PostgreSQL Subquery
PostgreSQL Subquery
A PostgreSQL Subquery is a query nested inside another query. This feature is essential for performing complex queries, retrieving data based on calculations or conditions, and breaking down large queries into simpler parts.
Syntax
SELECT column1, column2, ...
FROM table_name
WHERE column_name operator (SELECT column_name
FROM table_name
WHERE condition);
The Subquery has the following components:
column1, column2, ...: The columns to retrieve in the outer query.table_name: The name of the table to retrieve data from.column_name: The column to compare in the subquery.operator: The comparison operator (e.g., =, <, >, IN) to use in the outer query.condition: The condition to filter rows in the subquery.
Example PostgreSQL Subquery Queries
Let's look at some examples of PostgreSQL Subquery queries:
1. Subquery in WHERE Clause
SELECT first_name, last_name
FROM employees
WHERE salary > (SELECT AVG(salary)
FROM employees);
This query retrieves the first_name and last_name of employees whose salary is greater than the average salary of all employees.
2. Subquery in FROM Clause
SELECT department_name, avg_salary
FROM (SELECT department_id, AVG(salary) AS avg_salary
FROM employees
GROUP BY department_id) AS dept_avg
JOIN departments ON dept_avg.department_id = departments.id;
This query retrieves the department_name and average salary of each department by using a subquery in the FROM clause.
3. Subquery in SELECT Clause
SELECT first_name, last_name,
(SELECT department_name
FROM departments
WHERE departments.id = employees.department_id) AS department_name
FROM employees;
This query retrieves the first_name and last_name of employees along with their department_name by using a subquery in the SELECT clause.
Full Example
Let's go through a complete example that includes creating tables, inserting data, and using subqueries in different parts of a query.
Step 1: Creating Tables
This step involves creating tables named employees and departments to store employee and department data.
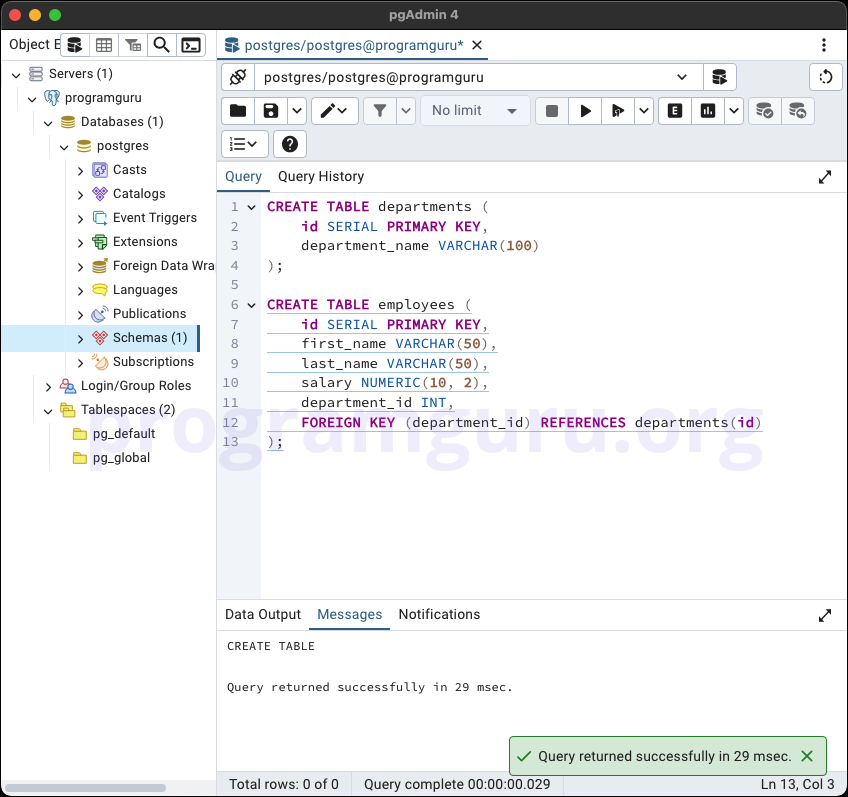
CREATE TABLE departments (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
department_name VARCHAR(100)
);
CREATE TABLE employees (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
first_name VARCHAR(50),
last_name VARCHAR(50),
salary NUMERIC(10, 2),
department_id INT,
FOREIGN KEY (department_id) REFERENCES departments(id)
);
In this example, we create two tables: departments with columns for id and department_name, and employees with columns for id, first_name, last_name, salary, and department_id.
Step 2: Inserting Data into the Tables
This step involves inserting some sample data into the departments and employees tables.
INSERT INTO departments (department_name)
VALUES ('HR'), ('Finance'), ('Engineering');
INSERT INTO employees (first_name, last_name, salary, department_id)
VALUES ('John', 'Doe', 50000, 1),
('Jane', 'Smith', 60000, 2),
('Jim', 'Brown', 55000, 3);
Here, we insert data into the departments table with department names and into the employees table with employee details including their department IDs.

Step 3: Using Subqueries
This step involves querying the employees and departments tables using subqueries.
Subquery in WHERE clause
SELECT first_name, last_name
FROM employees
WHERE salary > (SELECT AVG(salary) FROM employees);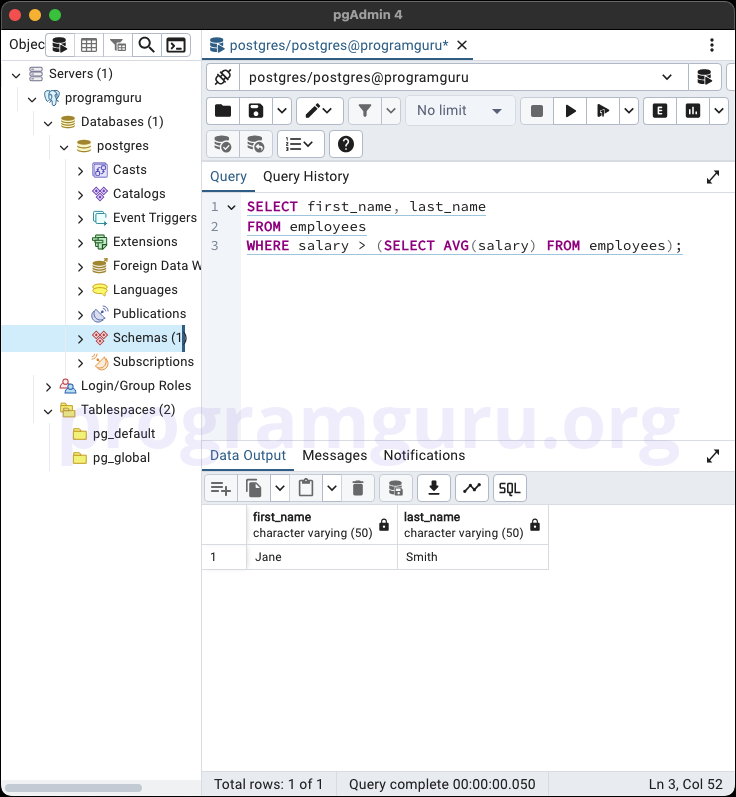
Subquery in FROM clause
SELECT department_name, avg_salary
FROM (SELECT department_id, AVG(salary) AS avg_salary
FROM employees
GROUP BY department_id) AS dept_avg
JOIN departments ON dept_avg.department_id = departments.id;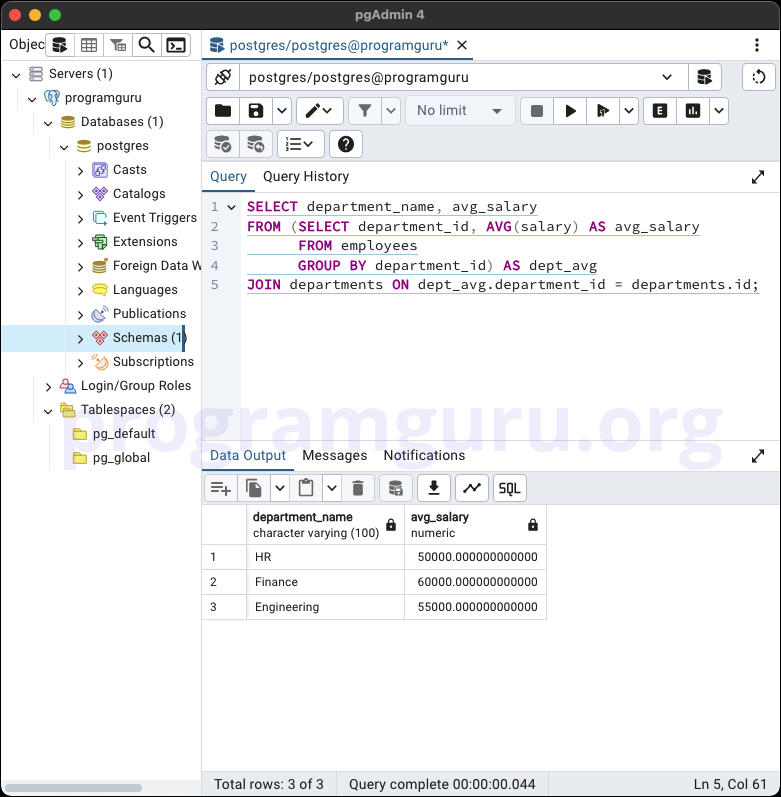
Subquery in SELECT clause
SELECT first_name, last_name,
(SELECT department_name
FROM departments
WHERE departments.id = employees.department_id) AS department_name
FROM employees;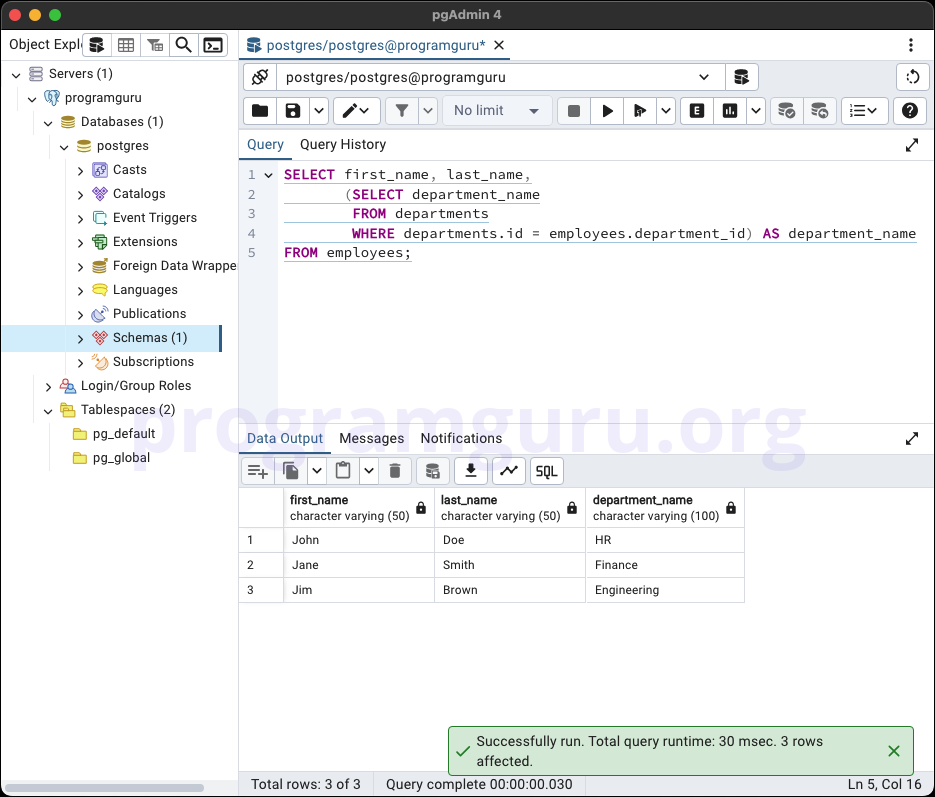
These queries demonstrate the use of subqueries in different parts of a query to retrieve specific data from the employees and departments tables.
Conclusion
The PostgreSQL Subquery feature is a powerful tool for performing complex queries and retrieving specific data based on conditions or calculations. Understanding how to use subqueries and their syntax is essential for effective data manipulation and retrieval in PostgreSQL.