MySQL ORDER BY Clause
MySQL ORDER BY Clause
The MySQL ORDER BY clause is used to sort the result set of a query by one or more columns. This is essential for organizing data in a specific order.
Syntax
SELECT column1, column2, ...
FROM table_name
ORDER BY column1 [ASC|DESC], column2 [ASC|DESC], ...;
The ORDER BY clause has the following components:
column1, column2, ...: The columns by which to sort the result set.table_name: The name of the table from which to retrieve the data.[ASC|DESC]: Optional keywords to specify the sorting order (ascending or descending). The default is ascending (ASC).
Example MySQL ORDER BY Clause
Let's look at some examples of the MySQL ORDER BY clause:
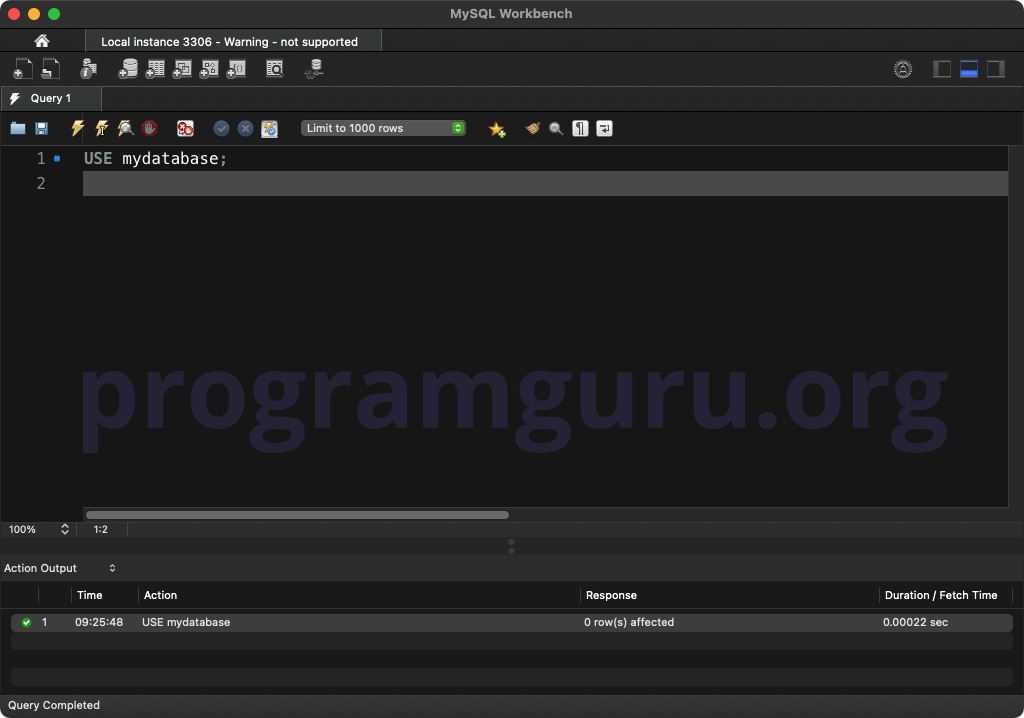
Step 1: Using the Database
USE mydatabase;
This query sets the context to the database named mydatabase.
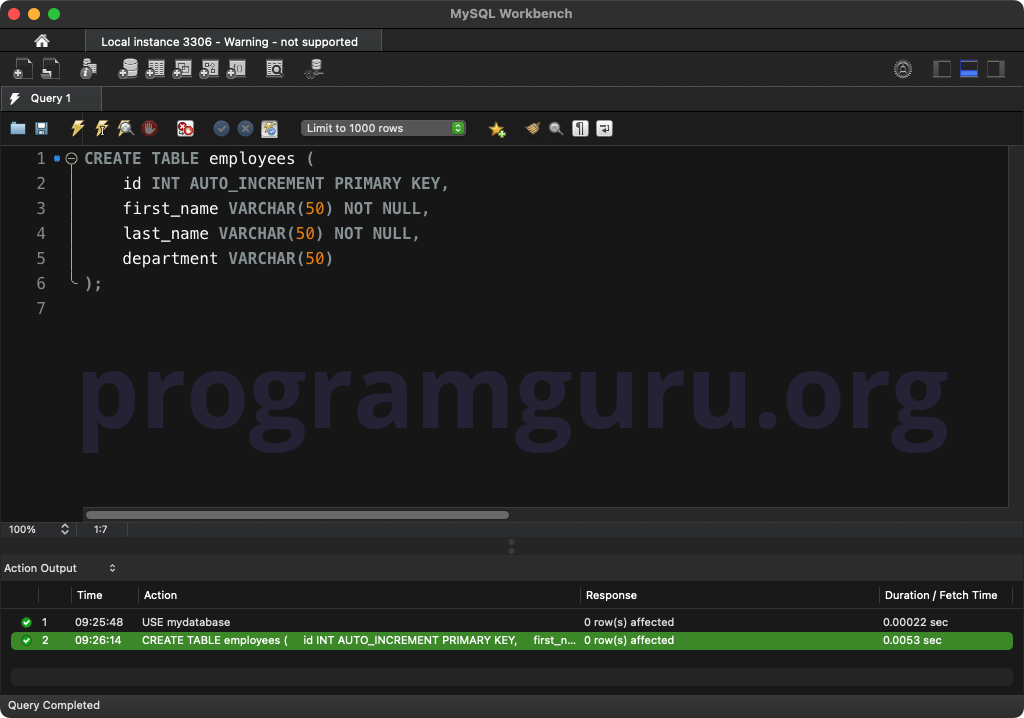
Step 2: Creating a Table
Create a table to work with:
CREATE TABLE employees (
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
first_name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
last_name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
department VARCHAR(50)
);
This query creates a table named employees with columns for id, first_name, last_name, and department.
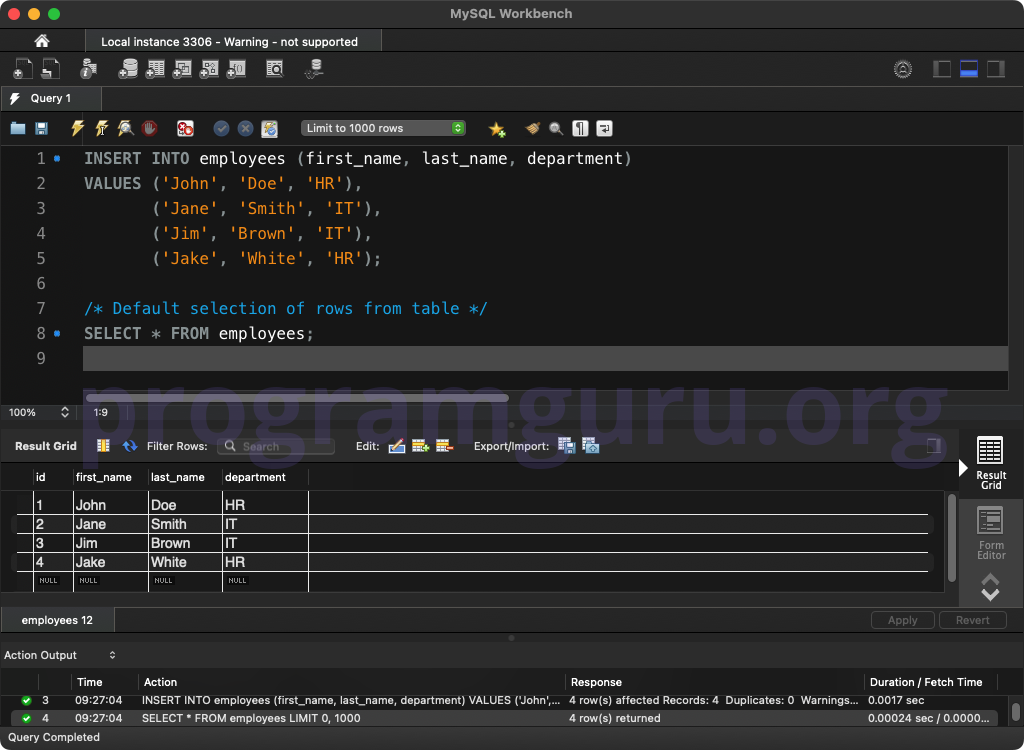
Step 3: Inserting Initial Rows
Insert some initial rows into the table:
INSERT INTO employees (first_name, last_name, department)
VALUES ('John', 'Doe', 'HR'),
('Jane', 'Smith', 'IT'),
('Jim', 'Brown', 'IT'),
('Jake', 'White', 'HR');
This query inserts four rows into the employees table.
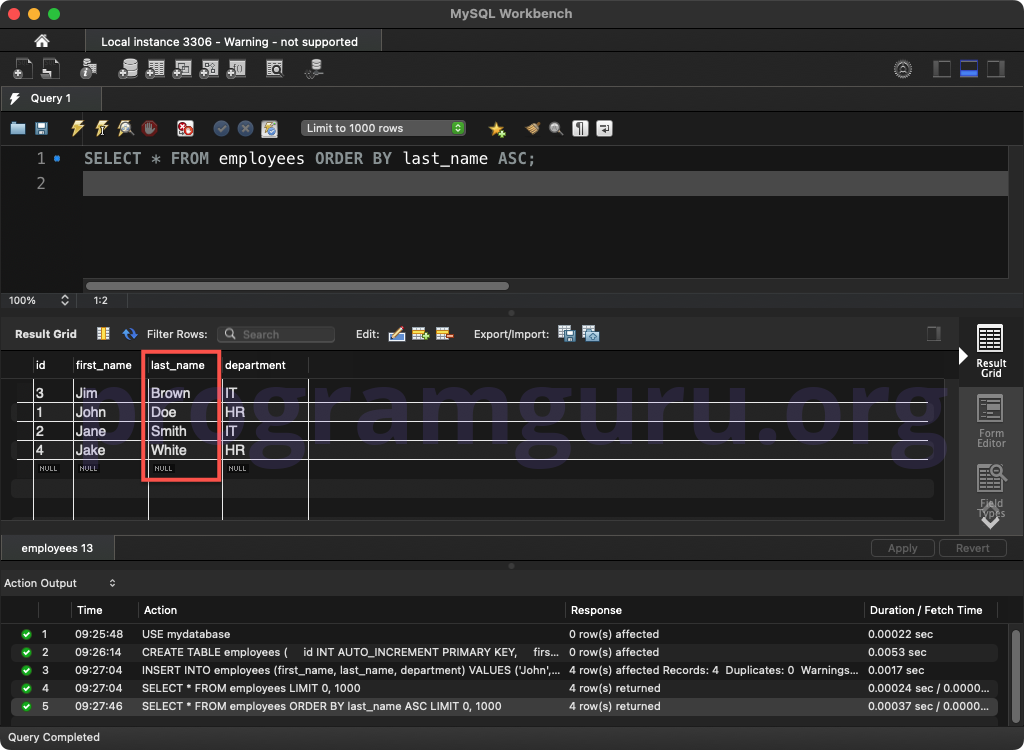
Step 4: Ordering by a Single Column
Order the result set by a single column:
SELECT *
FROM employees ORDER BY last_name ASC;
This query retrieves all columns from the employees table, sorted by the last_name column in ascending order.
Step 5: Ordering by Multiple Columns
Order the result set by multiple columns:
SELECT *
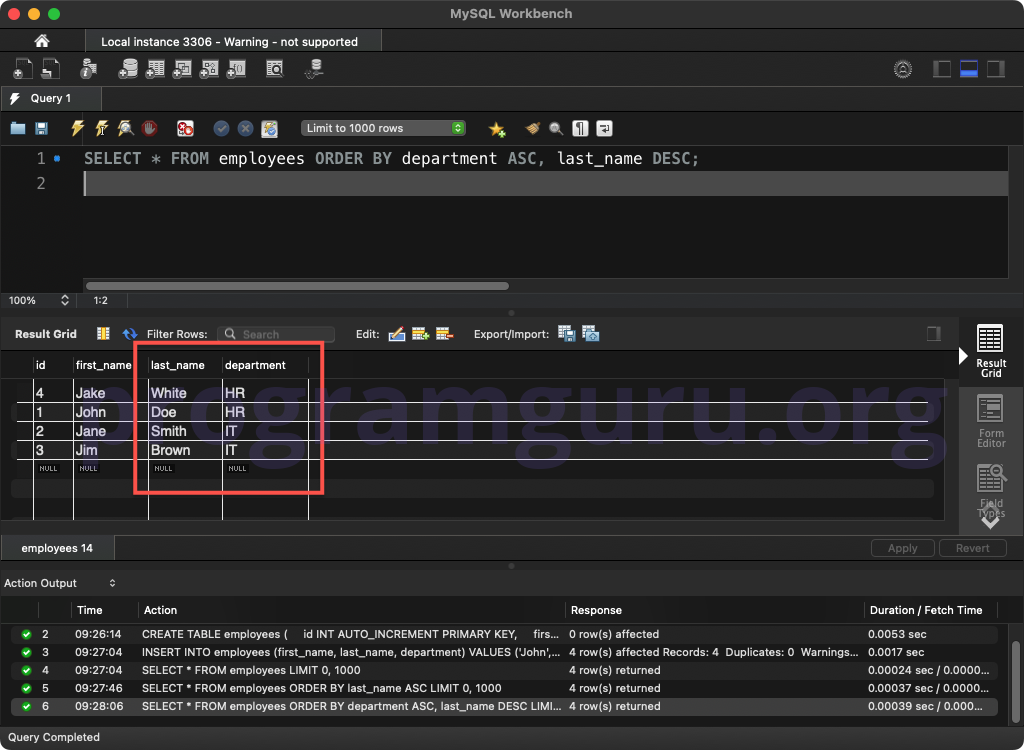
FROM employees ORDER BY department ASC, last_name DESC;
This query retrieves all columns from the employees table, sorted by the department column in ascending order and then by the last_name column in descending order.
Step 6: Using ORDER BY with WHERE Clause
Order the result set with a condition:
SELECT *
FROM employees
WHERE department = 'IT' ORDER BY first_name DESC;
This query retrieves all columns from the employees table where the department is 'IT', sorted by the first_name column in descending order.

Step 7: Ordering with LIMIT
Order the result set and limit the number of rows:
SELECT *
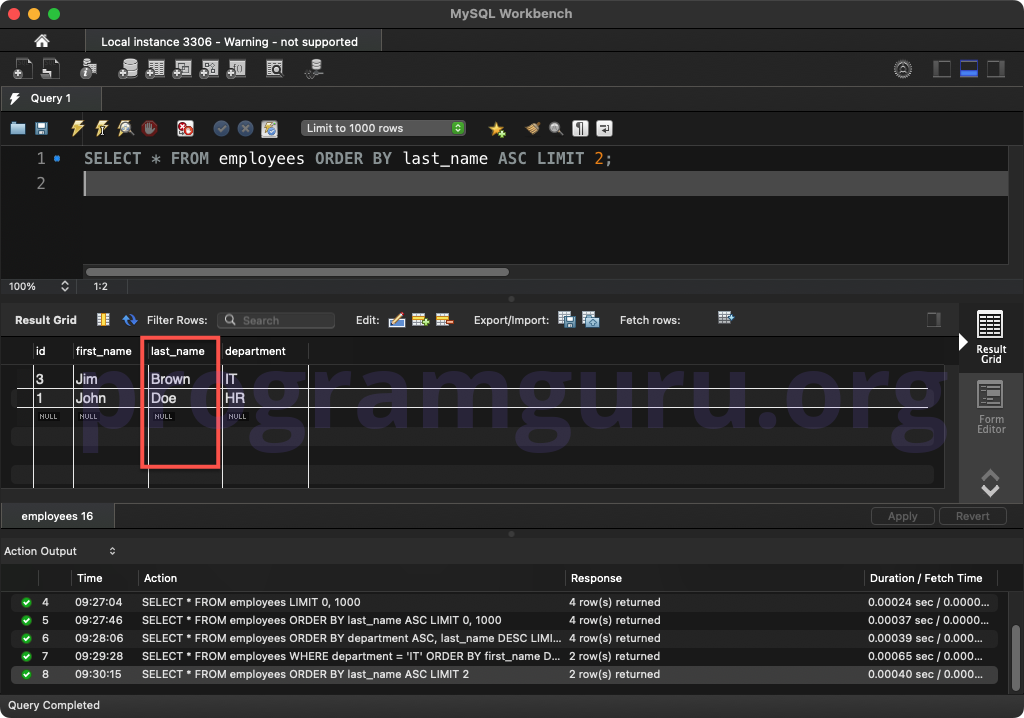
FROM employees ORDER BY last_name ASC LIMIT 2;
This query retrieves all columns from the employees table, sorted by the last_name column in ascending order, and limits the result set to the first 2 rows.
Conclusion
The MySQL ORDER BY clause is a powerful tool for sorting the result set of a query. Understanding how to use the ORDER BY clause is essential for organizing data and presenting it in a meaningful way in MySQL.