PostgreSQL Temporary Table
PostgreSQL Temporary Table
The PostgreSQL TEMPORARY TABLE statement is used to create a temporary table that exists only for the duration of a session or transaction. This statement is essential for storing intermediate results or data that do not need to be permanently stored in the database.
Syntax
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE table_name (
column1 datatype1 [constraints],
column2 datatype2 [constraints],
column3 datatype3 [constraints],
...
) [ON COMMIT {PRESERVE ROWS | DELETE ROWS | DROP}];
The CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE statement has the following components:
table_name: The name of the temporary table to be created.column1, column2, column3, ...: The columns in the temporary table, each followed by its datatype and optional constraints.ON COMMIT: Optional. Specifies the behavior of the temporary table at the end of a transaction:PRESERVE ROWS: Keeps the rows in the temporary table.DELETE ROWS: Deletes all rows in the temporary table.DROP: Drops the temporary table.
Example PostgreSQL Temporary Table Statement Queries
Let's look at some examples of PostgreSQL CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE statement queries:
1. Basic Temporary Table Example
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE temp_employees (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
first_name VARCHAR(50),
last_name VARCHAR(50),
email VARCHAR(100)
);
This query creates a temporary table named temp_employees with columns for id, first_name, last_name, and email.
2. Temporary Table with ON COMMIT DELETE ROWS
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE temp_employees (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
first_name VARCHAR(50),
last_name VARCHAR(50),
email VARCHAR(100)
) ON COMMIT DELETE ROWS;
This query creates a temporary table named temp_employees that will have its rows deleted at the end of each transaction.
3. Temporary Table with ON COMMIT DROP
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE temp_employees (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
first_name VARCHAR(50),
last_name VARCHAR(50),
email VARCHAR(100)
) ON COMMIT DROP;
This query creates a temporary table named temp_employees that will be dropped at the end of each transaction.
Full Example
Let's go through a complete example that includes creating a temporary table, inserting data, and then querying the table.
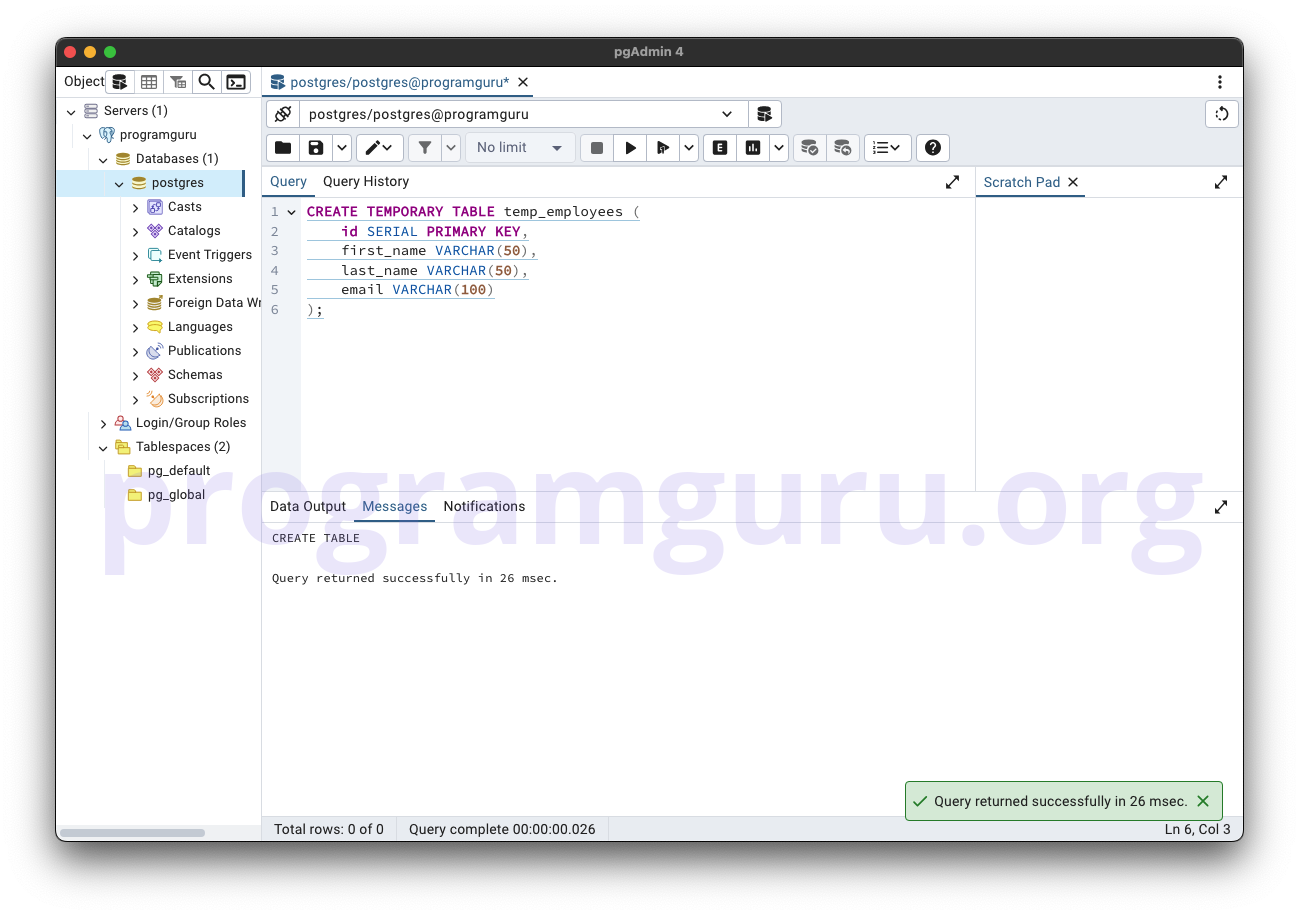
Step 1: Creating a Temporary Table
This step involves creating a new temporary table named temp_employees to store employee data temporarily.
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE temp_employees (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
first_name VARCHAR(50),
last_name VARCHAR(50),
email VARCHAR(100)
);
In this example, we create a temporary table named temp_employees with columns for id, first_name, last_name, and email.
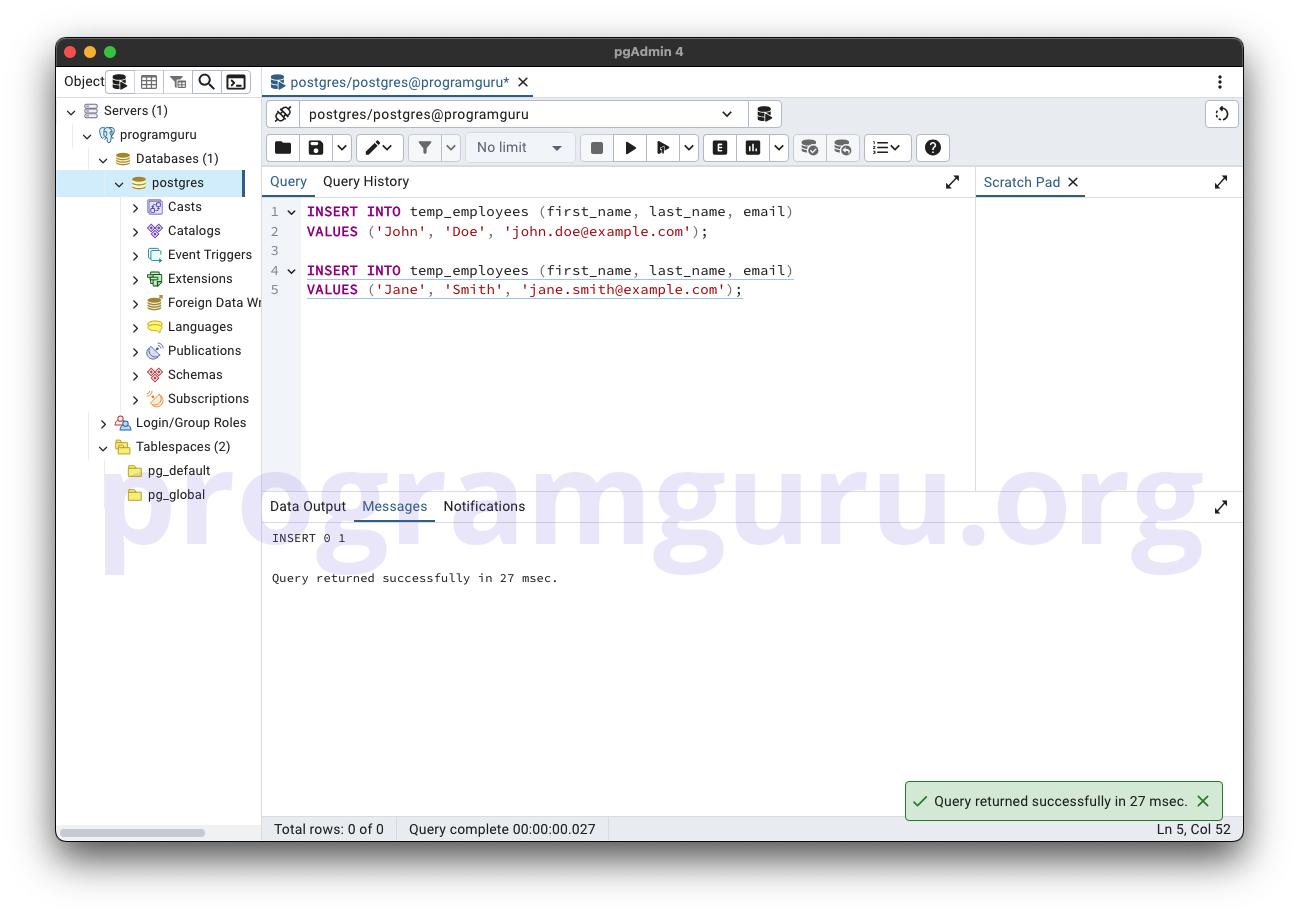
Step 2: Inserting Data into the Temporary Table
This step involves inserting some sample data into the temp_employees table.
INSERT INTO temp_employees (first_name, last_name, email)
VALUES ('John', 'Doe', 'john.doe@example.com');
INSERT INTO temp_employees (first_name, last_name, email)
VALUES ('Jane', 'Smith', 'jane.smith@example.com');
Here, we insert data into the temp_employees table, including values for the first_name, last_name, and email columns.
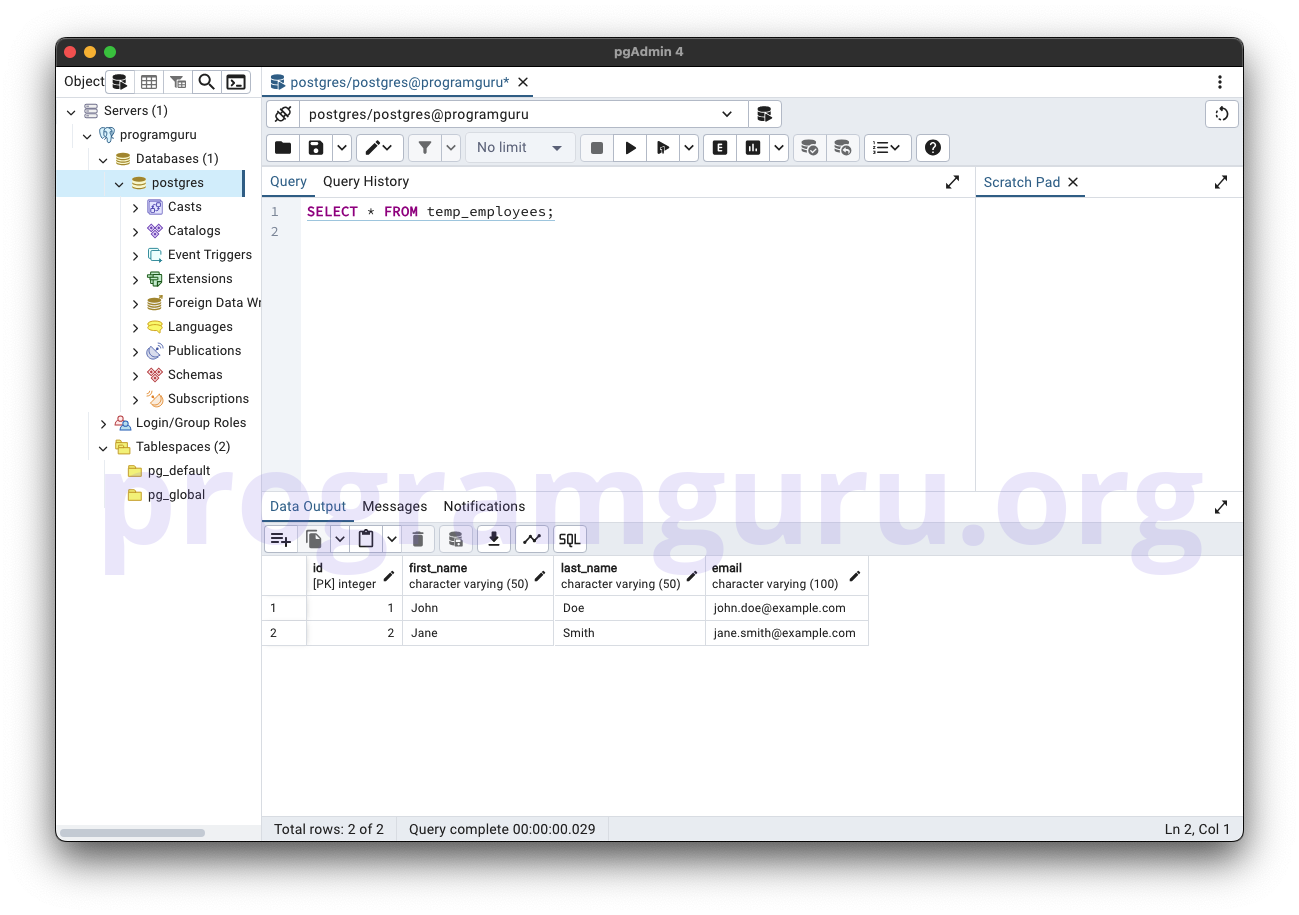
Step 3: Querying the Temporary Table
This step involves querying the temp_employees table to retrieve the inserted records.
SELECT * FROM temp_employees;
This query retrieves all rows from the temp_employees table.
Conclusion
The PostgreSQL TEMPORARY TABLE statement is a fundamental tool for creating tables that exist only for the duration of a session or transaction. Understanding how to use the CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE statement and its syntax is essential for effective database management and temporary data storage in PostgreSQL.