_id.
Step 2: Inserting Data into the Tables
This step involves inserting some sample data into the employees, departments, and projects tables.
INSERT INTO departments (department_name)
VALUES ('HR'), ('Finance'), ('Engineering');
INSERT INTO projects (project_name)
VALUES ('Project A'), ('Project B'), ('Project C');
INSERT INTO employees (first_name, last_name, email, salary, department_id, project_id)
VALUES ('John', 'Doe', 'john.doe@example.com', 50000, 1, 1);
INSERT INTO employees (first_name, last_name, email, salary, department_id, project_id)
VALUES ('Jane', 'Smith', 'jane.smith@example.com', 60000, 2, 2);
INSERT INTO employees (first_name, last_name, email, salary, department_id, project_id)
VALUES ('Jim', 'Brown', 'jim.brown@example.com', 55000, 1, 3);
Here, we insert data into the departments, projects, and employees tables.

Step 3: Using the INNER JOIN Clause
This step involves using the INNER JOIN clause to retrieve combined data from the employees, departments, and projects tables.
These queries demonstrate how to use the INNER JOIN clause to retrieve combined data from the employees, departments, and projects tables, including basic joins, joins with multiple conditions, using table aliases, and joining multiple tables.
-- Basic INNER JOIN
SELECT employees.first_name, employees.last_name, departments.department_name
FROM employees
INNER JOIN departments
ON employees.department_id = departments.id;
-- INNER JOIN with Multiple Conditions
SELECT employees.first_name, employees.last_name, departments.department_name
FROM employees
INNER JOIN departments
ON employees.department_id = departments.id AND employees.salary > 50000;
-- INNER JOIN with Aliases
SELECT e.first_name, e.last_name, d.department_name
FROM employees e
INNER JOIN departments d
ON e.department_id = d.id;
-- INNER JOIN with Multiple Tables
SELECT employees.first_name, employees.last_name, departments.department_name, projects.project_name
FROM employees
INNER JOIN departments ON employees.department_id = departments.id
INNER JOIN projects ON employees.project_id = projects.id;
Conclusion
The PostgreSQL INNER JOIN clause is a fundamental tool for combining rows from two or more tables based on a related column. Understanding how to use the INNER JOIN clause and its syntax is essential for effective data retrieval and manipulation in PostgreSQL databases.