MySQL DESCRIBE TABLE Statement
MySQL DESCRIBE TABLE Statement
The MySQL DESCRIBE TABLE statement is used to provide detailed information about the structure of a table. This statement is essential for understanding the schema of a table, including its columns, data types, and constraints.
Syntax
DESCRIBE table_name;
The DESCRIBE TABLE statement has the following component:
table_name: The name of the table whose structure is to be described.
Example MySQL DESCRIBE TABLE Statement
Let's look at an example of the MySQL DESCRIBE TABLE statement and how to use it:
Step 1: Using the Database
USE mydatabase;
This query sets the context to the database named mydatabase.
Step 2: Creating a Table
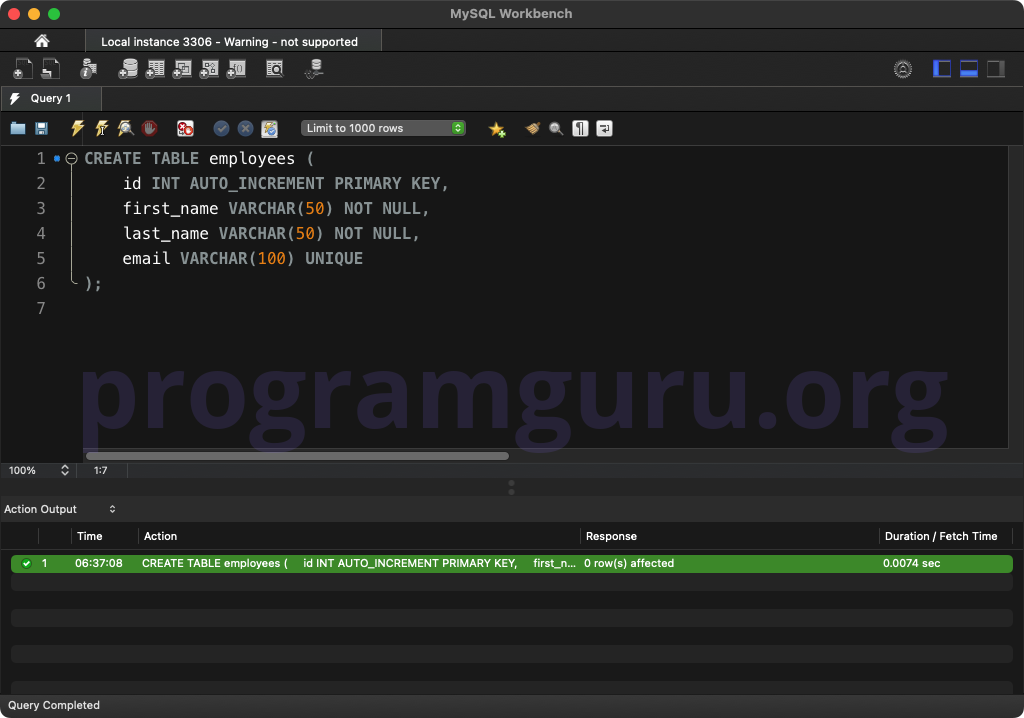
Create a table to work with:
CREATE TABLE employees (
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
first_name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
last_name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
email VARCHAR(100) UNIQUE
);
This query creates a table named employees with columns for id, first_name, last_name, and email.
Step 3: Describing the Table
Describe the table to get its structure:
DESCRIBE employees;
This query provides a detailed description of the employees table, including column names, data types, and constraints.

The output of the DESCRIBE statement includes the following information:
Field: The name of the column.Type: The data type of the column.Null: Whether the column can contain NULL values.Key: Whether the column is indexed (e.g.,PRIfor primary key).Default: The default value of the column.Extra: Any additional information (e.g.,auto_increment).
This output provides detailed information about each column in the employees table.
Conclusion
The MySQL DESCRIBE TABLE statement is a powerful tool for understanding the structure of tables. Knowing how to use the DESCRIBE TABLE statement is essential for effective database management and schema design in MySQL.