MySQL ELT() String Function
MySQL ELT() String Function
The MySQL ELT() string function returns the string at the specified index position within a list of strings. This function is essential for retrieving specific strings from a list based on their index in SQL queries.
Syntax
SELECT ELT(index, string1, string2, ..., stringN) AS result
FROM table_name;
The ELT() function has the following components:
index: The index position of the string to be retrieved (1-based).string1, string2, ..., stringN: A list of strings from which to retrieve the string at the specified index.result: An alias for the resulting string.table_name: The name of the table from which to retrieve the data.
Example MySQL ELT() String Function
Let's look at some examples of the MySQL ELT() string function:
Step 1: Using the Database
USE mydatabase;
This query sets the context to the database named mydatabase.
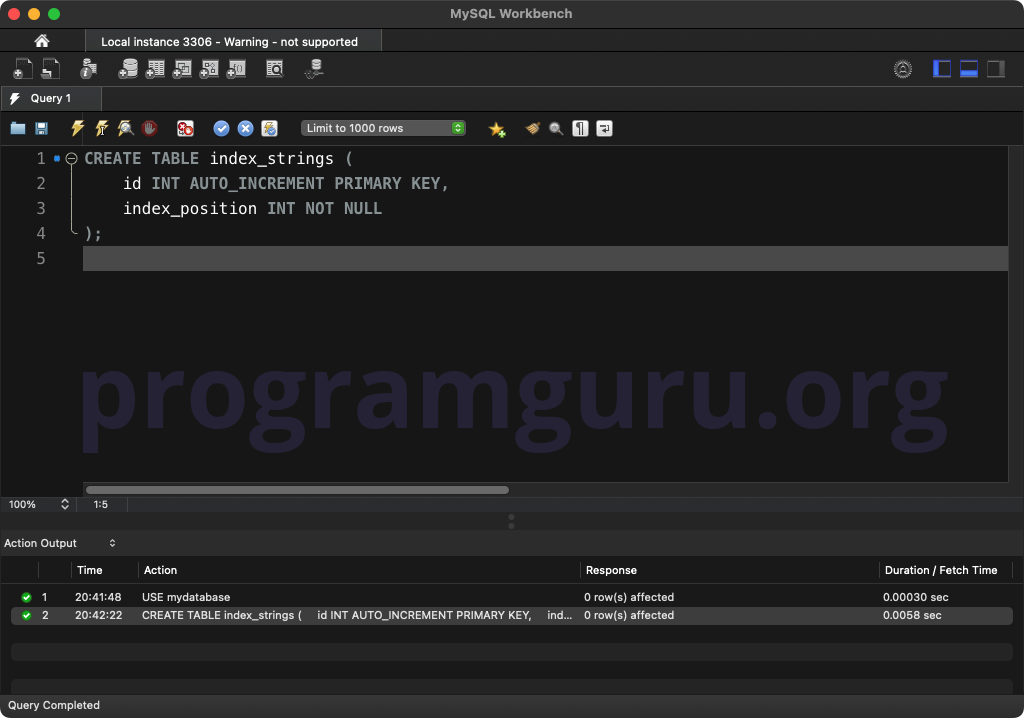
Step 2: Creating a Table
Create a table to work with:
CREATE TABLE index_strings (
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
index_position INT NOT NULL
);
This query creates a table named index_strings with columns for id and index_position.
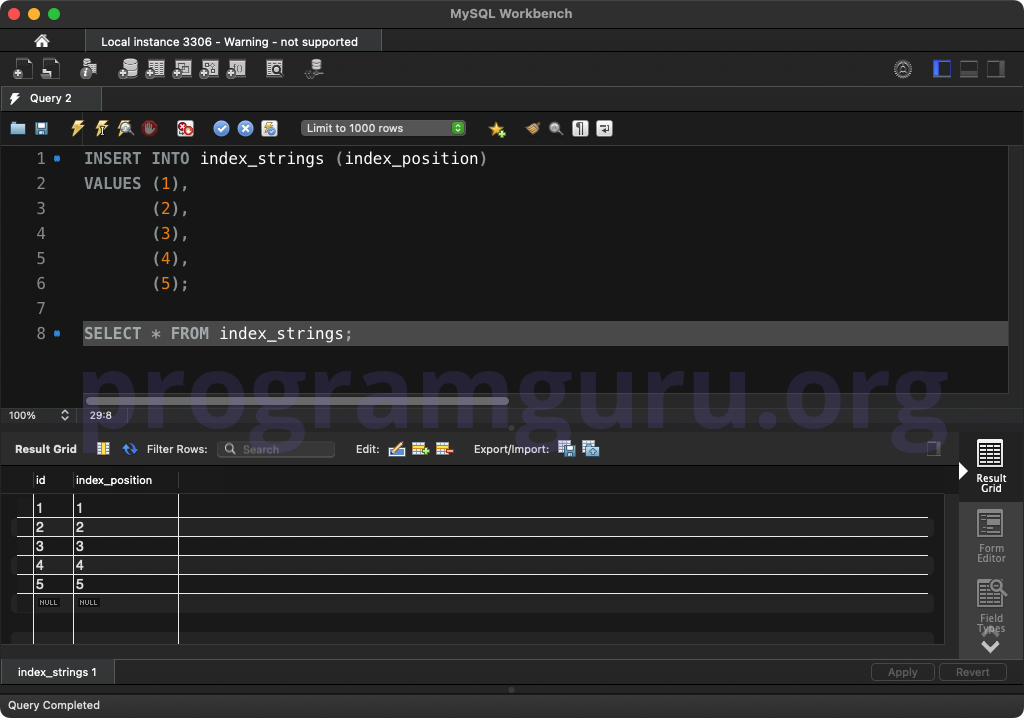
Step 3: Inserting Initial Rows
Insert some initial rows into the table:
INSERT INTO index_strings (index_position)
VALUES (1),
(2),
(3),
(4),
(5);
This query inserts five rows into the index_strings table.
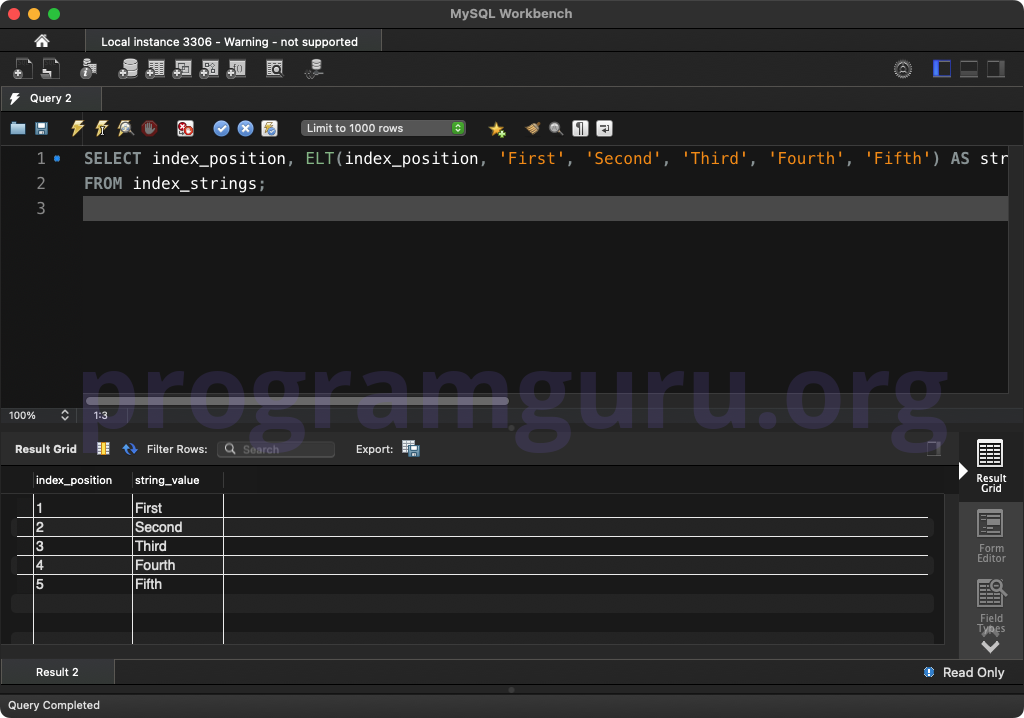
Step 4: Using ELT() with WHERE Clause
Use the ELT() function to retrieve the string at the specified index position:
SELECT index_position, ELT(index_position, 'First', 'Second', 'Third', 'Fourth', 'Fifth') AS string_value
FROM index_strings;
This query retrieves the index_position column from the index_strings table and returns the string at the specified index position.
Step 5: Using ELT() with Multiple Columns
Use the ELT() function with multiple columns:
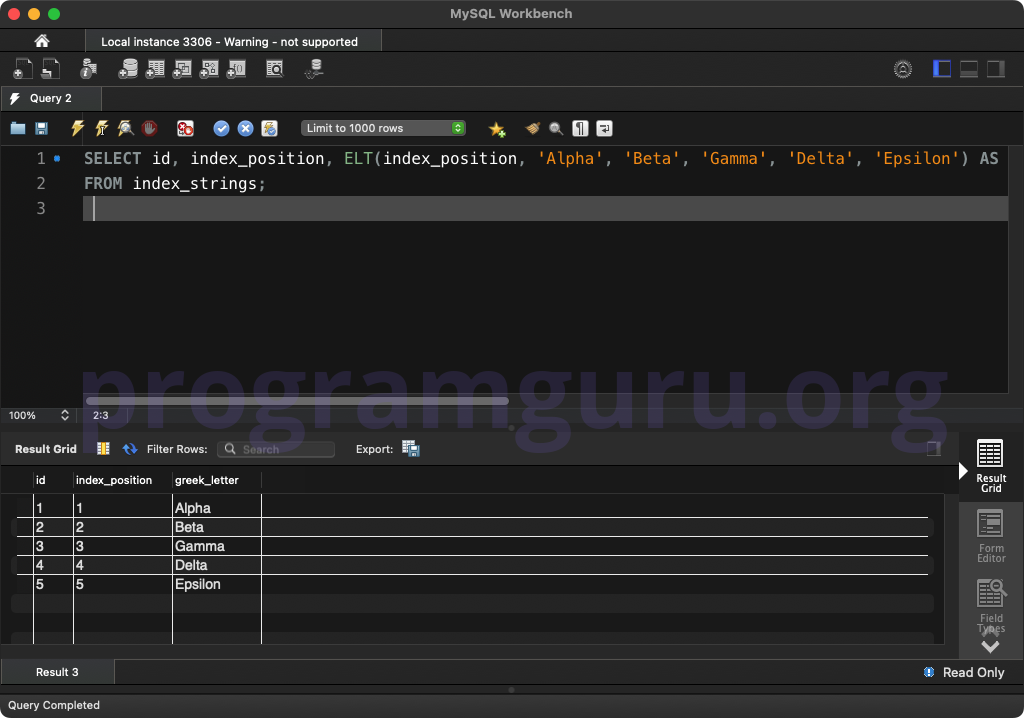
SELECT id, index_position, ELT(index_position, 'Alpha', 'Beta', 'Gamma', 'Delta', 'Epsilon') AS greek_letter
FROM index_strings;
This query retrieves the id and index_position columns from the index_strings table and returns the Greek letter at the specified index position.
Step 6: Using ELT() with Constants
Use the ELT() function with constants:
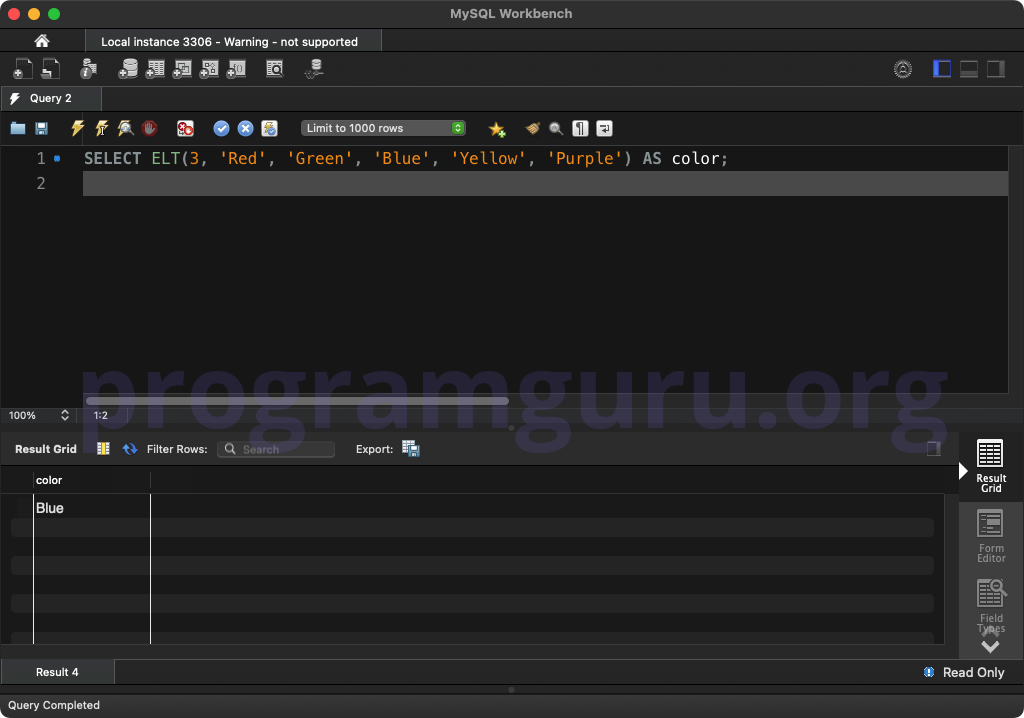
SELECT ELT(3, 'Red', 'Green', 'Blue', 'Yellow', 'Purple') AS color;
This query retrieves the color at the third position in the list of constants.
Conclusion
The MySQL ELT() function is a powerful tool for retrieving specific strings from a list based on their index in SQL queries. Understanding how to use the ELT() function is essential for effective data querying and analysis in MySQL.