MySQL DELETE ALL ROW(s) Statement
MySQL DELETE ALL ROW(s) Statement
The MySQL DELETE statement can be used to remove all rows from a table without deleting the table itself. This statement is essential for clearing the table's data while preserving its structure.
Syntax
DELETE FROM table_name;
The DELETE statement has the following component:
table_name: The name of the table from which to delete all rows.
Example MySQL DELETE ALL ROW(s) Statement
Let's look at an example of the MySQL DELETE statement used to delete all rows from a table:
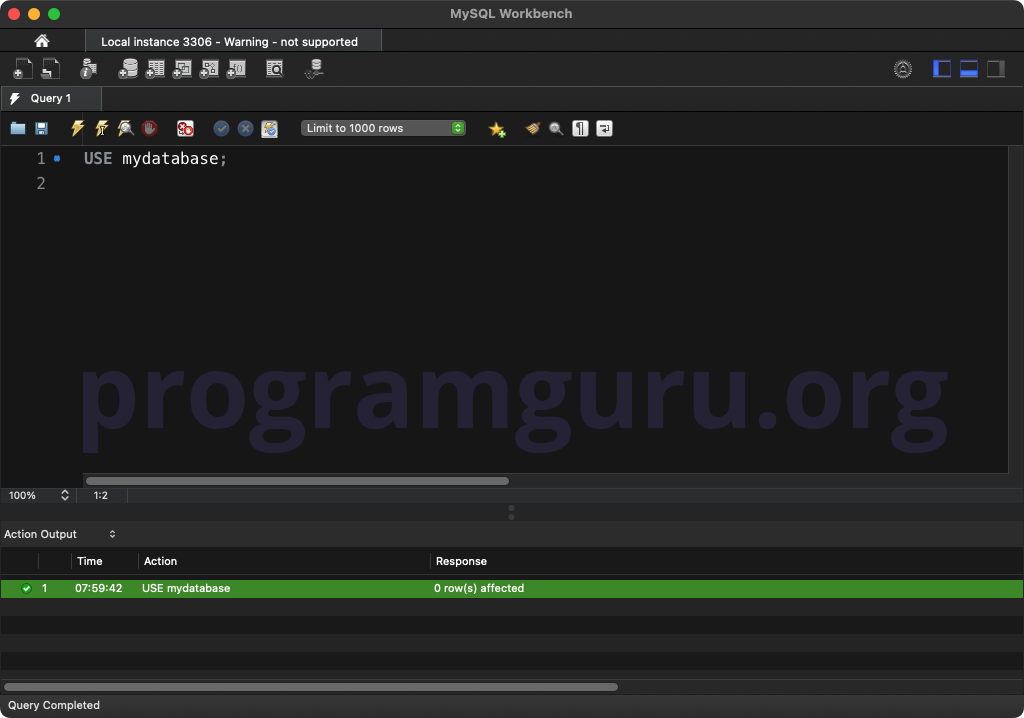
Step 1: Using the Database
USE mydatabase;
This query sets the context to the database named mydatabase.
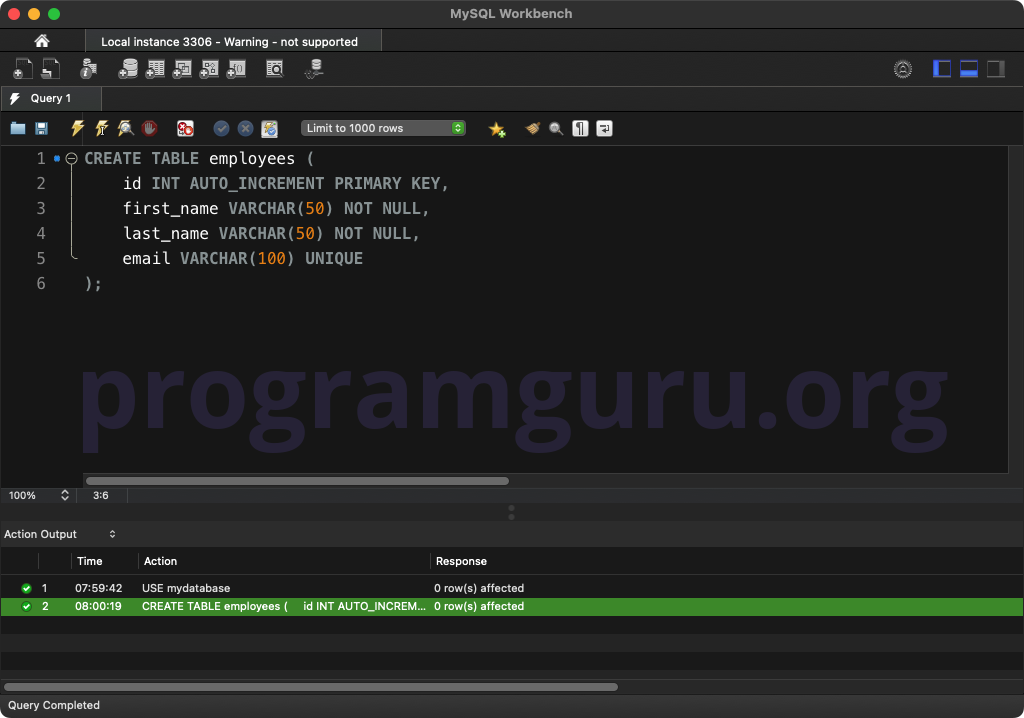
Step 2: Creating a Table
Create a table to work with:
CREATE TABLE employees (
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
first_name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
last_name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
email VARCHAR(100) UNIQUE
);
This query creates a table named employees with columns for id, first_name, last_name, and email.
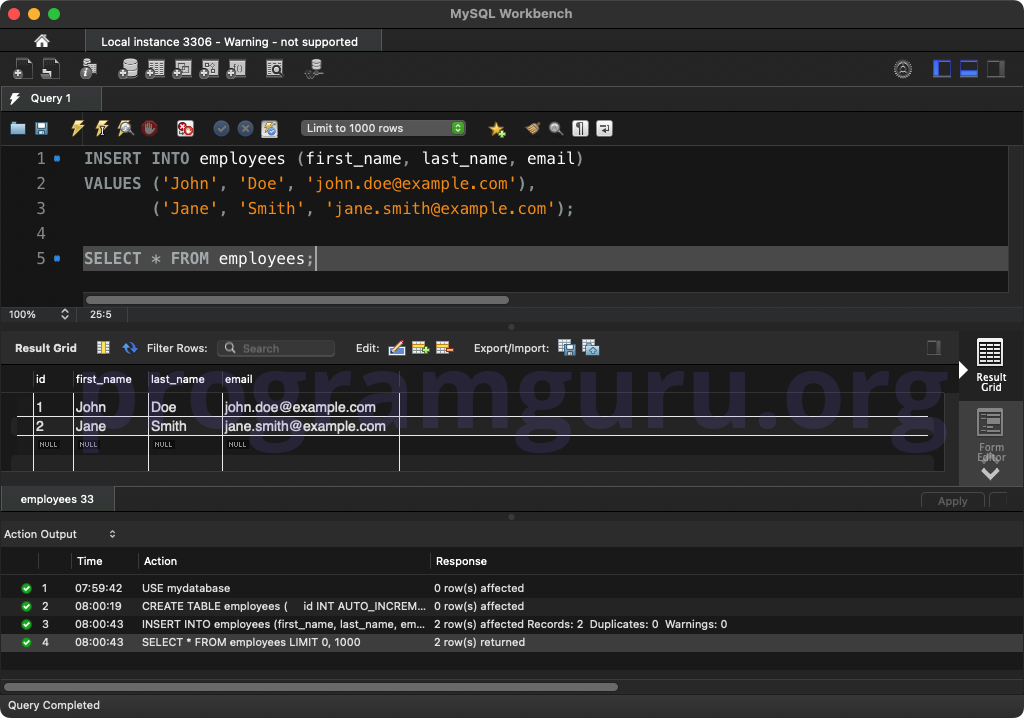
Step 3: Inserting Initial Rows
Insert some initial rows into the table:
INSERT INTO employees (first_name, last_name, email)
VALUES ('John', 'Doe', 'john.doe@example.com'),
('Jane', 'Smith', 'jane.smith@example.com');
This query inserts two rows into the employees table.
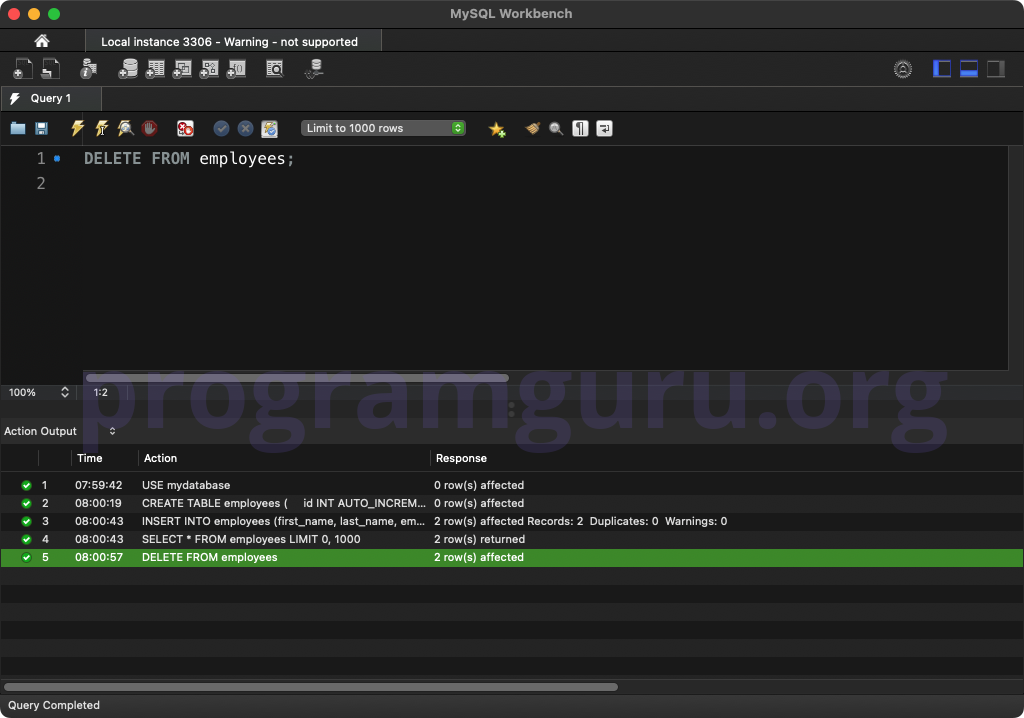
Step 4: Deleting All Rows
Delete all rows from the table:
DELETE FROM employees;
This query deletes all rows from the employees table.
Step 5: Verifying the Deletion
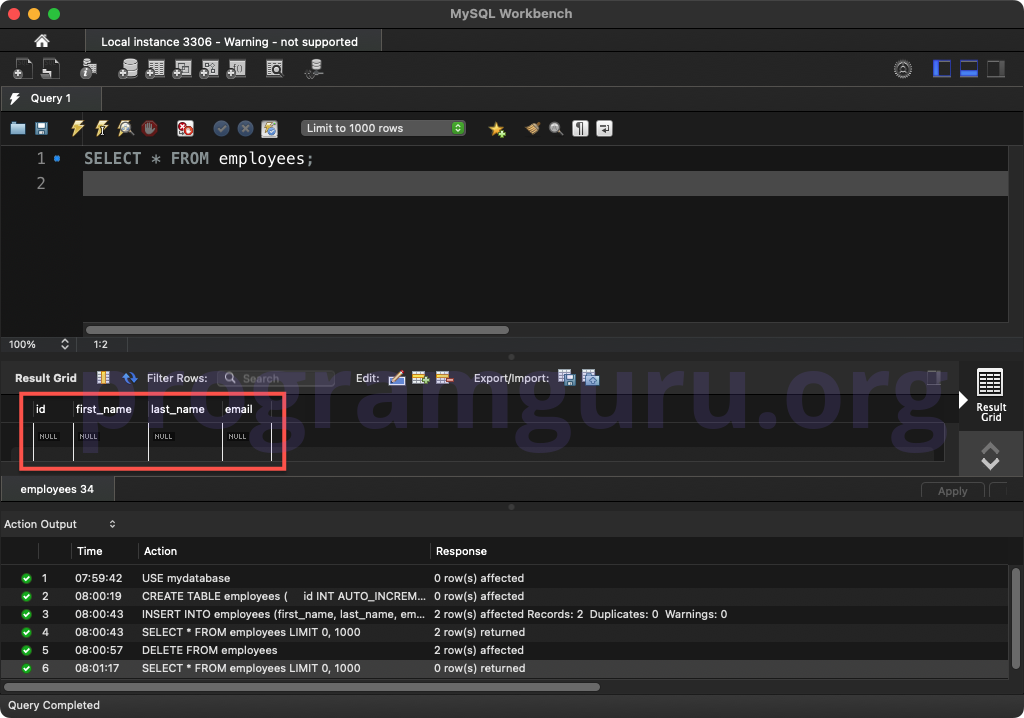
To verify that all rows have been deleted, you can select all rows from the table:
SELECT *
FROM employees;
This query retrieves all rows from the employees table. The result should be an empty set.
Conclusion
The MySQL DELETE statement is a powerful tool for removing all rows from a table without deleting the table itself. Understanding how to use the DELETE statement is essential for effective data management and maintenance in MySQL.