MySQL DROP TABLE Statement
MySQL DROP TABLE Statement
The MySQL DROP TABLE statement is used to delete an existing table from the database. This statement is essential for removing tables that are no longer needed.
Syntax
DROP TABLE [IF EXISTS] table_name;
The DROP TABLE statement has the following components:
IF EXISTS: An optional clause that prevents an error if the table does not exist.table_name: The name of the table to be deleted.
Example MySQL DROP TABLE Statement
Let's look at an example of the MySQL DROP TABLE statement and how to use it:
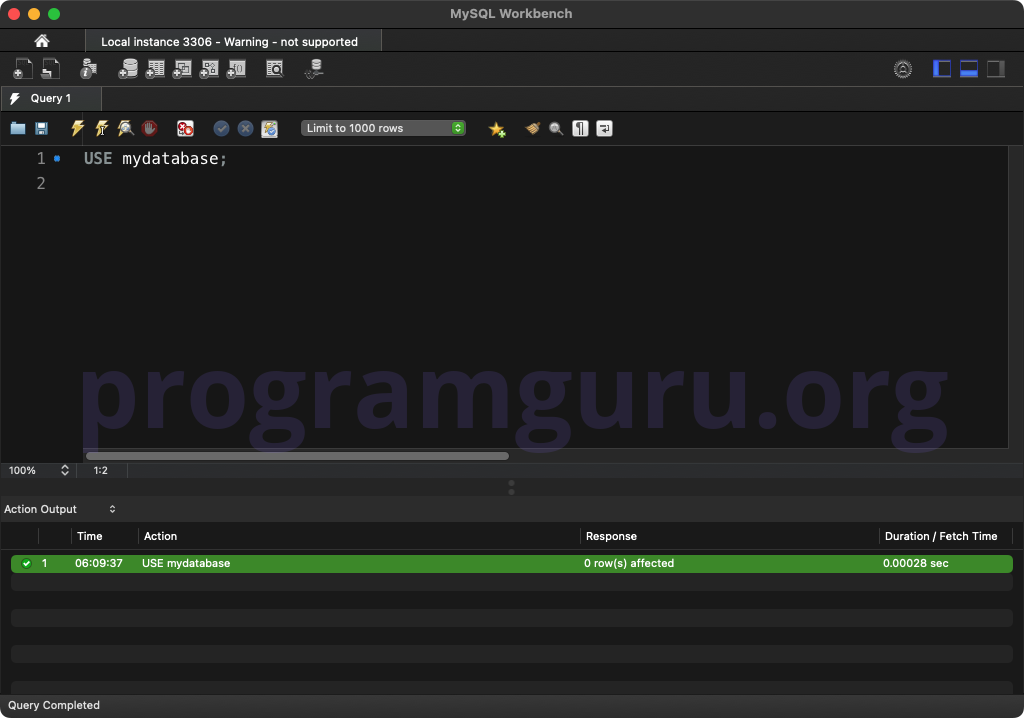
Step 1: Using the Database
USE mydatabase;
This query sets the context to the database named mydatabase.
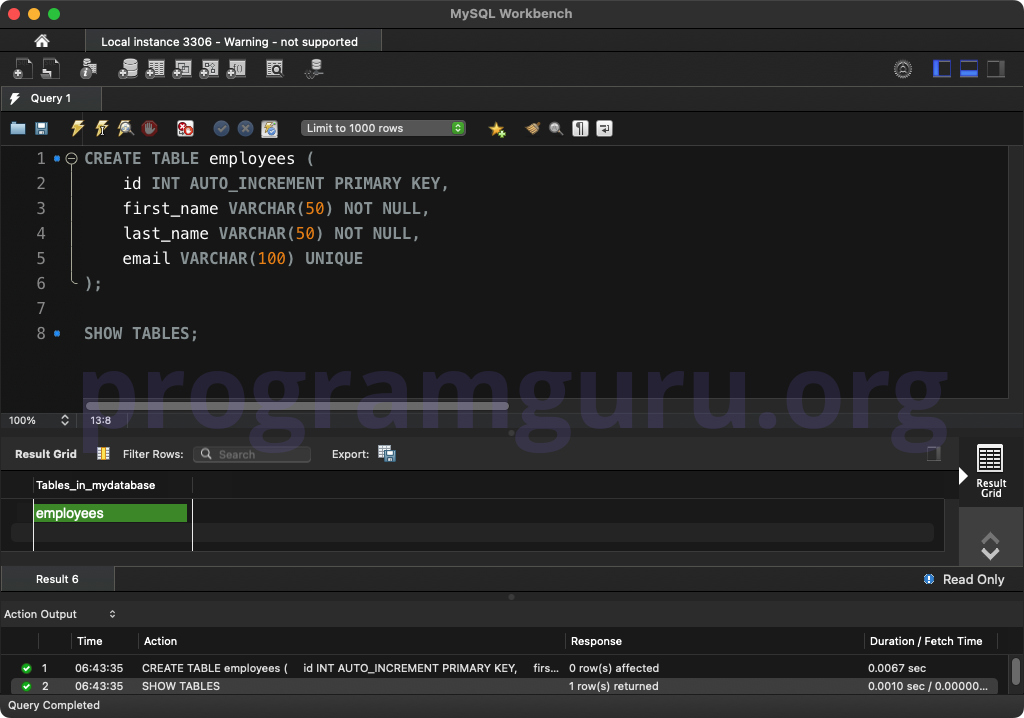
Step 2: Creating a Table
Create a table to work with:
CREATE TABLE employees (
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
first_name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
last_name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
email VARCHAR(100) UNIQUE
);
This query creates a table named employees with columns for id, first_name, last_name, and email.
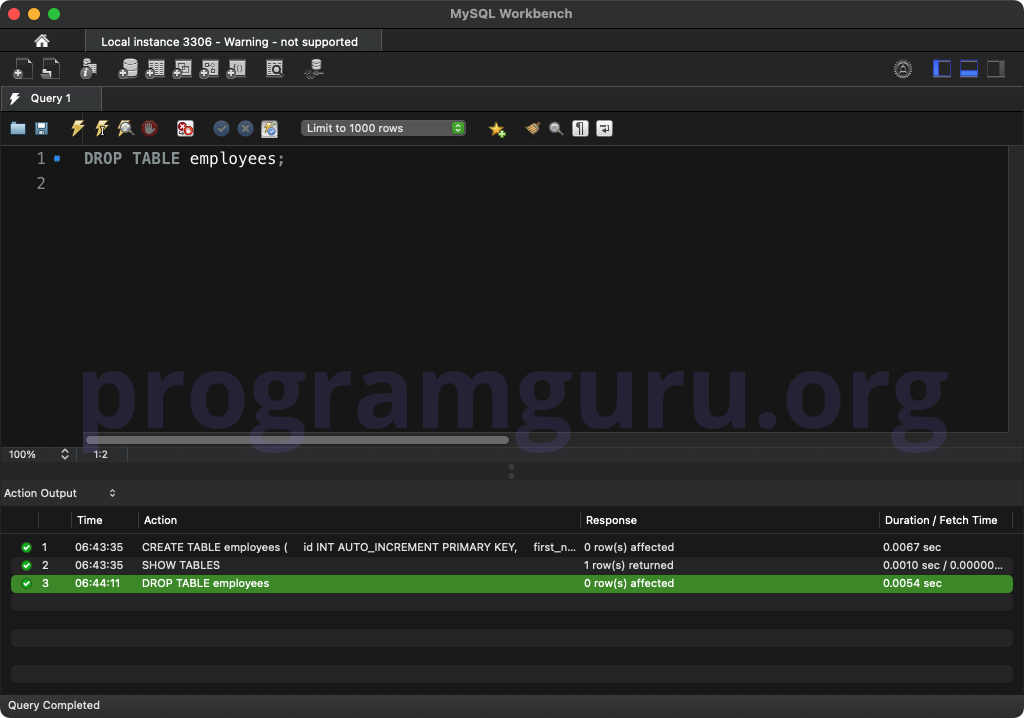
Step 3: Dropping the Table
Drop the table:
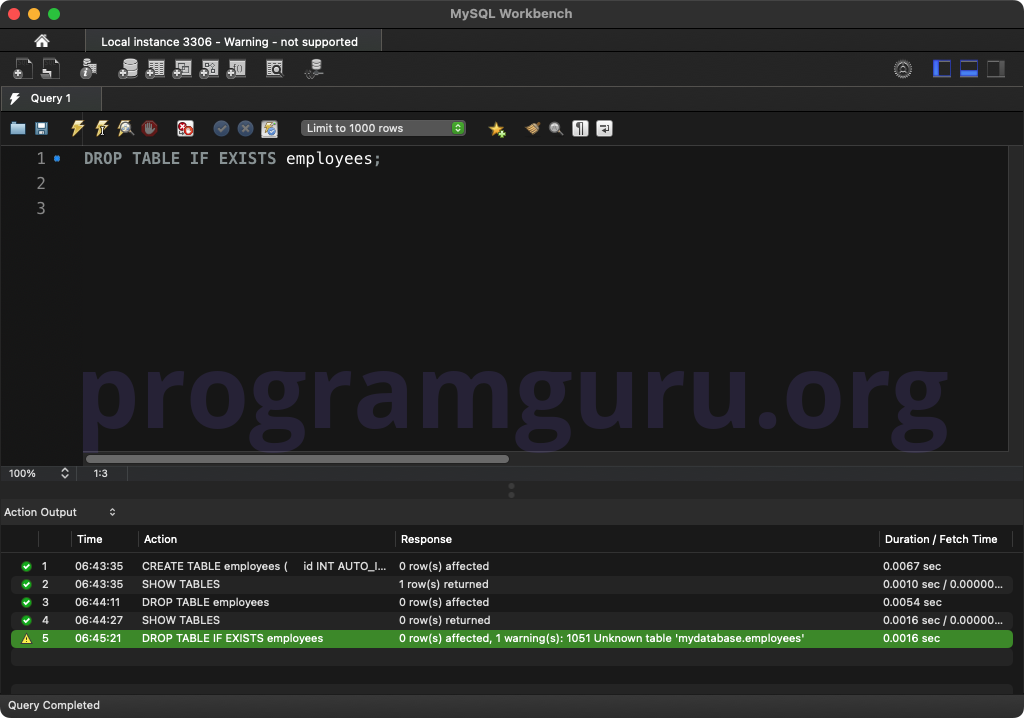
DROP TABLE employees;
This query deletes the table named employees from the database.
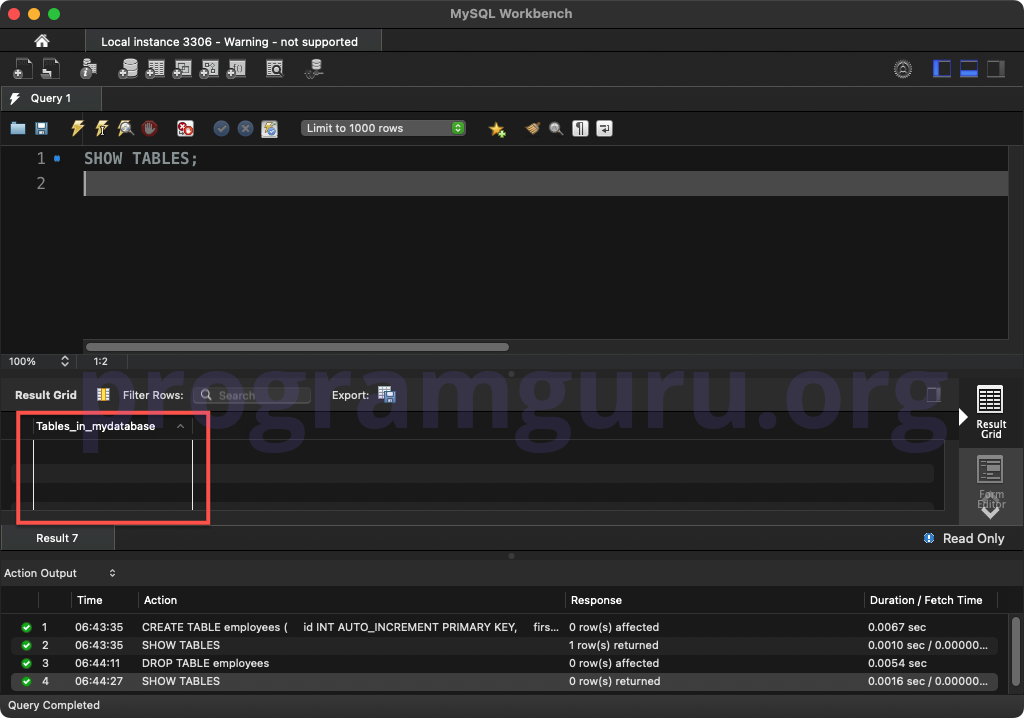
Step 4: Verifying Table Deletion
To verify that the table has been deleted, you can list all tables in the current database:
SHOW TABLES;
This query lists all tables in the current database. The result should no longer include the table employees.
Additional Example: Using IF EXISTS
To prevent an error if the table does not exist, use the IF EXISTS option:
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS employees;
This query deletes the table named employees only if it exists, preventing an error if it does not.
Conclusion
The MySQL DROP TABLE statement is a powerful tool for deleting tables that are no longer needed. Understanding how to use the DROP TABLE statement and verifying its deletion is essential for effective database management in MySQL.