MySQL Greater Than or Equal To Operator
MySQL Greater Than or Equal To Operator
The MySQL >= operator is used to compare two values. This operator is essential for filtering records where one value is greater than or equal to another.
Syntax
SELECT column1, column2, ...
FROM table_name
WHERE column1 >= value;
The >= operator has the following components:
column1, column2, ...: The columns to be retrieved.table_name: The name of the table from which to retrieve the data.column1 >= value: The condition to filter the records, wherecolumn1is greater than or equal to a specifiedvalue.
Example MySQL Greater Than or Equal To Operator
Let's look at some examples of the MySQL >= operator:
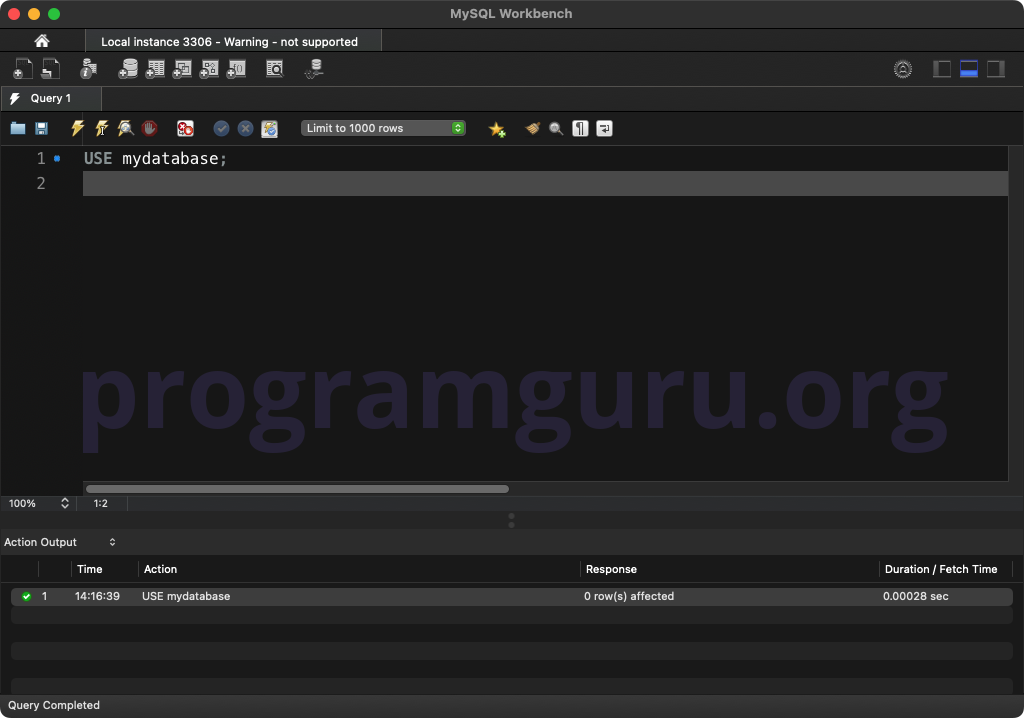
Step 1: Using the Database
USE mydatabase;
This query sets the context to the database named mydatabase.
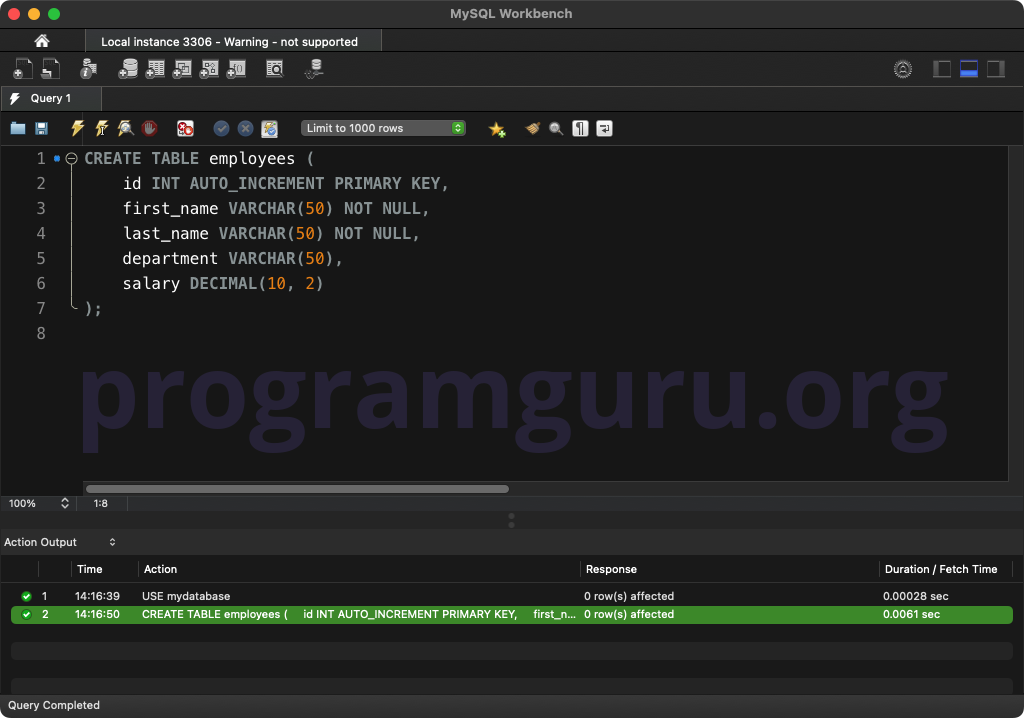
Step 2: Creating a Table
Create a table to work with:
CREATE TABLE employees (
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
first_name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
last_name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
department VARCHAR(50),
salary DECIMAL(10, 2)
);
This query creates a table named employees with columns for id, first_name, last_name, department, and salary.
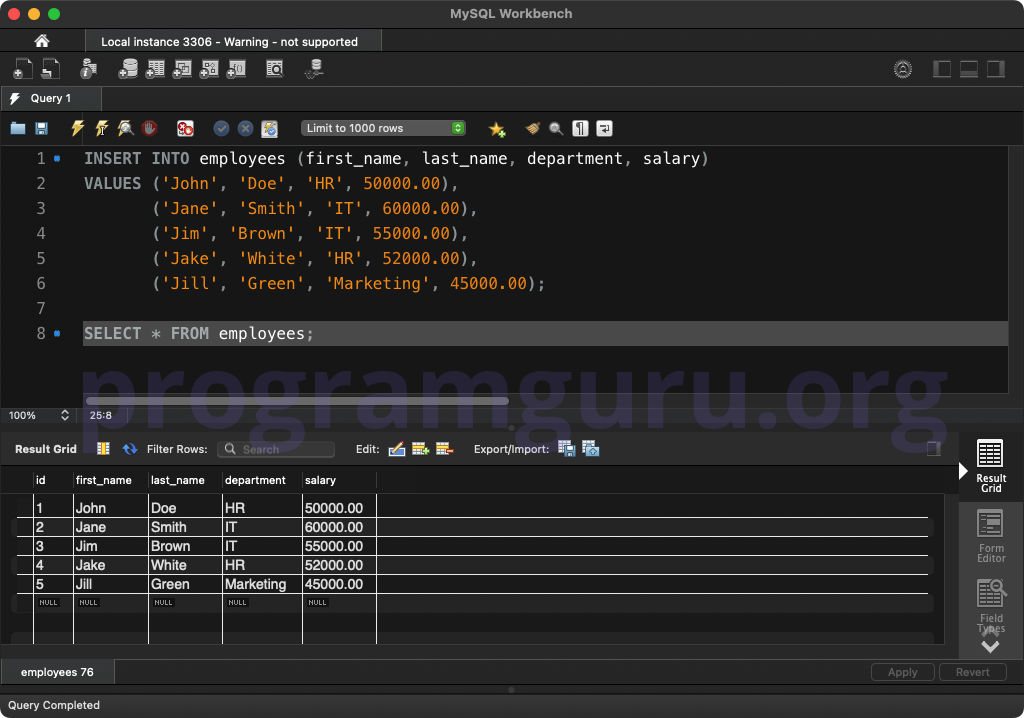
Step 3: Inserting Initial Rows
Insert some initial rows into the table:
INSERT INTO employees (first_name, last_name, department, salary)
VALUES ('John', 'Doe', 'HR', 50000.00),
('Jane', 'Smith', 'IT', 60000.00),
('Jim', 'Brown', 'IT', 55000.00),
('Jake', 'White', 'HR', 52000.00),
('Jill', 'Green', 'Marketing', 45000.00);
This query inserts five rows into the employees table.
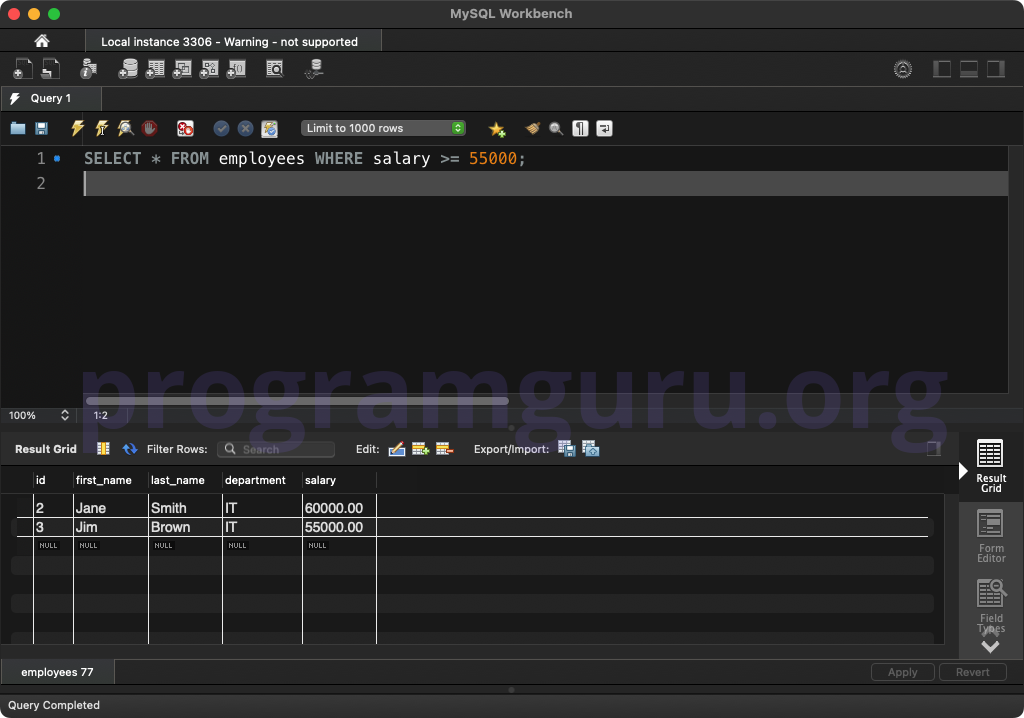
Step 4: Using Greater Than or Equal To Operator with WHERE Clause
Use the >= operator to filter records based on a condition:
SELECT *
FROM employees
WHERE salary >= 55000;
This query retrieves all columns from the employees table where the salary is greater than or equal to 55000.
Step 5: Combining Greater Than or Equal To with AND Operator
Use the >= operator with the AND operator to filter records based on multiple conditions:
SELECT *
FROM employees
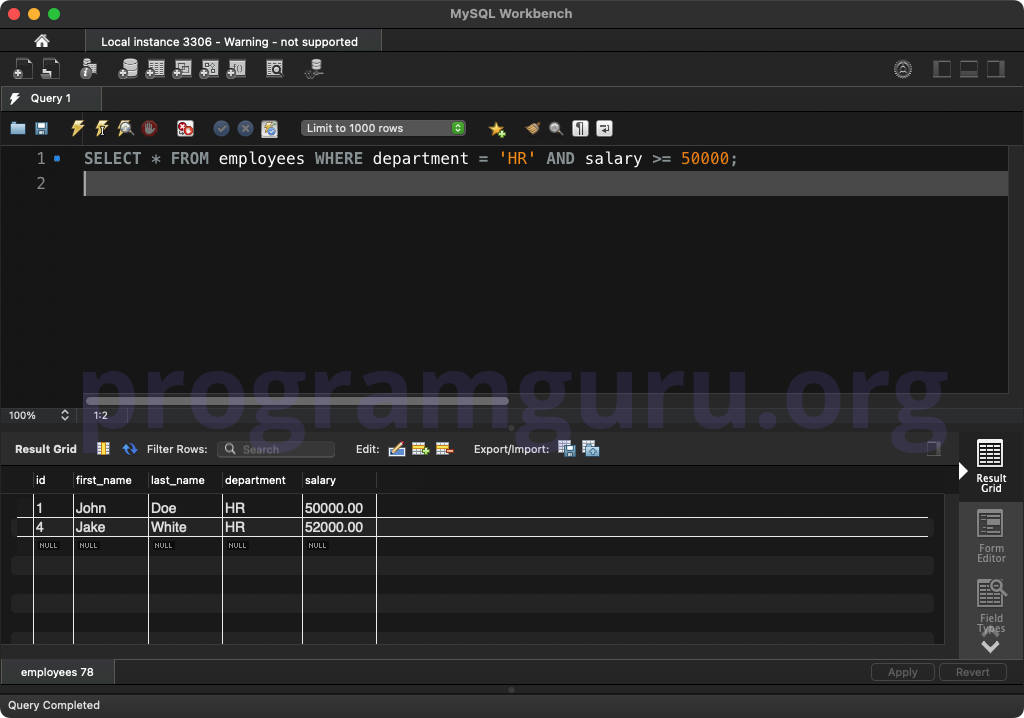
WHERE department = 'HR' AND salary >= 50000;
This query retrieves all columns from the employees table where the department is 'HR' and the salary is greater than or equal to 50000.
Step 6: Using Greater Than or Equal To with Multiple Columns
Use the >= operator with multiple columns:
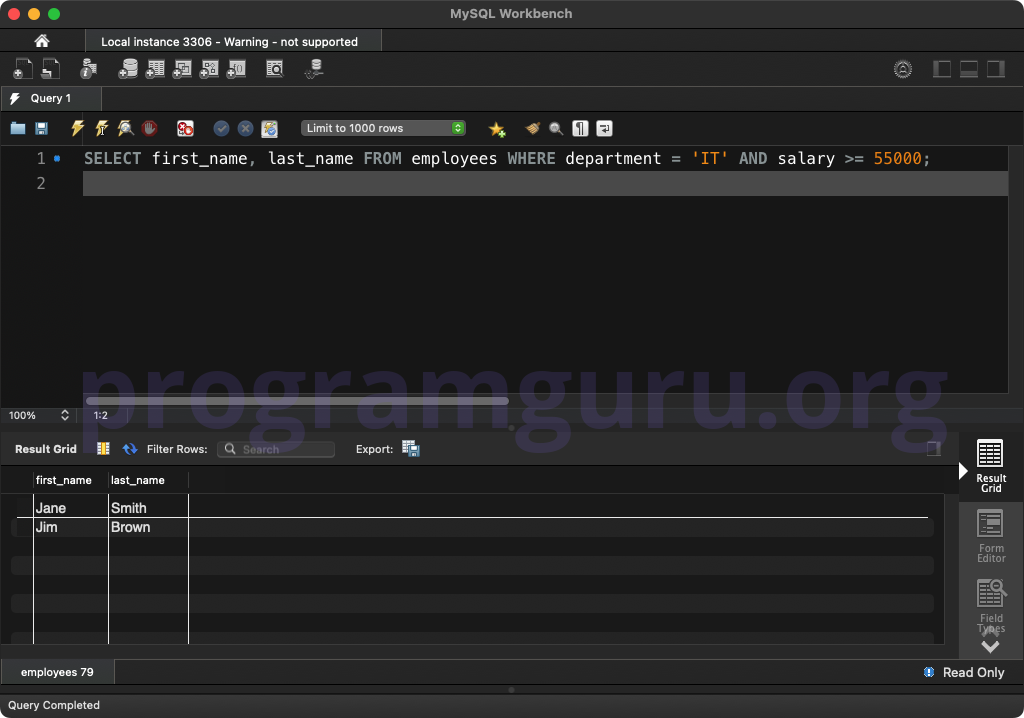
SELECT first_name, last_name
FROM employees
WHERE department = 'IT' AND salary >= 55000;
This query retrieves the first_name and last_name columns from the employees table where the department is 'IT' and the salary is greater than or equal to 55000.
Conclusion
The MySQL >= operator is a powerful tool for filtering records based on a comparison condition. Understanding how to use the >= operator is essential for effective data querying and analysis in MySQL.